In some industrial closed environments, vacuuming is required. The vacuum pressure sensor can be used to detect the vacuum degree of the closed environment in real time. Generally, vacuum pressure sensors that measure negative pressure have the function of detecting negative pressure and positive pressure at the same time. For example -100KPa~0~100KPa.
It is best to use pressure sensors or transmitters with diffused silicon products. We at Sino-Inst offer a wide range of vacuum pressure sensors, including measuring absolute pressure and composite (negative and positive) pressure ranges. The measurement unit can be kpa, mpa, bar, psig, mmhg, etc. And the signal output can be configured as 4-20mA, 0-10V, 0-5V, etc.
Featured Vacuum Pressure Sensors
More pressure measurement solutions
- Industrial Pressure Sensors for High Pressure Measurement
- Capacitive Pressure Transmitter | Manufacturer’s Guide & Product List
- Industrial Water Pressure Measurement and Monitoring
- Tank Level Measurement with Pressure Transmitters/DP Transmitters
- Featured Stainless Steel Pressure transducers | Best Price
- Liquid Nitrogen Pressure Measurement – Pipeline and Tank
- High Temperature Pressure Transducers|800℃~1200℃
- Fluid Pressure Sensors for Industrial Liquids Pressure Measurement
- Industrial HART Pressure Transmitters and DP Transmitters
- Industrial Pressure Transmitters: 7 Sensor Principles and 4 Main Types!
- Pipe Flow vs Pressure – Relationship & Calculate Tools
- Pressure Transducer Troubleshooting: Expert Insights & Tips
- Fluid Pressure Guide: Static Pressure Vs. Dynamic Pressure Vs. Total Pressure
- Steam Pressure Sensor/transducer for Industrial Steam Measurement
Vacuum vs. Negative Pressure
Both vacuum and negative pressure describe a pressure lower than atmospheric pressure. Essentially, vacuum and negative pressure are usually numerically equal, but they use different reference points.
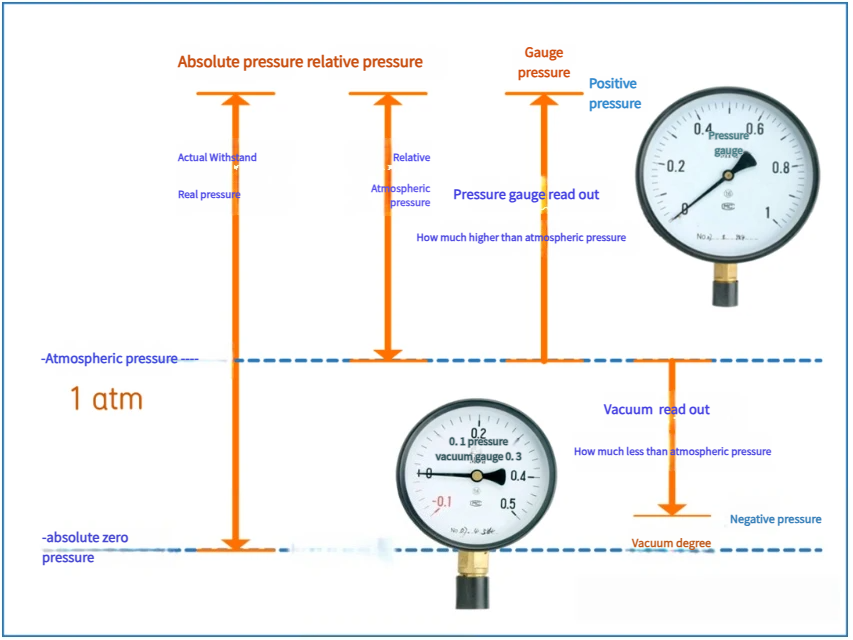
Vacuum:
- Definition: Refers to a state where the gas pressure in a given space is lower than one standard atmosphere.
- Vacuum Degree: Refers to the degree of rarefaction of the gas in a vacuum state. Industrially, vacuum degree is usually defined as: local atmospheric pressure – absolute pressure.
- Characteristics: Vacuum degree is a positive value. The smaller the absolute pressure, the higher the vacuum degree, representing a “emptier” space.
- Numerical Value: Usually a positive value (0 to 101.325 kPa).
Negative Pressure:
- Definition: Is a pressure expressed with local atmospheric pressure as the zero point (reference), and its value is lower than atmospheric pressure.
- Calculation Formula: Absolute pressure – local atmospheric pressure.
- Characteristics: Negative pressure is a negative value. For example, if the vacuum degree is 20 kPa, then the negative pressure is -20 kPa.
- Numerical Value: Usually a negative value (0 to -101.325 kPa).
Absolute vs. Gauge Vacuum Pressure
We typically categorize vacuum readings into two perspectives:
Gauge Vacuum: This measures the difference between the current process pressure and the ambient atmospheric pressure. It is often referred to as a negative pressure sensor reading, where a perfect vacuum is roughly -14.7 psi or -101.3 kPa at sea level.
For example, a miniature vacuum pump PH2506B has a measured value of -75 kPa, which means the pump can achieve a vacuum state 75 kPa lower than the atmospheric pressure at the measurement location.
Absolute Vacuum: This measures pressure relative to a perfect, total vacuum (zero pressure). This is the preferred method for high-precision scientific and industrial applications where barometric weather changes shouldn’t affect the data.
In practice, the absolute pressure value of a vacuum pump is between 0 and 101.325 kPa. Absolute pressure values need to be measured with an absolute pressure gauge. At 20°C and sea level (altitude = 0), the initial value of an instrument used to measure vacuum (absolute vacuum gauge) is 101.325 kPa (i.e., one standard atmosphere).
Vacuum Pressure Sensor Working Principle
The working principle of a vacuum pressure sensor is similar to that of a standard gauge pressure sensor. Using a flexible diaphragm, the pressure of the medium acts directly on the sensor’s diaphragm, causing a minute displacement proportional to the medium’s pressure. This changes the sensor’s resistance. The electronic circuit detects this change and converts it into a standard signal corresponding to this pressure.
Piezoresistive and Strain Gauge Technology
Piezoresistive vacuum sensors use silicon-based strain gauges bonded to the diaphragm. When vacuum acts on the diaphragm, its resistance changes proportionally. This device is robust, reliable, and provides a very fast response for standard vacuum measurements.
Capacitive Vacuum Sensors
When extremely high accuracy is required, capacitive vacuum sensors are ideal. They work by measuring the change in capacitance between a moving diaphragm and a fixed plate. This type of sensor is extremely sensitive to even the smallest pressure changes, making it the preferred negative pressure sensor in high-end laboratories or semiconductor applications.
FAQ
In industrial production, some equipment needs to work in a vacuum state. At this time, the working equipment or environment needs to be evacuated. To accurately control the vacuum degree, the vacuum pressure sensor is an ideal choice for detecting the vacuum degree.
As the name suggests, the vacuum pressure transmitter detects pressure changes in the vacuum environment. To control the vacuum equipment, the vacuum environment is always maintained at a certain degree of vacuum, because the vacuum pressure is generally -1~0bar
Vacuum pressure sensors and vacuum pressure transmitters are used in a wide range of applications, such as electronic equipment, medical equipment, fire trucks, vacuum pumps, chemical industry and other industries.
Engineers who choose this type of sensor need to carefully understand their own needs and choose products that suit their working conditions. Sino-Inst is a manufacturer and wholesaler of vacuum pressure sensors. If you have any technical questions, please feel free to contact us!
-1.jpg)












