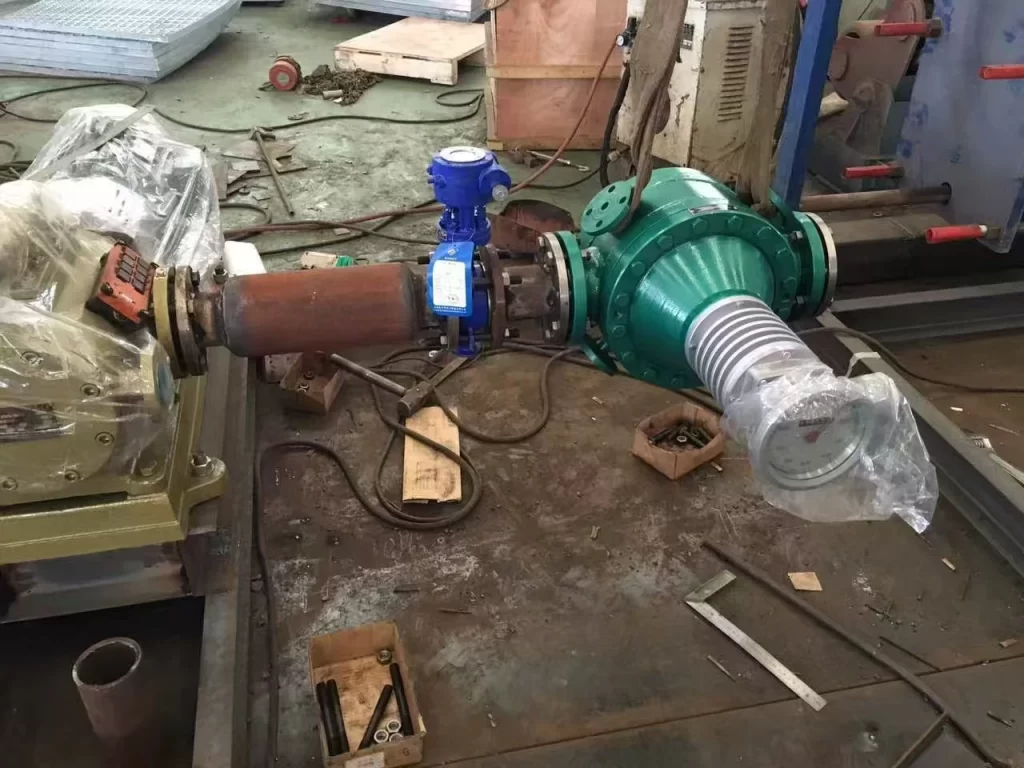
Measuring the flow of media at extreme temperatures in industrial processes has always been a challenging task, whether it’s high-temperature gas, high-temperature liquid, or extremely low-temperature liquid. Conventional flow meters may experience reduced accuracy or even damage when exposed to high-temperature media.
Based on years of experience in flow measurement, Sino-Inst has summarized flow measurement solutions for extreme temperatures, including both extremely high (900℃) and extremely low (-200℃) temperatures. Here, we primarily share information on high-temperature gas and high-temperature liquid flow measurement. We hope this will help you select the appropriate high temperature flow meter to achieve process efficiency, safety, and compliance in demanding industries such as power generation, petrochemical refining, and metallurgy.
Challenges in High-Temperature Flow Measurement
High-temperature industries form the core of numerous manufacturing sectors. In power generation, precise measurement of superheated steam flowing into turbines directly determines electricity generation efficiency. Within petrochemical refineries, furnaces and cracking units operate at extreme temperatures to break down crude oil into valuable products. Monitoring the flow of hydrocarbons, hydrogen, and catalyst gases is fundamental to controlling these reactions.
The unique physical properties of these high-temperature media—such as heat transfer fluids and superheated steam—along with complex, harsh operating conditions, present significant flow measurement challenges, primarily manifested in the following aspects:
Consider the metallurgical industry. Furnaces used to smelt and cast metals like steel, aluminum, and copper rely on precise control of combustion air, fuel, and exhaust gas flows. In glass manufacturing, the flow of molten glass and hot air within annealing furnaces must be meticulously managed to ensure product quality. Even in environmental applications, such as Continuous Emissions Monitoring Systems (CEMS) on smokestacks, high-temperature corrosive flue gases must be measured to comply with air quality regulations. In all these applications, fluid temperatures are far from comfortable room temperatures; they are often hot enough to make steel glow.
1. Temperature Drift Issues
In high-temperature environments, parameters like medium density and viscosity undergo significant changes with temperature. Take thermal oil as an example: its viscosity at 200°C may decrease by over 80% compared to ambient temperatures, leading to substantially increased measurement errors in flowmeters that rely on fixed parameters for calculation (errors may exceed ±15%).
2. Phase Change Risks
If high-temperature steam experiences a sudden temperature drop, it may undergo condensation phase transition, forming a two-phase gas-liquid flow that causes severe fluctuations in measurement signals.
3. High-Temperature Corrosion and Deformation
Prolonged exposure to temperatures above 300°C may cause intergranular corrosion in common stainless steels (e.g., 304). Internal flowmeter components (such as vortex generators or sharp edges of orifice plates) are susceptible to softening and wear due to high temperatures, leading to measurement drift.
Additionally, many flue gases are highly temperature-sensitive, characterized by elevated temperatures, severe contamination, and often chemical corrosiveness.
4. Differences in Thermal Expansion Coefficients
Mismatched thermal expansion coefficients between the instrument body and pipeline materials (e.g., carbon steel and stainless steel) may cause seal failure, stress concentration, leakage, or displacement of measuring elements (e.g., eccentric orifice plate installation).
5. High-Temperature Operational Risks
Field installation and commissioning require special protective measures when medium temperatures exceed 200°C. Maintenance operations become challenging, and shutdowns for servicing may disrupt production continuity.
6. Coking and Fouling Issues
High-temperature media like thermal oil may coke due to localized overheating, adhering to flowmeter inner walls (e.g., vortex sensor probes). This alters flow path geometry, causing measurement errors to increase annually (annual error growth may reach 5%-10%).
7. Material Compatibility
Prioritize high-temperature alloys (e.g., 316 stainless steel, Hastelloy C-276, Inconel 600), which maintain strength and corrosion resistance at 600°C, outperforming standard stainless steel.
8. Installation Process – Insulation and Support
The flowmeter body must be wrapped with an alumina-silica fiber insulation layer. Piping requires high-temperature expansion joints to prevent thermal stress from affecting instrument accuracy.
Featured High Temp Flow Meters
Sino-Inst supplies various types of high-temperature flow meters suitable for different temperature ranges and media characteristics. We need to consider the actual measurement parameters to select the appropriate high-temperature flow meter.
| Technology Type | Operating Principle | Typical Max Temp | Suitable Fluids | Key Advantages | Key Limitations |
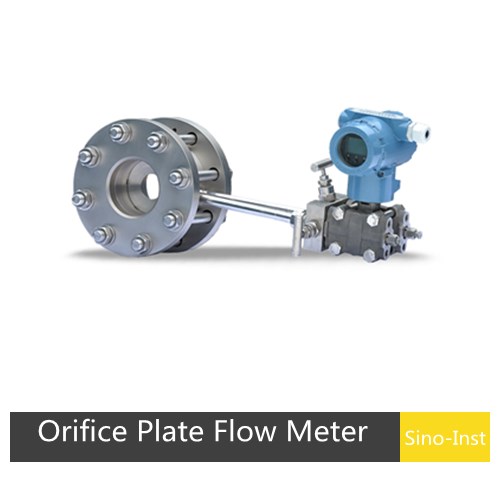
| Differential Pressure (DP) flow meter | Measures pressure drop across a restriction (Bernoulli’s Principle). | >1000°C (with proper design) | Liquids, Gases, Steam | Highly versatile, well-understood, no moving parts in flow. | Requires pressure/temp compensation for mass flow; potential for clogging. |
| Vortex flow meter | Measures frequency of vortices shed from a bluff body (von Kármán effect). | ~420°C (standard); higher with special construction. | Liquids, Gases, Steam | Robust, no moving parts, good for steam, high accuracy. | Requires minimum flow velocity; not for very viscous fluids. |
| Thermal Mass flow meter | Measures heat transfer from a heated sensor to the fluid. | ~350°C (with remote electronics); higher ratings available. | Clean Gases | Direct mass flow measurement, high sensitivity at low flows. | Primarily for gases; susceptible to coating or moisture. |
| Ultrasonic (Transit-Time) flow meter | Measures time difference of ultrasonic pulses traveling with and against the flow. | ~600°C (with high-temp transducers/buffers). | Clean Liquids, Gases | Non-intrusive (clamp-on), no pressure drop. | Requires clean fluid; accuracy can be affected by temperature gradients. |
| Coriolis flow meter | Measures tube vibration caused by the inertia of the flowing mass (Coriolis effect). | ~350°C (special models); limited by tube material. | Liquids, Gases | Highest accuracy, direct mass flow, measures density. | Very expensive, limited high-temp availability, can be heavy. |
| Oval Gear Flow Meter | Measures fluid flow by rotating two meshing oval gears. The pressure difference of the fluid drives the gears to rotate. | ~350°C (special models); | Liquids(Especially high viscosity fluids) | The measurement is stable, reliable, and highly accurate. The basic error is typically 0.5%R, and can reach 0.2%R. It is particularly suitable for measuring high-viscosity fluids. | Need to ensure a sufficient flow of the measured medium to prevent leakage errors from affecting measurement accuracy. If the liquid contains solid particles, a filter must be installed upstream of the pipeline; if it contains gas, an exhaust system should be installed. |
| Target Flow Meter | A resistance-type flow meter designed based on the principle of a force-balanced differential pressure transmitter. | -196℃~+500℃ | Liquids, Gases, Steam | Features integrated temperature and pressure compensation. Capable of directly outputting mass flow rate or standard cubic meters per minute. | High installation costs and narrow flow range. |
Read more about:
- Thermal Mass Flow Meter Technology
- Ultrasonic Flow Meter Technology
- Coriolis Mass Flow Meter Technology
- Differential Pressure Flow Meter Technology
- Vortex Flow Meter Technology
High Temperature Gas Flow Meter
High-temperature gases, such as flare gas, combustion air, and high-temperature mixed gases.
Combustion Control: Measuring the mass flow of air and fuel (e.g., natural gas) entering large boilers or furnace chambers enables precise control of the air-fuel ratio, thereby maximizing efficiency and minimizing emissions.
Flare Gas Monitoring: Environmental regulations typically require measurement of waste gas flow sent to flare stacks. These flows may be very low under normal conditions but can surge significantly during process abnormalities.
Compressed Air and Specialty Gases: Monitoring consumption of compressed air or other gases (e.g., nitrogen and argon) throughout the plant aids in energy management and leak detection.
Numerous other high-temperature gases require monitoring under operational conditions. We can select vortex flow meters, thermal mass flow meters, or differential pressure flow meters based on actual measurement parameters.
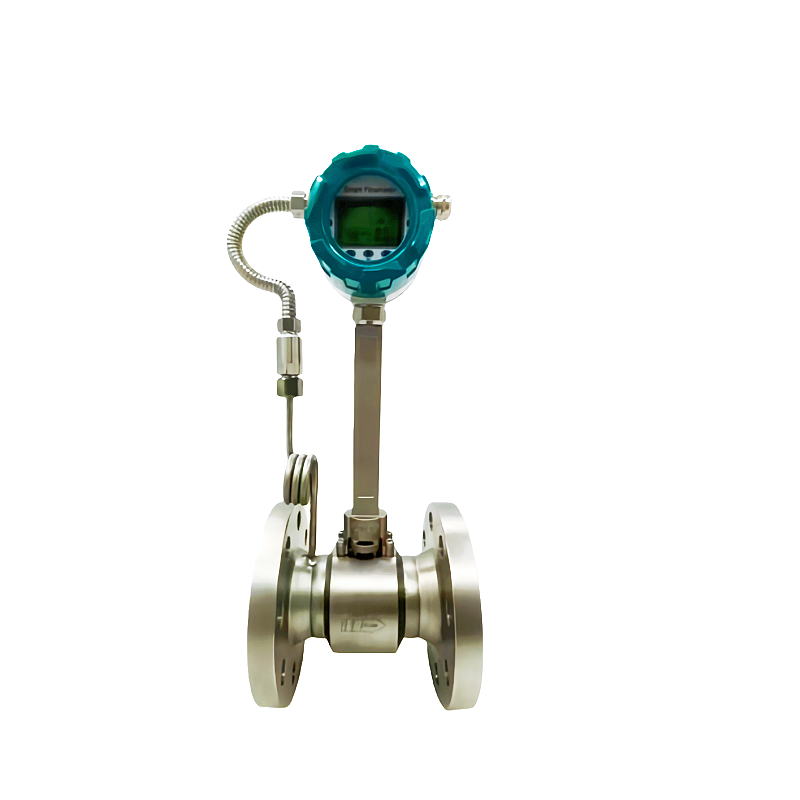

Vortex Flow Meter
Sino-Inst’s TVK vortex flow meter employs internationally advanced ADSP adaptive digital signal processing, utilizing digital signal processing technology to achieve adaptive filtering, system identification, signal detection, and analysis. This results in the following advantages:
- High temperature resistance up to 420℃, crystal resistance to high-temperature aging (thermoelectric, petrochemical, chemical, pharmaceutical, etc.).
- Range ratio of 1:40 (ultra-wide range achieving zero leakage in measurement), ultra-low lower limit, achieving a minimum vibration of 1.5 meters per second.
- Vibration resistance of 1.0g (spectral waveform analysis).
- High precision of 1.0 grade.
- The probe packaging uses multi-crystal packaging technology, extracting composite signals from both positive and negative electrodes, resulting in a more stable signal.
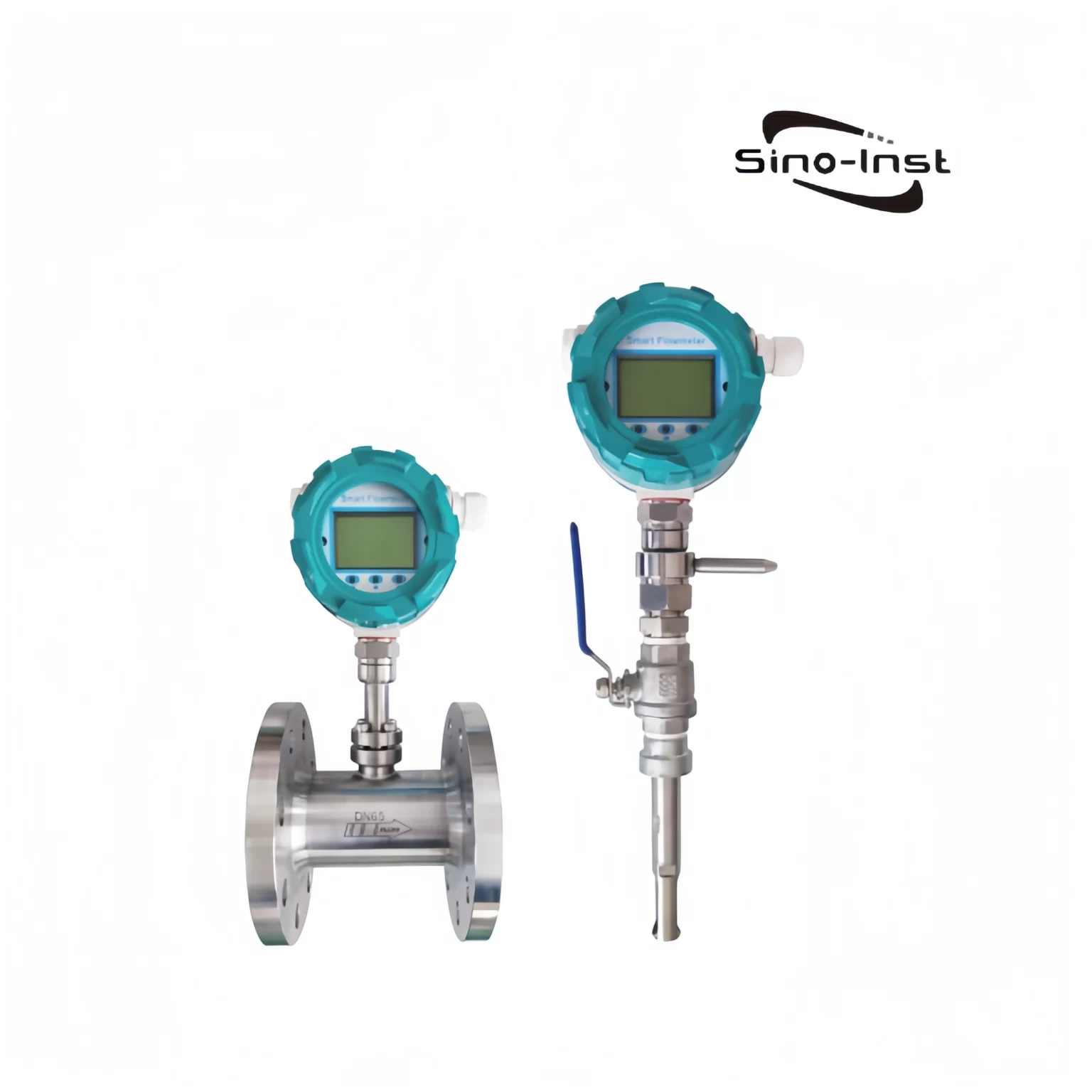

Thermal Mass Flow Meter
A thermal gas mass flow meter is an instrument that measures gas flow rate using the principle of thermal diffusion. It requires no temperature or pressure compensation, making it the preferred product for measuring the flow rate of dry gases. It is widely used in fields such as coal gas, natural gas, compressed air, and semiconductor process gases, effectively monitoring gas flow rate in pipelines.
| Diameter | DN15~DN6000mm |
| Accuracy | ±1% |
| Temp. range | -20~350℃ |
| Pressure | Medium pressure≤10MPa |
| Flow rate | 0.1-100m/s |
| Protection | IP67 (sensor part) |
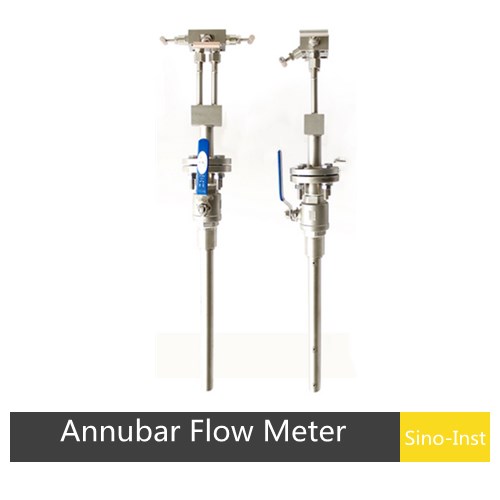

Annubar Flow Meter
Annubar flow meters are differential pressure flow meters based on the Pitot tube principle, widely used for measuring the flow of liquids, gases, and steam, and have the advantages of high accuracy and low pressure loss.
| Diameter | DN100~DN3000 |
| Accuracy | 1.0%,0.5%,0.2%. |
| Temp. range | -40~900℃ |
| Pressure | -0.4~40MPa |
| Medium | Liquid, Gas, Steam |
| Compensation form | pressure, temperature compensation |
High Temperature Liquid Flow Meter
Effective high-temperature fluid flow monitoring can save costs and improve production efficiency. Examples include high-temperature heat transfer oils and asphalt.
Vortex Flow Meter
Besides measuring gases and steam, vortex flow meters can also be used to measure the flow rate of high-temperature liquids. However, their applicability and performance are affected by the high temperature of the liquid. It is necessary to select an appropriate model and material, and take corresponding measures to ensure measurement accuracy and long-term stability.
High-temperature liquids may alter the flow characteristics of the fluid, especially changes in viscosity, which can affect the output accuracy of the flow meter. Therefore, for high-temperature liquids, selecting a vortex flow meter with temperature compensation is essential.
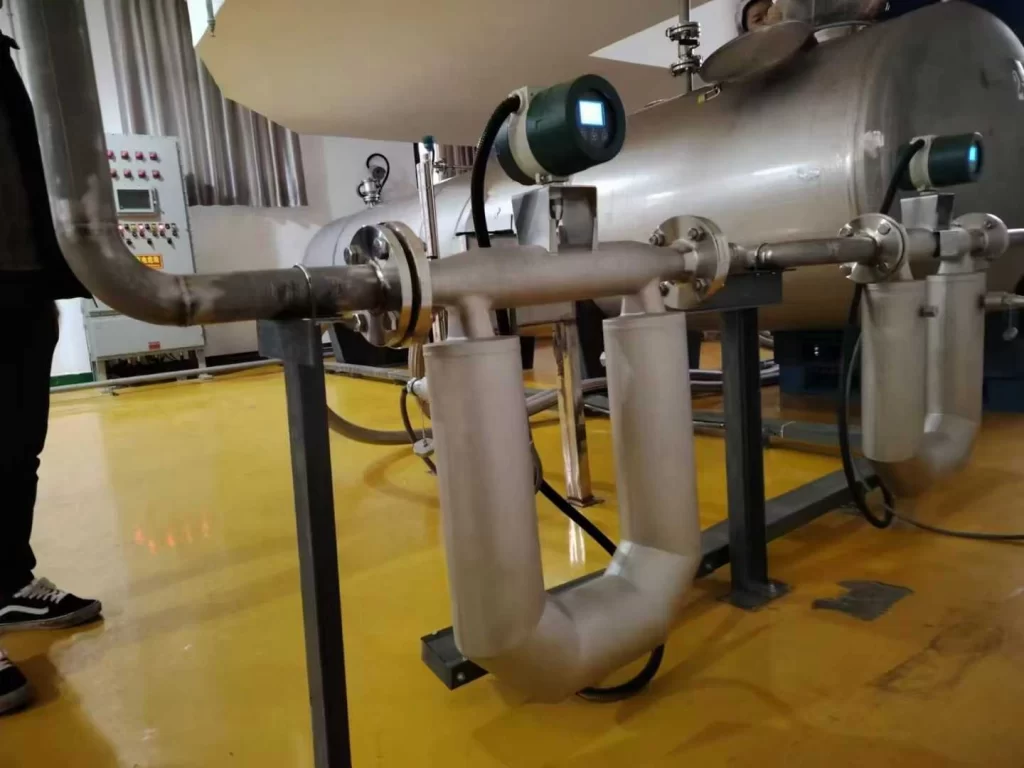

Coriolis Flow Meter
The Coriolis mass flow meter is a flow measurement device that uses a direct mass flow measurement method. It can accurately measure the mass flow rate of fluids in a pipeline. Furthermore, it boasts high stability, good reliability, a large range, and is suitable for high-viscosity fluids. The maximum temperature it can operate at is 350℃.
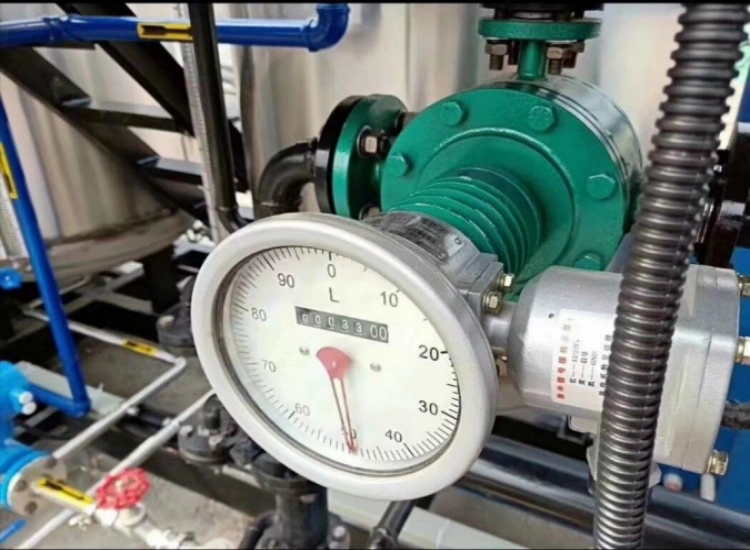

Oval Gear Flow Meter
With its advantages such as high precision, applicability to high-viscosity fluids, simple structure, and wide range of applications, the oval gear flow meter has become an important tool in the field of flow measurement.
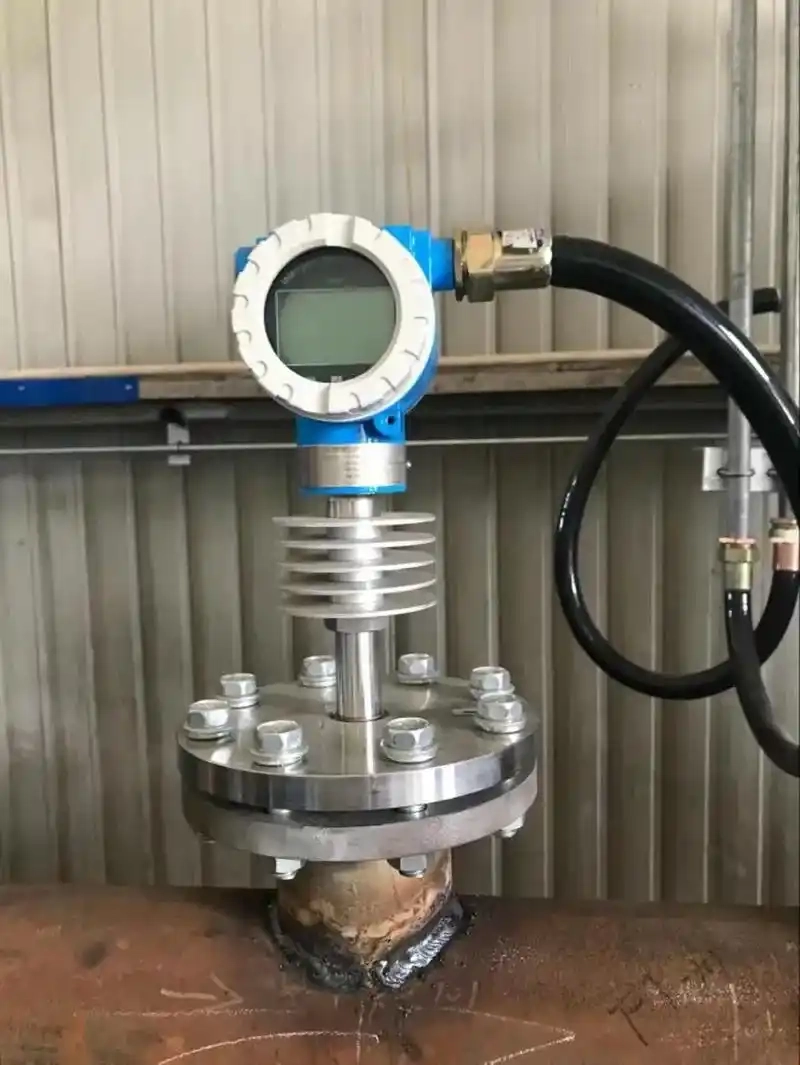

Target Flow Meter
Target flow meters also known as drag force flow meters. Insert a target (drag element), usually a flat disc or a sphere with an extension rod, into the flow field. They then measure the drag force on the inserted target and convert it to the flow velocity.
| Diameter | Φ10 ~ Φ2000, larger pipe diameter can be customized |
| Temperature | -196°C ~ 500°C |
| Pressure | 0~42MPa |
| Medium | gas, liquid (including high viscosity liquid, slurry), steam; |
| Velocity of flow | Suitable for low-velocity media, its measurable minimum flow rate is 0.08m / s |
Customized Solutions for High Temperature Flow Meters
Gravity Flow Meters for Diesel/Fuel Feed
Case Study: Custom Thermal Mass Flow Meter For Nitrogen Flow Measurement
Case Study – Liquid Nitrogen Flow Measurement
Case Study: Metal Tube Float Flowmeter for Glycerin Water Measurement
Case Study: Paint Flow Measurement
Case: Flow Meter for Liquid Cement Additive
Cryogenic Flow Meters Custom Cases
Variable Area Flow Meter Case: Oxygen Flow Measurement
Customer Case: Customized DN10 Flow Meter for Petrol
Application Case: Mass Flow Meter Measures Lime Slurry Flow and Density
FAQ
The challenges of high-temperature flow measurement extend beyond simply reading numbers; they also involve handling high-temperature media and harsh environments. High-temperature flow meters must not only be compatible with high-temperature media but also guarantee high-precision measurement.
Sino-Inst’s high-temperature differential pressure flow meters, vortex flow meters, and thermal mass flow meters have stood the test of time and possess broad applicability. Whether it’s high-temperature gas or high-temperature liquid, the selection process requires rigorous evaluation of the fluid, process conditions, and performance requirements.
We hope to help you transform your high-temperature flow meter selection into a cornerstone for stable, efficient, and safe industrial operation. Please feel free to contact our sales engineers!
-1.jpg)