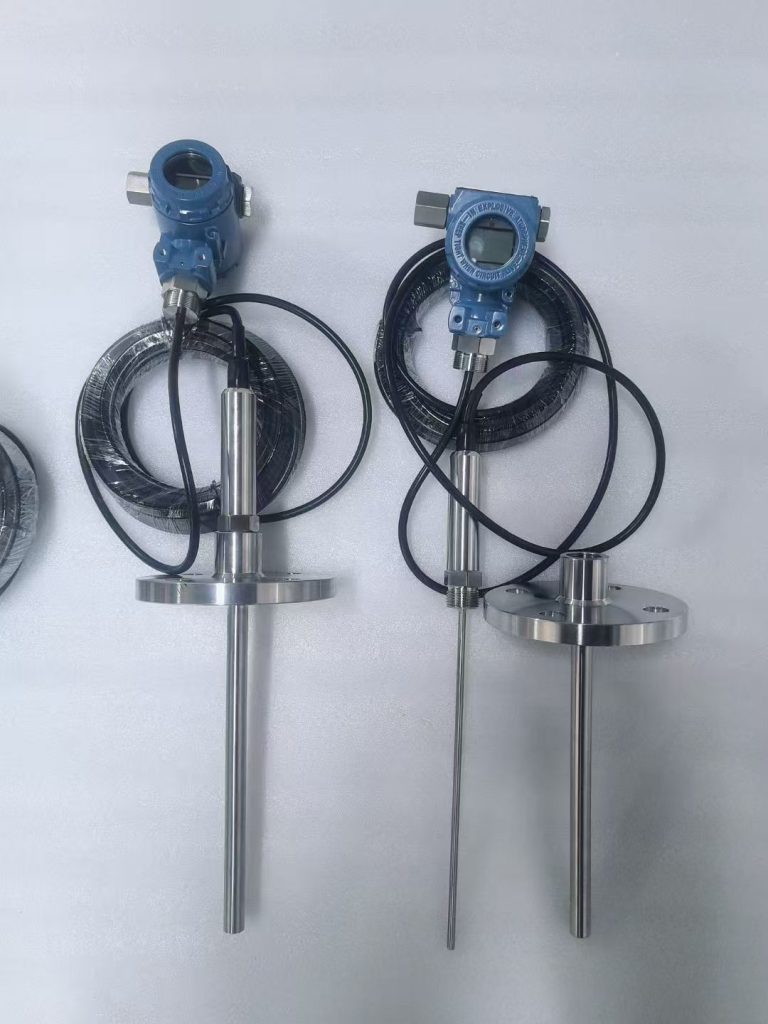
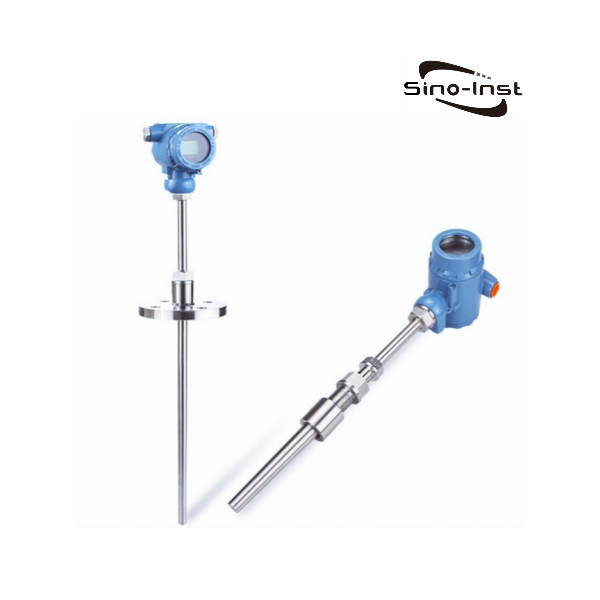
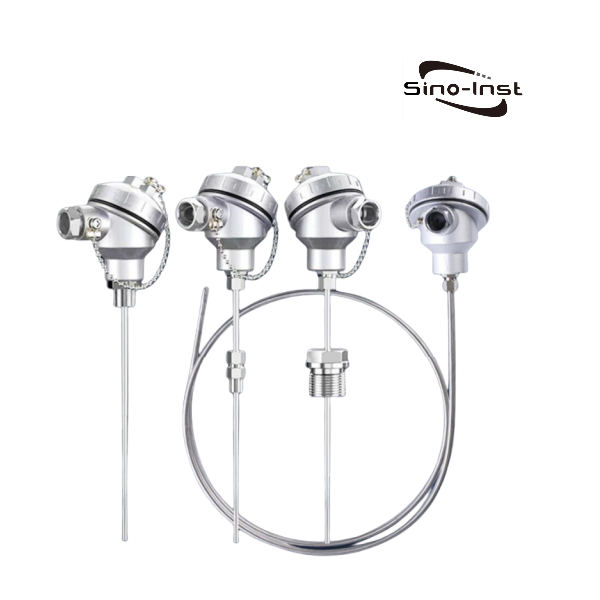
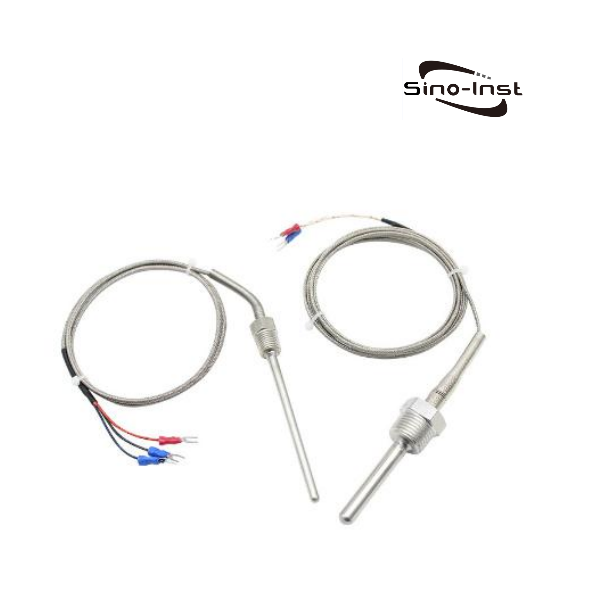
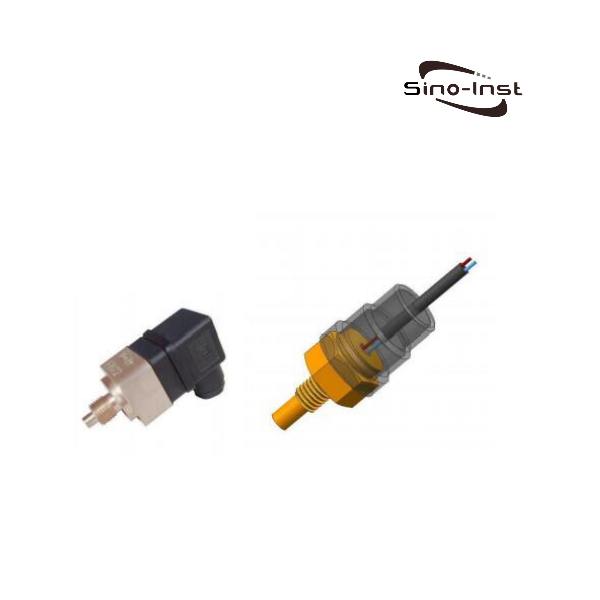
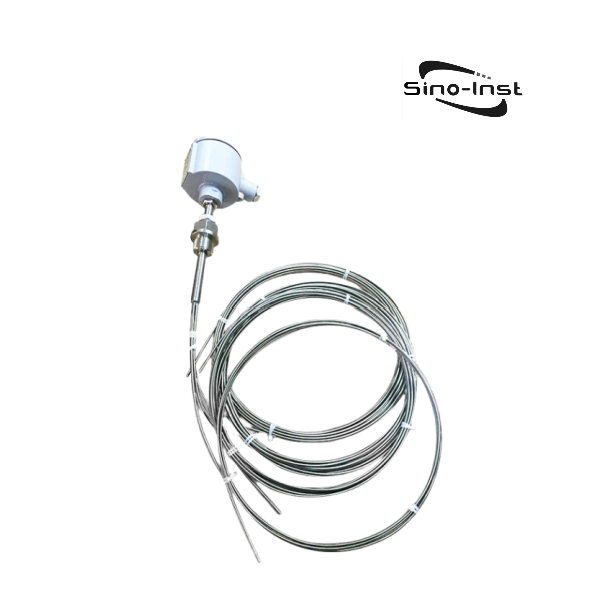
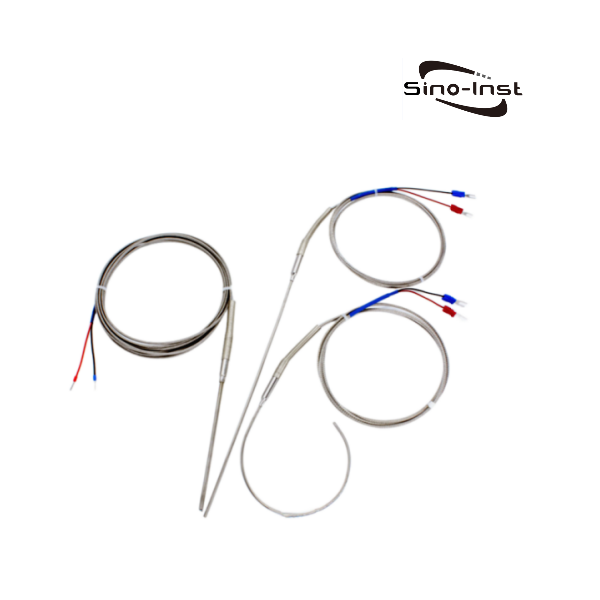
Temperature transmitters convert input signals from various sensors into standard output signals. Typically, these are 4-20 mA or 0-10 V. Examples include resistance sensors, thermocouples, and potentiometers.
Temperature transmitters connect temperature sensors to subsequent data processing and control systems. It ensures the stability and safety of the production process. Sino-Inst offers a variety of temperature transmitter configuration options. These options include customization of sensor type, transmitter signal, and mounting method.
What Is a Temperature Indicating Transmitter?
A temperature transmitter is a device that can convert the temperature signal detected by a temperature sensor into a standard electrical signal output.
The temperature transmitter uses thermocouples and thermistors as temperature-sensing elements. The output signal from the temperature sensing elements is sent to the transmitter module. It is converted into a 4-20 mA current signal, 0-5 V/0-10 V voltage signal, or RS-485 digital signal output that is linearly related to temperature.
Temperature transmitters are primarily used to measure and control temperature parameters. They are widely used for temperature control in power plants, oil and gas, and aerospace technology.
How Does a Temperature Transmitter Work?
The working principle of a temperature transmitter is to convert a temperature variable into a transmittable, standardized output signal. The transmitter’s output signal is then sent to a control device. Such as a loop controller, data logger, or display.
The temperature transmitter serves as the interface between the control system and the temperature sensor. It can isolate, amplify, correct nonlinearity, and convert the sensor’s input signal. It then converts it into a 4-20 mA current signal or a 0-5 V/0-10 V voltage signal that is linearly related to temperature.
Common Temperature Transmitters
Temperature transmitters can be categorized by measurement principle into thermocouple, RTD, and infrared non-contact types.
Based on the output method, they can be classified into analog, digital, and intelligent types.
Based on structural form, they can be categorized into integrated and split types.
The following are our featured temperature transmitters that can be used in various industries:
Application Areas of Temperature Transmitters
Differences Between Temperature Sensors, Temperature Transmitters, and Temperature Switches
| Characteristic | Temperature sensors | Temperature transmitters | Temperature switches |
| Function | It directly measures temperature and converts it into an electrical signal. | It can amplify, linearize, and convert the temperature signal into a standard signal output. | When the temperature reaches the preset value, it can automatically open or close the circuit. |
| Output Signal | Output resistance or digital signal | Can output current (4-20mA), voltage (0-10V), digital signal (RS485) | Directly trigger the switch action. No standardized signal output. |
| Structure | It is usually packaged from a single electronic component (such as a thermocouple, thermal resistor). Simple structure. | It consists of a temperature sensor and a conversion module. It has a complex structure. | It is composed of a temperature sensing element and a circuit control module. It can realize temperature triggering action. |
| Applications | Environmental monitoring, medical equipment | Process data transmission, equipment temperature control | Electrical overheat protection |
| Customization and Range | Fixed range. Output signal according to the rules | The temperature measurement range can be customized according to the needs. The output signal changes with the range | Preset fixed trigger temperature value. Not adjustable |
Installation of Temperature Transmitters
1. Confirm device parameters
Check whether the transmitter power supply voltage, input signal, and output signal match the system.
2. Select installation location
The installation location should avoid strong electromagnetic interference or high-temperature areas. Ensure good heat dissipation conditions. Some models require additional heat dissipation devices.
3. Sensor connection
For three-wire systems, connect the individually colored wires to terminals 11, and connect wires of the same color in parallel to terminals 9 and 10. The positive terminal of the thermocouple (TC) should be connected to terminal 10.
4. Power supply and output wiring
Connect the power supply wires to terminals 1 (positive) and 2 (negative), ensuring correct polarity. Connect the output signal wires to the PLC or controller according to system requirements. For example, a 4–20 mA output corresponds to the remote control terminal.
5.Pipe Mounting
Drill a hole in the pipe according to the flange or threaded base size, weld the base, and then tighten the transmitter. Some models can be mounted on a standard DIN rail using spring clips.
How to Calibrate a Temperature Transmitter?
1. Equipment Preparation
Device calibration requires a millivolt signal generator, a precision resistance box, and a standard potentiometer. Simulate thermocouple/RTD signal input.
2. Classification Operation
Thermocouple Type: The input signal must take cold junction compensation into account. The formula is Ei = E(t, 0) − E(t0, 0), Ei = E(t, 0) − E(t0, 0).
Thermocouple Type: A resistance box simulates the resistance values corresponding to different temperatures and directly adjusts the output signal.
3. Calibration Process
Zero Calibration: Enter the lower limit value (e.g., 0°C). Adjust until the output reaches 4 mA.
Span Calibration: Enter the upper limit value (e.g., 1300°C). Adjust until the output reaches 20 mA.
Full Span Verification: Select at least 5 evenly distributed points. Perform three forward and reverse travel tests and record the deviations.
4. Environmental Requirements
The calibration environment temperature must be maintained between 15°C and 25°C. Humidity must be between 40% and 70%.
5. Wiring Specifications
We must ensure correct polarity. Thermocouples must distinguish between positive and negative terminals. Thermistors use a three-wire system to minimize errors.
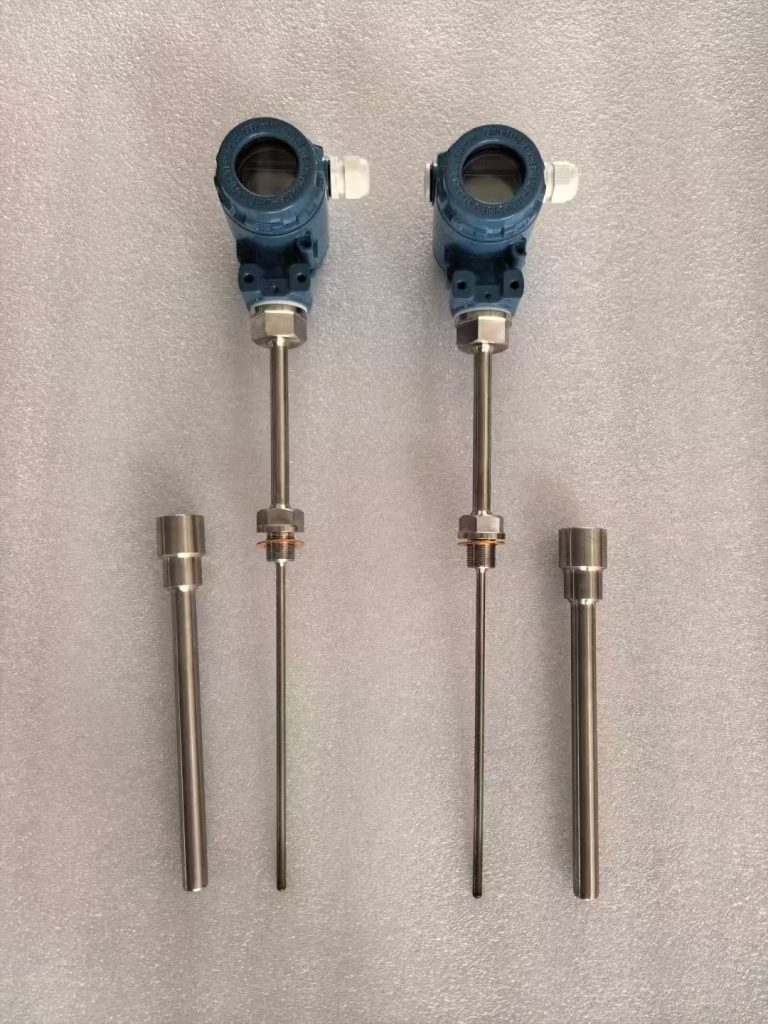

More Temperature Measurement Solutions
Industrial temperature sensors and temperature transmitters convert medium temperature into output signals. These can be resistance signals (PT100/PT1000), current signals (4-20mA), or digital signals.
Our 4-20mA temperature transmitters can be configured with PT100, K-type, N-type, and J-type thermocouples. They are suitable for use in harsh environments. Explosion-proof models include EXdⅡBT4, dⅡCT5, and dⅡCT6.
Sino-Inst offers over 50 industrial temperature sensors and transmitters. These include RTDs, thermocouples, PT100s, thermowells, and more. We also support customizable parameters to meet your industrial process application needs!
If you need to purchase explosion-proof temperature sensors or have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
-1.jpg)