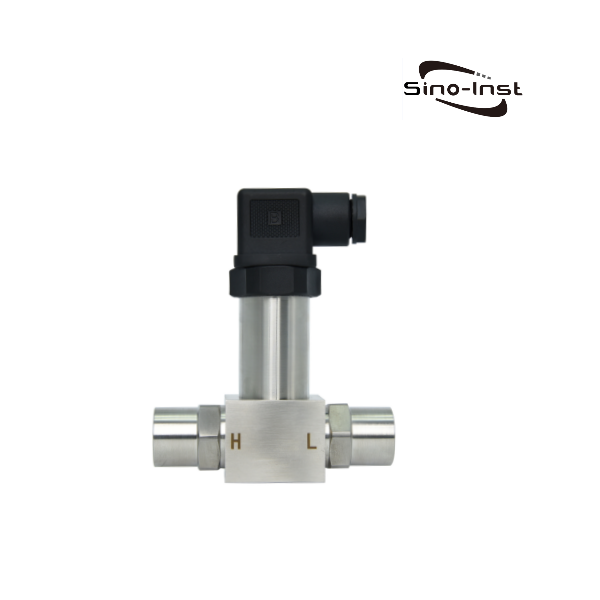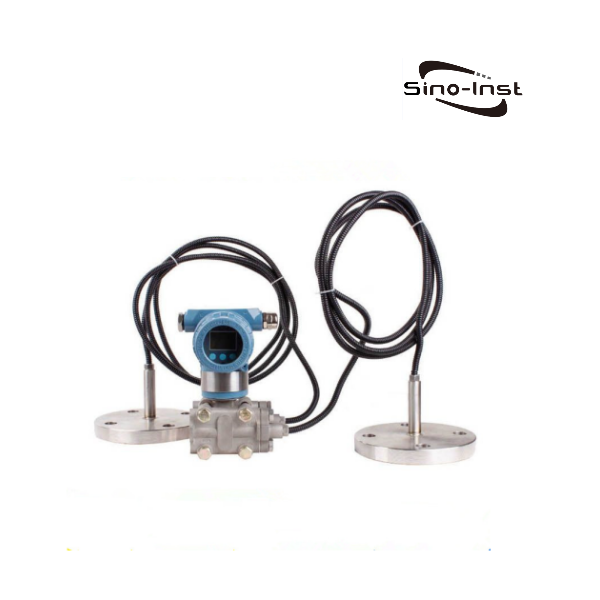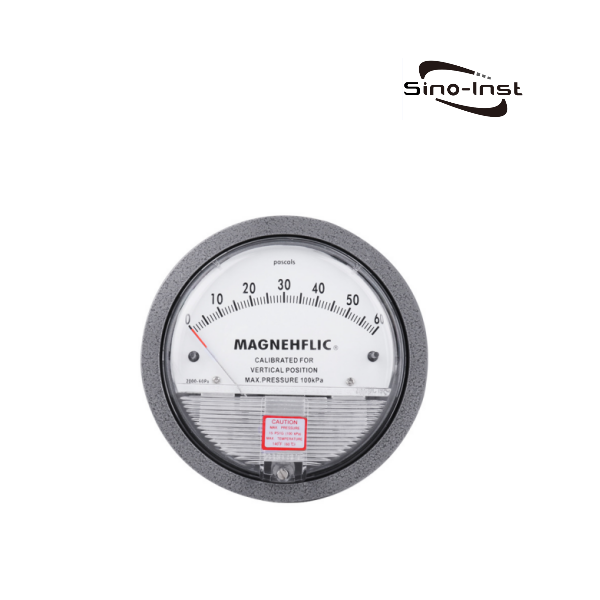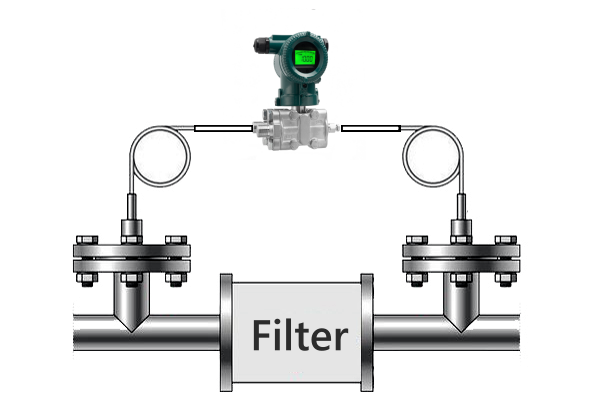
Filter Differential Pressure refers to the difference in inlet and outlet pressures when liquid or gas passes through the filter. By monitoring the differential pressure across the filter, the operator can understand how well the filter is performing.
In the filter, there is a pressure difference between the upstream of the filter and the downstream of the filter. Operators can confidently know when filters need to be replaced by monitoring the output signal from the differential pressure sensor. So, differential pressure sensors and differential pressure transmitters are essential for monitoring filter cleanliness in liquid or gas applications!
Filter differential pressure monitoring is important
Filter differential pressure refers to the difference in pressure between the fluid entering and leaving the filter when a liquid or gas passes through the filter. It is an important indicator to measure the performance and efficiency of the filter. It is also the basis for judging whether the filter needs to be replaced or cleaned.
In industry, environment and life, filters are widely used in the purification and separation processes of liquids and gases. The main function of the filter is to remove suspended particles, microorganisms, particulate matter, foreign matter and pollutants through physical or chemical means to ensure the purity and safety of the fluid.
When liquid or gas passes through the filter, the fluid will be affected by the resistance of the filter’s internal structure and materials, causing the pressure of the fluid to drop. This pressure difference is the filter differential pressure. The size of the filter pressure difference depends on many factors, including filter type, material, pore size, design, and the nature and flow rate of the fluid.
An increase in filter pressure differential may adversely affect fluid flow and filtration effectiveness. When the filter pressure difference exceeds a certain threshold, the flow rate of the fluid will slow down. It may even cause blockage and leakage of the fluid. In addition, the increase in filter pressure difference will also reduce the life and efficiency of the filter, causing the filter to need more frequent maintenance and replacement.
In order to accurately assess filter performance and determine whether the filter needs to be cleaned or replaced, filter differential pressure must be monitored and controlled. Commonly used methods include regularly detecting the inlet and outlet pressure of the filter and comparing the pressure difference. Using a differential pressure sensor to monitor pressure difference changes in real time. Using equipment such as a differential pressure gauge or pressure gauge for real-time or periodic measurement, etc.
By effectively monitoring and controlling the filter pressure difference, you can ensure that the filter is always in normal working condition and ensure the purity and safety of the fluid. In addition, cleaning or replacing the filter in time can also improve the life and efficiency of the filter and reduce maintenance costs and risks.
Featured DP Transmitters
Filter differential pressure monitoring process
For filter applications, the upstream side [A] is located before the filter [B]. The downstream side [C] is located after the filter. Differential pressure sensors can be used to monitor the differential pressure between AC.
- Upstream pressure (often referred to as line pressure or inlet pressure) drives the media through the filter. A line is installed before the filter and connected to the high side of the sensor.
- Filters remove contaminants from the media.
- Downstream pressure or outlet pressure then guides the media through the system with fewer contaminants than before. A line is installed at the lower end of the sensor to monitor differential pressure.
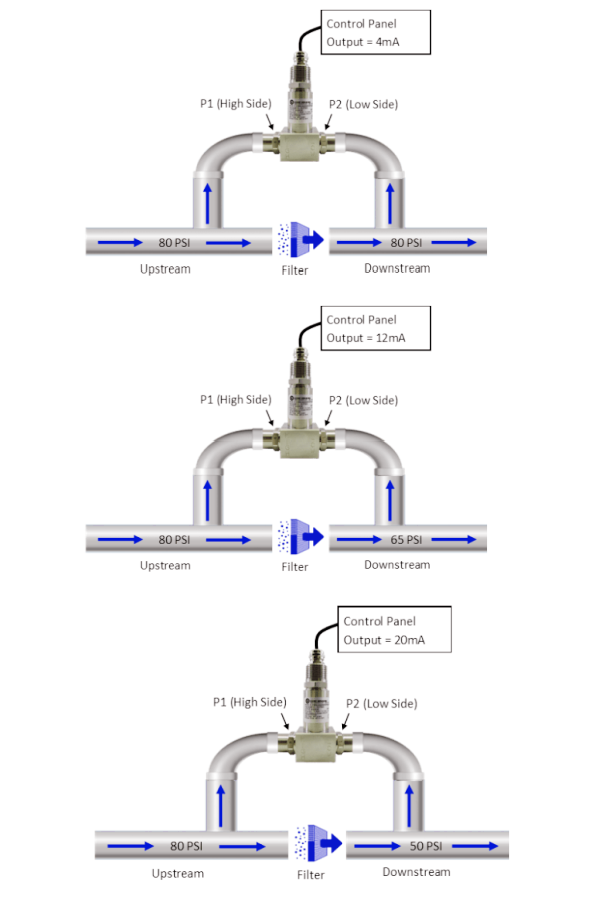
- When there are no contaminants in the filter, the system will measure 0 PSI differential pressure.
- As the filter becomes clogged, the pressure on the downstream side decreases. As a result, the differential pressure between the high side and the low side becomes larger.
- When using a differential pressure sensor, the device provides a linear output signal based on the differential pressure. Operators can monitor the condition of the filter locally or remotely based on differential pressure values.
Common Differential Filter Applications
Can I use two independent pressure sensors?
You may ask “Can I just use two separate pressure sensors to measure differential pressure?”
The answer is yes. Two independent pressure sensors can be used to measure differential pressure in filter applications.
However, there are some potential issues that we must take into consideration.
The first problem is related to compound errors.
If you use two pressure sensors, the accuracy of each sensor is ± 0.5%. The potential error then doubles to ±1%. If a differential pressure sensor is used, only the accuracy of a single sensor needs to be considered.
Additionally, while we temperature regulate each sensor during the manufacturing process, each sensor may also behave differently under different temperature conditions.
For example, if the application’s ambient temperature changes from room temperature to 55°C, the upstream sensor may have a TC span error of -0.5%. The TC span error of the downstream sensor is +0.5%. Using a dedicated differential pressure sensor eliminates this potential compound error.
The second issue is potential user error.
When using two single pressure sensors, the customer will need to create a program or manually calculate the difference in readings from the upstream and downstream sensors. This creates the possibility of making mistakes. If not detected early, equipment damage can occur due to insufficient flow in the system’s post-filter or contamination of the system media due to excessive filter clogging.
Our differential pressure sensors automatically calculate the pressure difference from P1 to P2 and transmit a linear output signal to your PLC or control panel.
More Pressure And Differential Pressure Measurement Solutions
- 2 Wire-3 Wire-4 Wire Pressure Transducer Wiring Diagram
- Industrial Analog Pressure Transducers | 4-20mA, 0-5/10V DC
- Submersible Pressure Transducers for Liquid Pressure and Level Measurement
- Explosion Proof Pressure Transducers- Intrinsically Safe – ExdIICT6-ExiaIICT6 Ga
- Pressure Transducer Troubleshooting: Expert Insights & Tips
- Fluid Pressure Guide: Static Pressure Vs. Dynamic Pressure Vs. Total Pressure
- Steam Pressure Sensor/transducer for Industrial Steam Measurement
- Industrial Pressure Transmitters: 7 Sensor Principles and 4 Main Types!
- Pipe Flow vs Pressure – Relationship & Calculate Tools
In short, the filter pressure difference refers to the difference in inlet and outlet pressures when liquid or gas passes through the filter. Understanding the meaning of filter differential pressure is particularly important for proper filter use and maintenance.
Timely monitoring and controlling the filter pressure difference can ensure the normal operation of the filter and the purity of the fluid. It can also improve the life and efficiency of the filter.
Sino-Inst produces and supplies compact differential pressure transmitters, intelligent differential pressure transmitters, high-precision monocrystalline silicon differential pressure transmitters, etc. Supports threaded installation, flange installation, high and low temperature and other parameter customization.
If you need to configure a monitoring system for the filter, or have related technical questions, please contact our engineers!
-1.jpg)



