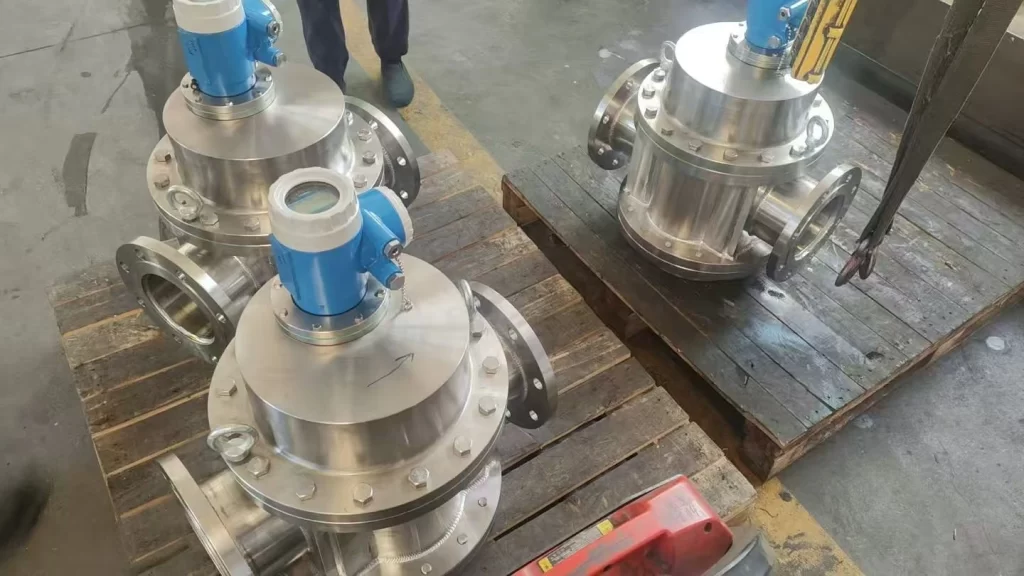
Flow measurement is a crucial aspect of industrial process parameter monitoring. Whether it’s gas, liquid, steam, or even solid powder, flow meters can accurately monitor flow rate. However, even the most advanced flow meters can fail. Flow meter failure affects measurement accuracy and can lead to downtime, economic losses, product damage, and violations.
What Causes Flow Meter Failure? Based on our years of experience in flow measurement at Sino-Inst, and combined with analysis of flow measurement across various industries, we have compiled a 11-point checklist to help you prevent flow meter failures.
Featured High-Quality Flow Meters
Category 1: Causes Related to the Flow Meter Itself
It’s possible that you chose the wrong flow meter and the wrong flow meter supplier from the very beginning.
- Flow Meter Manufacturing Quality
Flow meters may malfunction due to improper manufacturing or design flaws. In field use, flow meters exhibiting regular or frequent malfunctions should raise concerns, potentially requiring the selection of a more reliable product.
It’s difficult to judge the quality of a flow meter with the naked eye, especially the internal materials, structure, and circuit board quality. Therefore, we recommend against choosing excessively cheap flow meters; your cost will correspond to the quality of the flow meter.
- Incorrect Flow Meter Selection
Unprofessional flow meter suppliers may mislead you into selecting the wrong flow meter model.
For example, a DN50 pipe with a flow rate of only 2 m³/h. An irresponsible supplier might select a flow meter based solely on the pipe diameter, ignoring the actual flow rate. When the flow rate is too low, a pipe necking method or a different flow meter type may be necessary.
Therefore, when selecting a flow meter, you must clearly communicate the detailed parameters with our flow meter supplier.
Read more about: Industrial Inline Flow Meters | Selection List
- Parameter Settings & Flow Meter Calibration
This is a slightly more complex and technically challenging issue. If the supplier is unprofessional, or the user lacks understanding of flow meters, problems can easily arise during use due to incorrect flow meter parameter settings.
For example, ultrasonic flow meters require setting numerous parameters such as pipe diameter, wall thickness, material, fluid type, flow velocity, and pressure. Other flow meters may require setting parameters like frequency and K-factor.
Another category of parameters is flow meter calibration.
Depending on the type of flow meter, periodic calibration may be required. Even if the flow meter has good mechanical performance, improper calibration can lead to inaccurate or inconsistent readings.
We recommend choosing a professional flow meter supplier like Sino-Inst. We will provide you with complete flow meter manuals, and most flow meters have their parameters pre-configured before leaving the factory. We will also provide technical support if parameter modifications are needed.
Read more about: Flowmeter Calibration & Recalibration
Category 2: Reasons Related to the Measured Medium

- Corrosiveness of the Medium
The measured medium will directly contact the inside of the flow meter. Corrosive media may prevent the flow meter body or threads from opening, or even damage internal circuit boards or mechanical components.
For example, if you are measuring sulfuric acid solutions, you cannot choose a flow meter made of ordinary cast steel or 304 stainless steel. It is recommended to choose a flow meter made of PTFE or lined with PTFE.
This is an issue that needs to be considered in advance. If the measured medium or environment may be corrosive, be sure to inform us when purchasing the flow meter.
- Impurities in the Medium
Impurities in the medium may include scale, rust, sediment, viscous substances, and other particles.
For example, if your pipeline is made of cast iron, metal ions in groundwater or tap water will crystallize and adhere to the inner wall of the pipe, forming scale. These scales are composed of elements such as calcium, manganese, and sodium. If too many layers of scale accumulate, the flow channels within the pipe will narrow, restricting the flow rate.
Unlike scale, rust is a problem caused by oxidation inside the pipe. Rust can flake off and break off, causing blockages inside the flow meter or adhering to the flow meter’s observation window.
Also, deposits, viscous substances, or algae can adhere to the internal structure of the flow meter, leading to mechanical component failure.
If your pipeline is old, it is recommended that you choose a flow meter without obstructions or moving mechanical parts. Alternatively, you can install a filter before the flow meter.
- Air Bubbles
When liquid flows in from the inlet, air may also mix in, forming bubbles along with impurities in the liquid. These bubbles can accumulate due to temperature changes. Air bubbles can significantly affect liquid flow measurement.
For example, In vortex flow meters, air bubbles interfere with the formation of Karman vortices.
In ultrasonic flow meters, the propagation of ultrasonic waves can be suppressed by air bubbles, leading to malfunctions or incorrect readings.
In electromagnetic flow meters, air bubbles may cause unstable flow rates.
For pipelines with a small number of air bubbles, a Coriolis mass flow meter is recommended. Coriolis flow meters measure mass flow and are therefore unaffected by air bubbles. Alternatively, we recommend configuring a bubble elimination system for your pipeline.
- Pulsating Flow
When pulsation is significant, the instantaneous flow rate may momentarily exceed the flow meter’s rated flow rate. In this case, the flow meter displays a flow rate lower than the actual flow rate through the pipeline. For example, positive displacement reciprocating pumps are prone to significant pulsation.
To reduce pulsation, consider using vibration dampers such as accumulators. Furthermore, when pulsation causes the flow meter reading to change over time, extending the flow meter’s response time can ensure stable readings.
Category 3: Installation Reasons
- Insufficient Straight Pipe Section
The ideal installation location for a flowmeter is where the fluid flow upstream and downstream is a single-phase steady flow. This ensures that the influence of local resistance pipe fittings upstream and downstream on the fluid flow state does not directly interfere with the flowmeter’s measurement accuracy.
Ensuring sufficient straight pipe sections before and after the flowmeter helps stabilize and homogenize the fluid flow. This reduces vortices and uneven velocity distribution caused by local pipe resistance, thereby improving measurement accuracy.
The required straight pipe section varies for each type of flowmeter. Besides being related to the flowmeter’s measurement principle, it also depends on the type and arrangement of upstream and downstream resistance components (such as elbows, gate valves, regulating valves, etc.). Generally, a minimum of 15d upstream and 5d downstream straight pipe section is required for flowmeters. For electromagnetic flowmeters, 5d upstream and 3d downstream are required. Refer to the user manual for specific details.

Of course, some types of flowmeters do not require a pre-reserved straight pipe section. Examples include gear flowmeters and Coriolis mass flowmeters.
Read more about: Flowmeter Installation: Upstream and Downstream Straight Run Requirements
- Sealing Issues
Poor sealing of the flowmeter is one of the main causes of malfunction. Poor sealing can allow rainwater, condensation, dust, and humid gases to enter the flow meter.
Therefore, a good seal at the wire inlet is essential, and proper installation and maintenance procedures must be followed. Silicone sealant and glass glue can be used to improve sealing.
Category 4: Pipeline Environmental Factors
- Pipeline Vibration
When fluid flows through a pipeline or valves open and close, the pipeline itself vibrates. Furthermore, vibrations generated during equipment and device operation may also be transmitted to the pipeline.
Vibration is a common problem affecting flow meters. Vibration can cause flow meter bolts to loosen, pressure guide tube clamps to loosen, flow meter terminals to loosen, and weld cracks to appear.
For example, Coriolis and vortex flow meters may fail to measure flow accurately due to vibration. Electromagnetic and ultrasonic flow meters generally do not have this problem.
To reduce the impact of vibration on flow meters, measures such as using spring washers on bolts and tightening fixing bolts can be taken, and vibration prevention measures should be implemented in cooperation with process and equipment personnel.
- Electromagnetic Interference
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is electronic noise that interferes with cable signals and reduces signal integrity. EMI is usually generated by electromagnetic radiation sources such as motors and machines. This interference can lead to degraded equipment performance, data transmission errors, communication interruptions, and even hardware damage.
By taking comprehensive measures such as selecting appropriate installation locations, optimizing electrical connections, improving equipment anti-interference capabilities, performing regular maintenance and calibration, and adopting anti-interference technologies, the impact of electromagnetic interference on measurements can be effectively avoided, ensuring the accuracy and stability of the flow meter.
More Flow Measurement Cases and Solutions
Understanding the reasons why flow meters are prone to failure in the field is crucial for improving process control and production efficiency. These failures can be reduced through appropriate quality control, personnel training, environmental monitoring, and maintenance procedures, ensuring the reliability and stability of flow meters.
We, Sino-Inst, are a professional flow meter supplier. We will carefully select and supply the best-performing flow meters for you based on your specific on-site measurement conditions. Please feel free to contact us anytime!
-1.jpg)