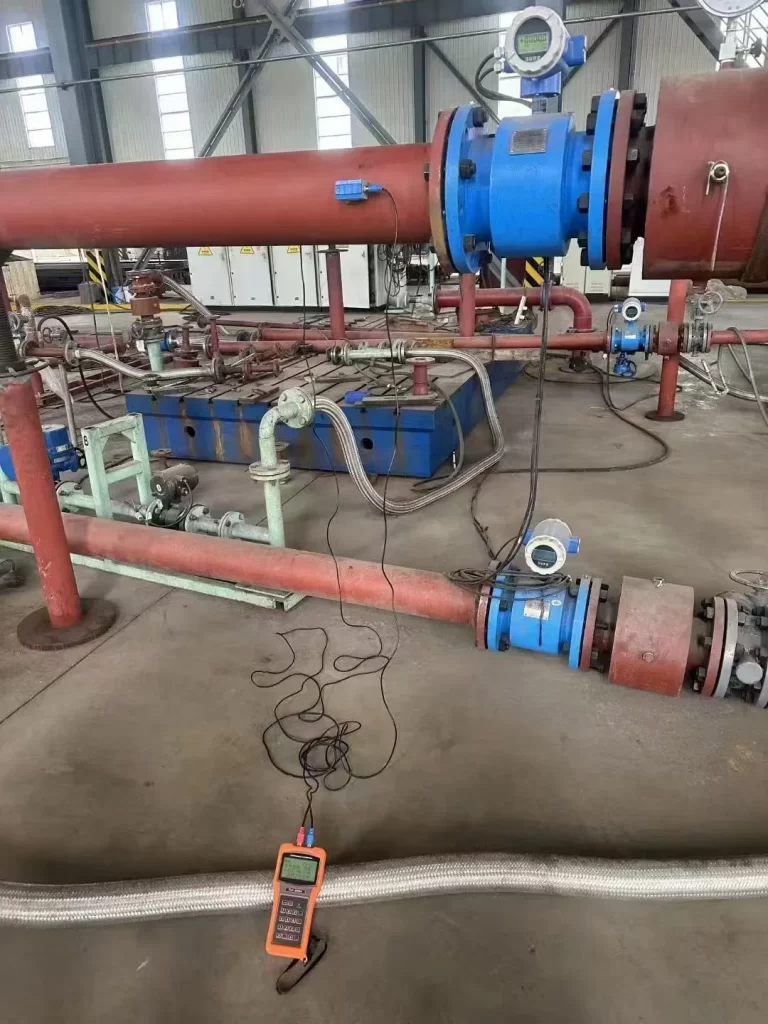

Flow meters are widely used across various industries to measure and control the flow rate of gases or liquids. Calibration and recalibration of flow meters are crucial for production processes. Flow meter calibration involves comparing the actual measurement results with higher-precision measurements to verify and adjust the flow meter’s accuracy. Correcting potential measurement errors and restoring the true flow rate of the fluid ensures smooth industrial processes and controllable economic costs.
Any high-precision, high-performance flow meter requires calibration after a period of use. This ensures that the flow meter’s output signal accurately reflects the actual flow rate of the fluid (liquid or gas).
What is Flowmeter Calibration?
Flowmeter calibration is the process of adjusting flowmeter metering to meet standards. The preset scale or meter of the flowmeter is compared with the standard measurement scale during the process. In many industries that require high-precision measurements with a negligible percentage of error, calibration is an important aspect of instrumentation. Oil, gas, petrochemical and manufacturing.
The flowmeter is calibrated by comparing and adjusting its metering to meet predetermined standards. Flowmeter manufacturers typically calibrate their products internally after production. Or send it to an independent calibration facility for adjustment.
Before Calibration: Understanding Flow Meter Characteristics
Flow meters based on different principles have varying measurement principles, sensing element construction, applicable fluid ranges, and accuracy classes. Examples include:
- Differential pressure flow meters based on Bernoulli’s equation;
- Electromagnetic flow meters utilizing electromagnetic induction;
- Turbine flow meters based on rotor rotation;
- Ultrasonic flow meters based on ultrasonic propagation;
- Gear flow meters based on gear rotation;
- Vortex flow meters capturing vortex shedding frequencies;
- Mass flow meters based on Coriolis forces.
Before calibration, it is essential to fully understand the technical manual of the flow meter to be calibrated, clearly identifying its key parameters, including but not limited to the flow range, nominal accuracy value, fluid medium requirements, and operating temperature and pressure range. This is a prerequisite for targeted calibration.
Methods of Flowmeter Calibration
Common flow calibration methods are: speed type, volume type, mass type, etc.
Apply more speed-type flow measurement methods. For current flowmeters, standard throttling devices do not need to be tested. The remaining flowmeters are almost always calibrated at the factory. During the use of the flowmeter, it should also be calibrated frequently.
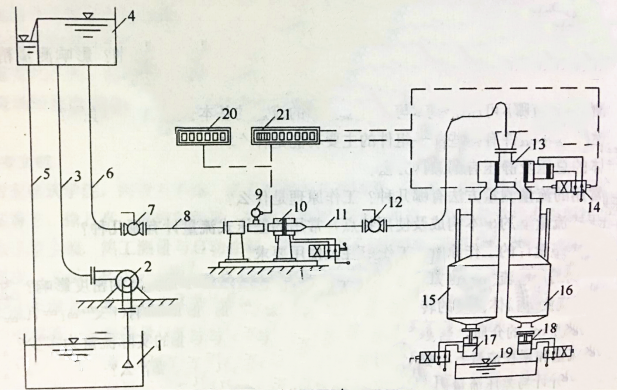
There are several main methods for calibrating and recalibrating flowmeters:
Volume Method
The volume method is most commonly used. This is a method of measuring the volume of fluid flowing into a constant volume container during a measurement time to obtain the flow rate. The following figure is a schematic diagram of the typical structure of a static volumetric water flow verification device. Calibrate the flowmeter with pulse output, and replace with other output flowmeters.
- The commutator 13 is used to change the flow direction of the fluid so that water flows into a standard container. Can choose standard container 15 or 16 according to the flow size.
- When the commutator 13 is started, the pulse count controller 21 is triggered. To ensure the simultaneous measurement of water and pulse signal counting.
- During calibration, the test fluid drawn from the liquid storage container by the pump is pumped into the high-level water tank. Then pass the calibrated flowmeter.
- When the standard container 15 is selected, the water discharge valve 17 is closed and the water discharge valve 18 is opened. The commutator 13 is placed at a position where the water flow is directed to the standard container 16.
- After the flow is stable, the commutator 13 is started. The water flow is changed from the standard container 16 to the standard container 15 and the pulse counter is triggered to accumulate the pulse number of the calibrated flow meter.
- When a predetermined amount of water or a preset number of pulses is reached, the commutator switches automatically. The water flow is changed from the standard container 15 to the standard container 16. The volume V of the fluid entering the standard container during this period is read from the scale of the reading glass tube of the container. Record the pulse number N of the calibrated flow meter displayed by the pulse count control 21.
- The pulse number N of the calibrated flowmeter is compared with the obtained standard volume V to determine the meter constant and accuracy of the calibrated flowmeter.
- The instantaneous flow rate of the flow meter is indicated by the frequency indicator 20.
Mass Method
During calibration, a pump is used to draw the test fluid from the liquid storage container through the calibrated flowmeter and enter the liquid container. The temperature of the fluid was measured while weighing out. To determine the density of the fluid being measured at that temperature. Divide the weight of the measured fluid by the density of the fluid at the measured temperature to obtain the volume of the fluid.
Compare it with the meter’s volume indication (cumulative pulse number). The meter constant and accuracy of the calibrated flowmeter can be determined. The accuracy of this method can reach 0.1%.
Standard Device Comparison Method
This method uses a nationally certified standard flow meter (such as a standard gauge, volumetric tube, or weighing system) connected in series with the flow meter being calibrated. Data is compared through synchronous measurement. This method offers high accuracy and is suitable for liquid and gas media in pipe diameters of DN15-DN500.
On-Site Online Calibration
For large flow meters that cannot be disassembled (such as electromagnetic or ultrasonic flow meters), a portable calibrator is used for in-situ testing. By installing an external clamp-on sensor, flow velocity profile data is acquired in real time to correct for pipe coefficients.
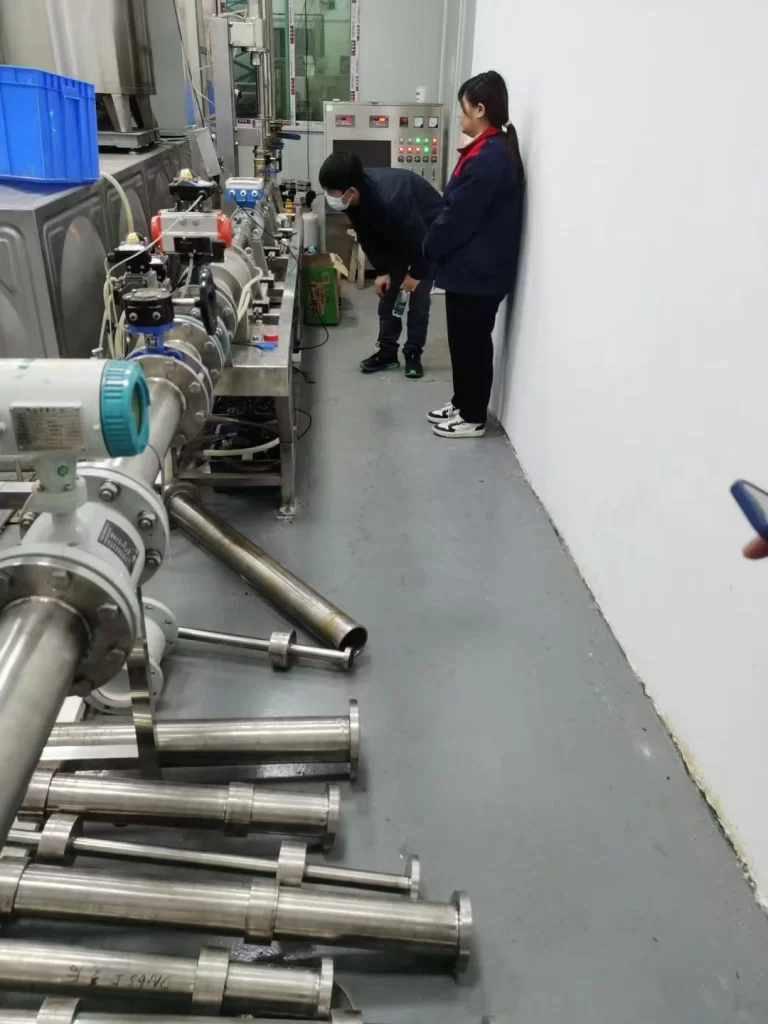

Flowmeter Calibration Devices
A flowmeter calibration device is one of the most commonly used calibration devices in the industry. Usually used when calibration needs to be repeated.
The design of the flowmeter calibration system is similar to a workbench, and its functions include:
- Shielding of the instrument under test;
- Source bracket (in lead shield);
- Connection unit for tested detector units, including low voltage source and counter;
- Ionizing radiation source manipulator;
- Control unit;
- Software for managing calibration equipment and storing data;
After all parts of the calibration equipment are assembled. The responsible technician should ensure that the selected method is entered into the system and that the software initiates the calibration process. The software will select the relevant source so that it can follow the instructions entered and organize the required data. Then store all the data in the database and print the certificate as needed.
How Often is Calibration Needed?
The frequency of calibration varies from industry to industry. There are no rules set. Some applications and processes will need to measure more accurately than others. If accuracy is not an issue, then you can reduce the frequency of calibration. Maybe once a quarter. If you are using highly toxic chemicals or materials, it is advisable to perform a calibration weekly or monthly. If you are unsure how often your business needs to calibrate all operations, industry experts can advise you.
Whenever you replace flowmeter parts or think that the flowmeter may be damaged, you need to calibrate it before using it. Once again, professionals will be able to determine the impact of changes made to the flowmeter.
Post-Calibration: Data Analysis and Processing
- Error Calculation and Assessment:
After completing a series of calibration measurements, for data collected at different flow points, the error calculation formula corresponding to the flowmeter’s accuracy class is strictly followed. Key indicators such as indication error and repeatability error are calculated separately.
For example, indication error = (Measured value of the flowmeter under calibration – Standard value) / Standard value × 100%. These quantitative indicators allow for a direct assessment of the flowmeter’s performance and determine whether it meets the requirements of the usage scenario. If the error exceeds the allowable error range, further troubleshooting, adjustment, or recalibration is required.
- Calibration Certificate Generation:
The calibration process details, including flowmeter information, calibration equipment, calibration conditions (temperature, pressure, flow range, etc.), measurement data, and error calculation results, are fully recorded and compiled to generate a calibration certificate.
The calibration certificate is not only an “identity card” for the flowmeter’s current accuracy status, providing users with reliable metrological traceability, but also a crucial credential for subsequent quality control, equipment maintenance, and handling potential disputes.
How to Calibrate a Magnetic Flowmeter
The measurement principle of electromagnetic flowmeter is Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. The electromagnetic flowmeter measures the flow of conductive fluid according to the electromotive force induced when the conductive fluid passes through an external magnetic field. The main components of the sensor are: measuring tube, electrode, excitation coil, iron core and yoke case. Products are mainly used to measure the volumetric flow of conductive liquids and slurries in closed pipelines, including acids, alkalis, salts and other highly corrosive liquids. Electromagnetic flowmeter is widely used in petroleum, chemical industry, municipal management, water conservancy construction and other fields.
Quick calibration of the electromagnetic flowmeter:
- Select the corresponding pump according to the diameter and flow rate of the pipeline to be subjected to the verification test;
- After the flowmeter is correctly connected, it should be powered on and warmed up for about 30 minutes according to the requirements of the verification regulations;
- If a high-level trough water source is used, check whether the overflow signal of the stabilized water tower appears. Before the formal test, it should be in accordance with the requirements of the verification regulations. Use the verification medium to circulate in the piping system for a certain period of time. At the same time, check whether there are leaks in the sealed parts of the piping;
- Before the formal verification is started, the verification medium should be filled with the sensor of the flowmeter under test. Then the downstream valve should be closed for zero adjustment;
- At the start of the inspection, the valve at the front of the pipeline should be opened first. Slowly open the valve behind the flowmeter under test to adjust the flow at the verification point;
- During the calibration process, the flow stability of each flow point should be within 1% to 2%-the flow method. The total law can be within 5%. The temperature change of the test medium shall not exceed 1 ℃ when the verification process of one flow point is completed. It shall not exceed 5 ℃ when the entire verification process is completed;
- After each test, the valve at the front of the test pipeline should be closed first, and then the pump should be stopped to avoid emptying the voltage stabilization facility. At the same time, the remaining verification medium in the test pipeline must be vented. Close the control system and the air compressor.

Technical Support
Flow Meter Calibration Services
Sino-Inst provides flowmeter calibration services. Periodic calibration of the flow meter instrument ensures that the measurement value of the flow meter reaches the accuracy required by its specifications. We can customize flowmeter calibration services for you to meet your specific requirements.
Flow calibration capabilities:
- Turbine Flow Meter Calibration
- Electromagnetic Flow Meter Calibration
- Coriolis Flow Meter Calibration
- Vortex Flow Meter Calibration
- Ultrasonic Flow Gauge Calibration
- Rotometer Flow Calibration
- Thermal Mass Flow Meter Calibration
- Venturi Meter Flow Calibration
- DP Flow Meter Calibration
- Gas Flow Meter Calibration
- Laminar Flow Meter Calibration
- Liquid Flow Meter Calibration
- Optical Flow Meter Calibration
- Paddle Wheel Flow Meter Calibration
- Velocity Meter Calibration
- Viscosity Cup Calibration\Viscosity Meter Calibration
More Flow Measurement Solutions
Accurately calibrated flow meters provide stable and reliable metering capabilities for industrial production, energy management, and other fields, avoiding numerous problems such as cost overruns and quality degradation caused by flow measurement errors.
Sino-Inst is a professional manufacturer with many years of experience in the flow meter field. We have an elite team proficient in various calibration technologies, enabling us to provide you with high-quality flow meter products of various models, covering all mainstream measurement principles to meet diverse operating conditions. Furthermore, we offer comprehensive one-stop services throughout the entire lifecycle of flow meter calibration, maintenance, and fault diagnosis.
-1.jpg)