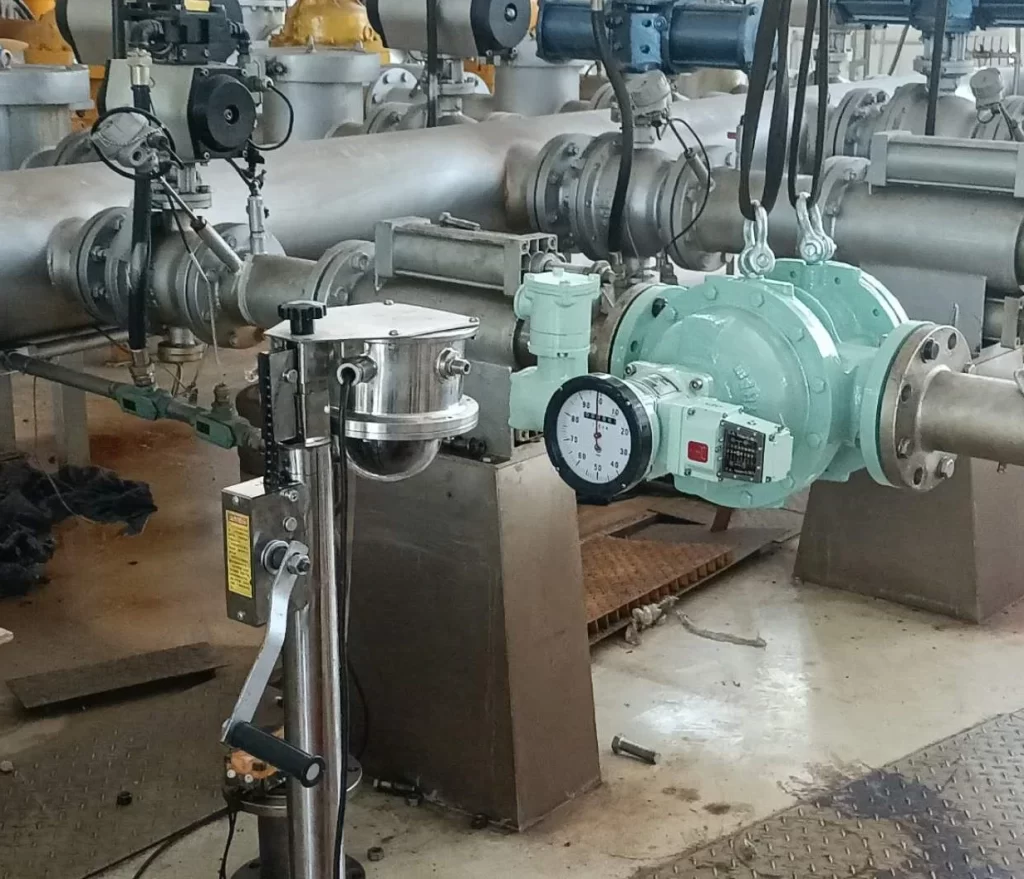
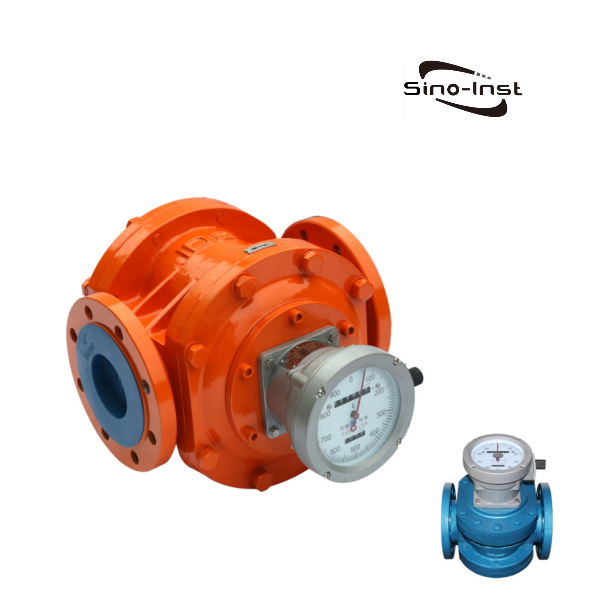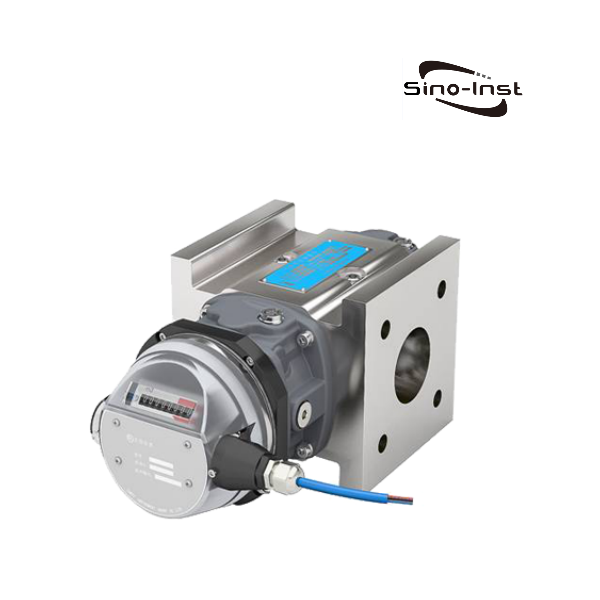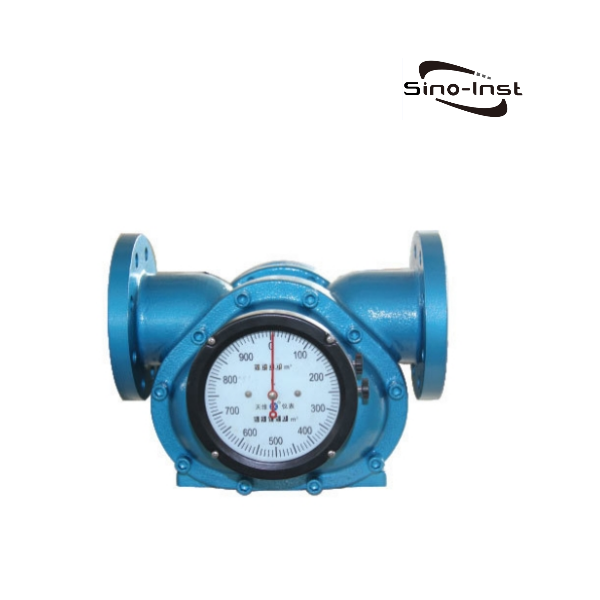
Positive displacement flow meters(PD Meter) are versatile and cost-effective. They can be used to measure clean, corrosive fluids and gases. When you need a high-precision flow meter at a reasonable price, a positive displacement flow meter is often the best choice.
This article will explain how positive displacement flow meters work, the technology behind different types of positive displacement flow meters, their main advantages, and their application areas.
What Is a Positive Displacement Flow Meter?
Positive displacement flow meters, also known as constant displacement flow meters or PD flow meters, are a type of flow meter with high accuracy. They divide fluid into fixed volume units using mechanical elements. The cumulative flow is calculated based on the number of times the measuring chamber is repeatedly filled and discharged.
Positive displacement flow meters are among the most accurate flow meters. Sometimes they can achieve accuracy as low as 0.2% of the actual flow rate. They are suitable for flow measurement in industries such as chemical, petroleum, pharmaceutical, metallurgical, and food processing.
Furthermore, these flow meters can operate without a power source. There are no requirements for upstream or downstream straight pipe sections during installation. They are ideal for measuring the flow rate of viscous fluids, such as oil, fuels, and solvents.
How Do Positive Displacement Flow Meters Work?
A volumetric flow meter uses mechanical measuring elements to divide a fluid into individual, known volume portions. The total fluid volume is measured by the number of times the measuring chamber is repeatedly filled and discharged with that volume portion of fluid.
The working principle of a typical volumetric flow meter (elliptical gear type) is shown in Figure 1. Two elliptical gears roll against each other in contact rotation. P1 and p2 represent the inlet and outlet pressures, respectively, and obviously, p1 > p2.
The lower gear (a) rotates counterclockwise under the pressure difference on both sides, acting as the driving gear. The upper gear, due to equal pressure on both sides, does not generate rotational torque and is the driven gear. It is driven by the lower gear and rotates clockwise.
In position 1(b), both gears generate rotational torque under the action of the pressure difference and continue to rotate. When installed in position 1(c), the upper gear becomes the driving gear, and the lower gear becomes the driven gear, continuing to rotate to the same position as in Figure 1(a), completing one cycle.
One cycle of operation discharges the fluid volume from four crescent-shaped cavities formed by the gears and the housing wall; this volume is called the flow meter’s “circulating volume”.
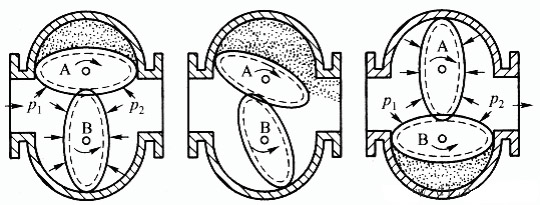
The flow meter’s “circulating volume” is υ. The number of gear rotations in a given time is N. Then the volume of fluid flowing through the flow meter during that time is V.
Therefore, V = Nυ
Types of Positive Displacement Flow Meters
Common types of positive displacement flow meters include oval gear flow meters, rotary impeller flow meters, scraper flow meters, rotary piston flow meters, and screw flow meters. They all share the same core principle: the periodic movement of mechanical components to divide a fixed volume of fluid.
Oval Gear
Oval gear flow meters are a type of positive displacement flow meter. They are among the most accurate flow meters.
Oval gear flow meters measure flow rate by the rotation of internal gears as fluid flows through them. The total flow volume is measured by the number of times the measuring chamber is repeatedly filled and discharged.
Oval gear flow meters can be manufactured from various materials, such as cast iron, cast steel, 304 stainless steel, and 316 stainless steel.
They are widely used for measuring high-viscosity media, such as diesel, gasoline, kerosene, heavy oil, paraffin wax, asphalt, fuel oil, hydraulic oil, engine oil, and crude oil.
Helical Gear
Helical gear volumetric flow meters use meshing helical gears as rotors to divide fluid into fixed volumes for measurement.
The rotor (helical gear) of the helical gear flow meter rotates under the influence of fluid pressure differential. A fixed volume of fluid is discharged per revolution. The total fluid volume can be calculated by measuring the number of gear rotations.
Helical gear flow meters offer an accuracy of ±0.5%R, and the measurement results are independent of fluid properties. They are suitable for measuring the flow rate of high-viscosity media (such as heavy oil and resins).
Helical gear flow meters require horizontal or vertical installation, with the axis parallel to the ground. A filter or venting device must be installed when the flow meter contains solid particles or gases.
Reciprocating/Oscillating Piston
An oscillating piston flow meter consists of a housing, inner and outer cylinders, a rotating piston, baffles, and a magnetic coupling. Its core component is the rotating piston, which is driven to rotate eccentrically by the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet. The magnetic coupling transmits the number of rotations to the counting mechanism to achieve flow measurement.
Each piston is mechanically or magnetically driven to inject fluid into the cylinder and then discharge it. Each stroke represents a finite measurement of the fluid (this can be a single-piston or multi-piston device).
Oscillating piston flow meters have a large flow capacity and a simple structure. They are typically used for viscous fluids, such as oil metering on engine test benches.
These flow meters are also used in residential water systems, allowing small amounts of impurities to pass through, such as pipe scale and fine sand. However, they cannot pass large particles or abrasive solids.

Nutating Disk
The measuring element of a oscillating disc flow meter consists of a flat disc surrounding a central sphere. This element is mounted within a measuring chamber with arc-shaped sidewalls, allowing it to rotate.
The disc, mounted on the sphere, “oscillates” about its axis in response to fluid flow. Each rotation represents a certain amount of fluid passing through. The circular disc of the oscillating disc flow meter is mounted on a main shaft within a cylindrical chamber.
By tracking the movement of the main shaft, the flow meter can determine the number of times fluid is captured and discharged from the chamber. This information is used to determine the flow rate.
The oscillating disc flow meter is the most commonly used and most accurate type of volumetric flow meter. It is an economical and efficient choice for metering industrial fluids. It can be used in a variety of applications, including condensate recirculation, boiler feedwater, and additive dispensing.
Rotary Vane
A rotary vane flow meter consists of two or more vanes. The rotating impeller divides the space between the vanes into individual volumes. Each rotation (or vane passage) is counted.
Flow rate = Measuring chamber volume × Rotation speed × 4
Diaphragm
A diaphragm flow meter is a device that measures and transports fluids through the reciprocating motion of a flexible diaphragm. It is primarily used in fluid measurement and transport applications.
The core component of a diaphragm flow meter is the flexible diaphragm. Fluid is drawn in from the inlet side of the oscillating diaphragm and then discharged from the outlet. The flow rate is determined by counting the oscillation cycles of the diaphragm.
Diaphragm flow meters are compact, highly corrosion-resistant, and suitable for high-viscosity, corrosive, or easily clogged fluids. They offer flexible flow adjustment and high accuracy.
Bi-rotor and Tri-rotor
Twin rotor flow meters are primarily used for the precise measurement and control of liquid flow. They consist of a pair of helical rotors. As liquid flows through a fixed chamber, the rotors rotate. Each rotation discharges a fixed amount of fluid, and the flow meter calculates the flow rate based on the number of rotations.
Twin rotor flow meters can achieve accuracy classes of 0.5 and 0.2, with repeatability errors not exceeding 1/3 of the basic error limit. They can handle high-viscosity fluids, making them ideal for industrial applications.
Triple rotor flow meters utilize three synchronously rotating rotors to measure the flow rate of liquids in closed pipes. Their internal components have no direct metal-to-metal contact, resulting in low friction and a long service life. They are suitable for measuring industrial liquids such as crude oil and refined oil.
Compared to ordinary rotor flow meters, triple rotor flow meters achieve volumetric measurement through the synchronous rotation of three rotors. They offer higher accuracy and are suitable for high-flow-rate applications.
Advantages and Considerations
Advantages
Positive displacement flow meters offer numerous advantages, making them superior to other flow meter technologies in certain applications.
- Suitable for high-precision metering requirements, especially for high-viscosity liquids.
- Minimal maintenance required.
- Excellent high-pressure and hydraulic performance.
- No straight-line requirement, unaffected by turbulence.
- Direct reading of cumulative values without external power source.
- Pipe conditions (such as straight pipe length) have no significant impact on metering accuracy.
- Accuracy remains unaffected over a wide range of viscosity or temperature.
- More economical than some other technologies suitable for similar applications.
Considerations
Certain characteristics of positive displacement flow meter technology make them unsuitable for certain applications. Some positive displacement flow meters require viscous or lubricating media to protect the gears.
Polygonal displacement flow meters are typically only capable of unidirectional flow measurement. They are only suitable for clean media and not for applications where cavitation is present.
If made of metal, positive displacement flow meters are significantly heavier than non-positive displacement flow meters. This is because the valve body of the flow meter is usually thicker, resulting in a much higher cost.

Selection Considerations
Gear flow meters, as a type of positive displacement flow meter, are commonly used instruments for measuring fluid flow. Proper selection directly affects the accuracy, stability, and service life of the measurement. Therefore, the following key considerations should be taken into account when selecting a positive displacement flow meter.
1. Fluid Medium Characteristics
Consider whether the medium is chemically corrosive. This determines the material selection for components in contact with the medium. Such as 304 stainless steel, 316 stainless steel, Hastelloy, or special coatings.
Alternatively, consider whether the medium contains solid particles or impurities. If particles are present, a filter must be installed upstream of the flow meter to prevent gear jamming or wear. In severe cases, other types of flow meters should be considered.
Consider the dynamic viscosity of the medium at the operating temperature. Gear flow meters are suitable for measuring medium to high viscosity fluids. The higher the viscosity, the lower the internal leakage, which is more advantageous for measurement.
2. Operating Parameters
Flow Range: Determines the minimum, normal, and maximum flow rates. When selecting the range, the maximum flow rate should not exceed the flow meter’s upper limit. The normal flow rate is recommended to be between 20% and 80% (or 1/2 to 2/3) of the flow meter’s range.
Operating Temperature: The actual temperature of the medium. This affects material selection, sealing material selection, and whether a high-temperature heat dissipation device is required.
Operating Pressure: The maximum operating pressure of the system. Ensure the flow meter’s rated pressure meets the requirements to prevent damage from overpressure. Common pressure ratings include 1.6MPa, 2.5MPa, 4.0MPa, and 6.3MPa.
3. Installation Conditions and Environment
Pipe Diameter. The flow meter diameter and pipe diameter can differ. However, they must be connected via a reducer (contraction or expansion pipe), ensuring sufficient straight pipe length.
Installation Direction. There are usually horizontal or vertical requirements. Most gear flow meters have specific installation direction requirements; follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Consider the ambient temperature, humidity, explosion-proof requirements, and protection rating of the flow meter. In harsh environments such as dusty conditions, select products with a high protection rating.
4. Output and Function
Consider signal output requirements: Is an output signal needed, and if so, what type? For example, 4-20mA, pulse, HART, Modbus, etc. For remote display, control, or integration with a DCS/PLC system.
Does the local display require a mechanical pointer meter, LCD display, cumulative flow display, reset function, etc.? For easy on-site viewing of instantaneous and cumulative flow.
5. Accuracy and Economy
Accuracy class. For example, ±0.5%, ±0.2%. For trade settlement or precision measurement, a higher accuracy class (e.g., 0.2 or 0.5) should be selected.
Total cost. Consider purchase cost, installation cost, maintenance cost, calibration cost, and spare parts cost. Choose a product with a high cost-performance ratio while meeting performance requirements.
How Accurate Is a Positive Displacement Flow Meter?
Positive displacement flow meters are among the most accurate types of flow meters. They are particularly suitable for measuring high-viscosity liquids (such as oils). However, they are not suitable for liquids containing impurities or with low viscosity. And their adaptability to large-diameter applications is poor.
The accuracy of positive displacement flow meters is typically between 0.25% and 0.5%. Some high-precision models can reach ±0.2%. However, their accuracy is affected by leakage flow, gear ratio constant, etc. These errors can be corrected using formulas.
Industrial Applications
Positive displacement flow meters (PD flow meters), as one of the three major mainstream flow meters, stand alongside differential pressure flow meters and float flow meters, occupying an important position in numerous application areas. They are particularly suitable for accurate total quantity measurement of expensive media, such as oil and natural gas, ensuring precise resource metering and effective management.
In the markets of industrialized countries, positive displacement flow meters, especially PD flow meters, have shown strong sales performance. Statistics show that these flow meters account for approximately 13% to 23% of sales, demonstrating their widespread application in industrial metering equipment.
- Oil and Gas
- Water and Wastewater Treatment
- Chemicals
- Power Generation
- Pharmaceuticals
- Food and Beverage
- Pulp and Paper
- Metals and Mining
- Aerospace
- Hydraulic Testing
FAQ
More Flow Measurement Cases and Solutions
Positive displacement flow meters play a vital role in various industries. They accurately measure fluid flow rates with a precision of ±0.1% to ±0.5%. They are particularly suitable for measuring the total volume of high-viscosity media and expensive fluids such as oil and natural gas. You can choose the appropriate flow meter type based on your application requirements and fluid characteristics.
Sino-inst possesses extensive experience and expertise. We offer a wide range of high-quality Positive displacement flow meters to meet the needs of diverse industrial applications. You can choose the appropriate flow meter type based on your application requirements and fluid characteristics.
The Sino-inst team is always ready to assist you. If you need to purchase a volumetric flow meter or learn more, please contact us today!
-1.jpg)







