Ultrasonic vs Magnetic Flow Meter, are you confused about which one to choose? Sino-Inst, based on our years of experience in flow measurement services, has compiled this blog, hoping to help you!
Ultrasonic flow meters and electromagnetic flow meters are both commonly used liquid flow meters. Because of their different working principles, they both have their own advantages and disadvantages. Next, let’s analyze them in detail.
Sino-Inst offers over 20 types of featured electromagnetic and ultrasonic flowmeters. You are sure to find one that is suitable for you. Alternatively, you can contact our sales engineers to select for you.
Featured Products
Comparison: Ultrasonic vs Magnetic Flow Meters
First, let’s take a brief look at the difference between the two in terms of parameters.
| Parameter | Electromagnetic flowmeter | Ultrasonic flowmeter |
| Measurement accuracy | High (±0.2%~±1%) | Medium to high (±1%~±2%, time difference method; ±2%~±5%, Doppler method) |
| Flow Range | 0.1 m/s to 10 m/s | 0.03 m/s to 12 m/s |
| Range ratio | Wide (1:100~1:1000) | Narrower (1:50~1:200) |
| Measurable pipe DN | DN2~DN3000 | DN6~DN6000 |
| Response Time | 0.5s to 1s | Less than 0.1s (time difference method is better than Doppler method) |
| Fluid adaptability | Only conductive liquids (such as tap water, sewage, acid and alkali liquid) | Conductive/non-conductive liquid (such as pure water, oil, gas) |
| Straight pipe section requirements | Low (5D in front and 3D in the back, D is the pipe diameter) | Higher (10D before and 5D after, time difference method needs to be more stringent) |
| Pressure Range | Up to 16 MPa | Up to 42 MPa |
| Pressure loss | Extremely small (no obstruction) | Extremely small (no obstruction) |
| Output Signal | 4-20mA, Pulse signal, RS485, HART | 4-20mA, Pulse signal, RS485 |
| Pressure Range | Up to 16 MPa | Up to 42 MPa |
| Operating Temperature | -25°C to 120°C, maximum customization 150℃ | -40°C to 160°C |
| Structural form | Pipe segment type, insert type; The transmitter can be integrated or split. | Clamp-on type, plug-in type, pipe segment type; The host can be portable, fixed, or modular. |
Next, let us introduce the measurement principles of the two.
1. Operating Principles: ultrasonic vs magnetic
Working principle of electromagnetic flowmeter
Electromagnetic flowmeter works based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. When a conductive fluid passes through a magnetic field, an electromotive force (voltage) is generated in the fluid. This voltage is proportional to the flow rate of the fluid. By measuring this voltage, the flow rate of the fluid can be calculated.
Therefore, electromagnetic flowmeters are only suitable for conductive liquids (conductivity ≥ 5μS/cm), and the measurement accuracy has nothing to do with the conductivity of the fluid.
Read more about: Magnetic Flowmeter Technology
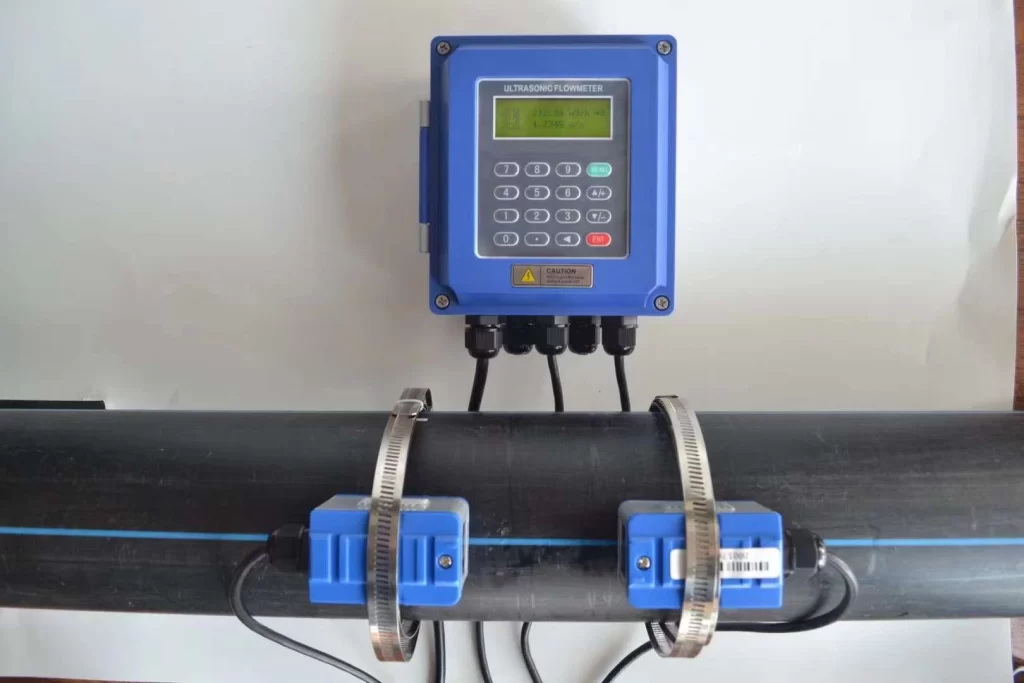

Working principle of ultrasonic flowmeter
Ultrasonic flowmeters use the time difference or Doppler effect of ultrasonic waves propagating in the fluid to measure the flow rate and then calculate the flow rate.
For example, the time difference type calculates the flow rate by emitting an ultrasonic signal and measuring the time difference of its propagation in the fluid. Depending on the flow direction and speed of the fluid, the propagation time of the ultrasonic signal will be different, so the flow rate can be inferred.
Ultrasonic flowmeters are suitable for conductive or non-conductive liquids (such as pure water, sewage), but attention should be paid to the influence of bubbles or particles in the fluid on the measurement accuracy.
Read more about: Ultrasonic Flow Meter Technology
2. Applications: Media Compatible
The measuring medium of the electromagnetic flowmeter is strictly limited to conductive liquids, such as sewage, acid and alkali solutions, slurries, etc. It cannot be used to measure gas, steam or insulating liquids. The selection of the measuring tube lining material (such as rubber, polytetrafluoroethylene) and the electrode material needs to be adapted according to the corrosiveness, abrasiveness and other characteristics of the medium.
Electromagnetic flowmeter applications:
- Industrial water treatment: such as water plants and sewage treatment plants, high-precision measurement of conductive liquids is required.
- Chemical process: measurement of corrosive conductive media such as acid and alkali solutions and salt solutions.
- Irrigation system: long-term stable operation with low maintenance requirements.
Ultrasonic flowmeters have no requirements for the conductivity of the medium and can measure non-conductive liquids (such as pure water and oils). However, due to the measurement principle, media containing a large number of bubbles, solid particles or uneven sound velocity distribution may cause inaccurate measurement signals. In particular, the Doppler method has certain threshold requirements for scatterer concentration.
Ultrasonic flowmeter applications:
- Temporary measurement: such as pipeline maintenance and flow calibration, without cutting off the pipeline.
- Large-diameter pipelines: lower cost than electromagnetic flowmeters, easy to install.
- Non-conductive liquids: such as pure water and oil (Doppler method is required to measure fluids containing particles).

3. Accuracy
The measurement accuracy of electromagnetic flowmeters is usually between ±0.5% and ±1%, with good repeatability and long-term stability. It is not affected by medium density, viscosity, and temperature (within the allowable range of the sensor). However, it is susceptible to electromagnetic interference and requires good grounding protection.
The typical accuracy range of ultrasonic flowmeters is ±1% to ±2%. However, scaling on the inner wall of the pipe, installation spacing deviation, or changes in the refraction angle of the sound beam may cause the measurement error to expand; the Doppler method has a relatively low accuracy (±1% to ±2%) and is susceptible to fluid flow fluctuations.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of electromagnetic flowmeters are as follows:
Advantages:
- High precision: When measuring conductive liquids, electromagnetic flowmeters usually have high precision and are suitable for occasions that require accurate flow measurement.
- Wide range of application: It can measure various conductive liquids, including sewage, chemical liquids, etc.
- No pressure loss: Due to its non-contact measurement principle, it will not cause pressure loss to the fluid.
- Corrosion resistance: Many electromagnetic flowmeters use corrosion-resistant materials and are suitable for harsh environments.
Disadvantages:
- High requirements for fluids: It can only measure conductive fluids and cannot be used for insulating liquids (such as oils).
- Installation requirements: A certain straight pipe section is required, and the installation location requirements are high.
- High cost: Compared with other types of flowmeters, the price of electromagnetic flowmeters is usually higher.
The advantages and disadvantages of ultrasonic flowmeters are as follows:
Advantages:
- Non-contact measurement, suitable for measuring corrosive or high-viscosity fluids. It can be used to measure fluid flow that is difficult to touch and difficult to observe and large-diameter flow.
- Easy to install: It can be installed outside the pipeline, reducing the modification of the pipeline.
- Wide range of application: It can measure conductive and non-conductive fluids, and has stronger applicability.
- Low maintenance cost: Since there are no moving parts, maintenance is relatively simple.
Disadvantages:
- Affected by the environment: Ultrasonic flowmeters are easily affected by factors such as temperature, pressure and bubbles, which may cause measurement errors.
- Relatively low accuracy: In some cases, the accuracy of ultrasonic flowmeters may not be as good as electromagnetic flowmeters.
- Sensitive to fluid properties: Changes in fluid density, temperature and composition may affect the measurement results.
- Installation uncertainty will cause large errors in flow measurement.
5. Installation Factors
Different types of flow meters have different installation requirements. The installation comparison between electromagnetic flow meter and ultrasonic flow meter is as follows:
Electromagnetic flowmeter
- Installation method: The pipeline needs to be cut off and installed directly in the pipeline. The full pipe state must be ensured.
- Installation requirements: Straight pipe sections must be reserved in front and back (usually 10D in front and 5D in the back, D is the pipe diameter) to avoid magnetic field interference.
- Maintenance: The electrodes need to be cleaned regularly (especially when measuring sewage or slurry).
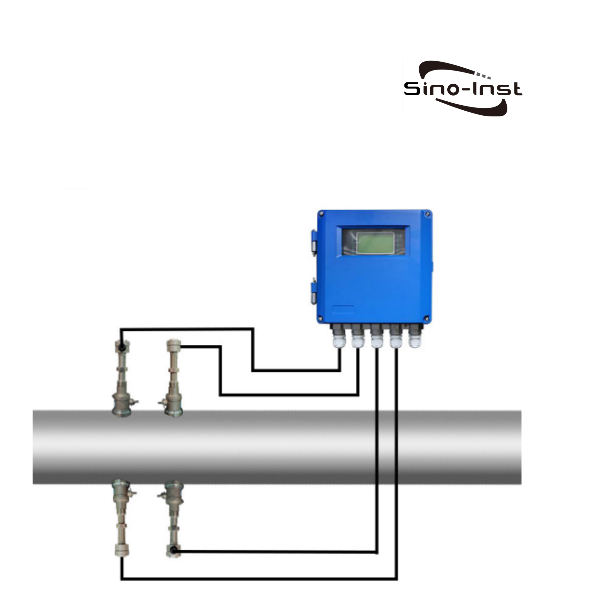
Ultrasonic flowmeter
- Installation method:
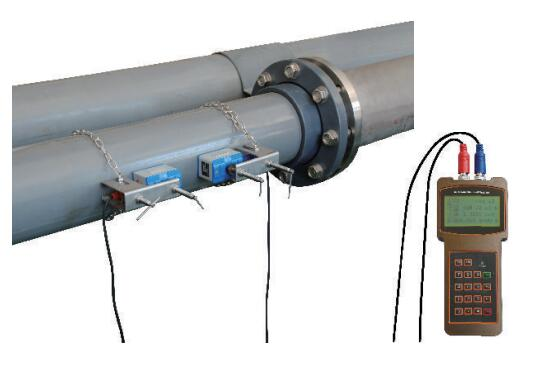
- External clamp type: No need to cut the pipeline, the sensor is clamped on the outer wall of the pipeline, suitable for temporary detection or large diameter scenarios.
- Insert type/pipe segment type: It is necessary to open a hole in the pipeline or pre-install the pipe segment, suitable for long-term fixed installation.
- Installation requirements: The sensor must be in close contact with the pipeline (coupling agent is required for the external clamp type), and the straight pipe section requirements are relatively low (usually 5D in front and 3D in the back).
- Flexibility: Suitable for mobile measurement or complex pipeline layout.

6. Cost and maintenance
Initial cost
Electromagnetic flowmeter: relatively high (especially for large diameter or corrosion-resistant types).
Ultrasonic flowmeter: relatively low (time difference clamp type is the most economical).
Operating cost
Electromagnetic flowmeter: electrodes and linings need to be checked regularly, but the failure rate is low.
Ultrasonic flowmeter: almost maintenance-free, but sensor fouling or vibration should be avoided.
Lifespan
Electromagnetic flowmeter: more than 10 years (high-quality products).
Ultrasonic flowmeter: 5~8 years (largely affected by the environment).
Choosing the Best Meter for Your Application
Based on the above characteristics, electromagnetic flowmeters are more suitable for continuous and accurate measurement of conductive liquids, especially in municipal water supply and drainage, chemical processes and other fields. Ultrasonic flowmeters have advantages in large-diameter pipeline measurement (such as heating pipe networks), non-conductive media (such as pharmaceutical purified water) and scenarios where pipeline modification is not convenient. At the same time, the Doppler method shows applicability in media containing certain suspended matter.
When choosing electromagnetic flowmeters and ultrasonic flowmeters, the following factors should be considered:
- The nature of the measured fluid: If the fluid is conductive, the electromagnetic flowmeter is a good choice. If the fluid is non-conductive, the ultrasonic flowmeter is more suitable.
- Measurement accuracy requirements: For applications requiring high precision, electromagnetic flowmeters may be more suitable.
- Installation environment: If the installation space is limited or the pipeline conditions are complex, the non-contact installation of ultrasonic flowmeters may be more advantageous.
- Cost budget: Select the appropriate flowmeter type according to the project budget.
Situations where electromagnetic flowmeters are preferred:
- Measurement of conductive liquids and high precision is required (such as trade settlement, process control).
- The fluid contains corrosive components (such as acid and alkali liquids).
- Long-term stable operation and sufficient budget.
Situations where ultrasonic flowmeters are preferred:
- Measurement of non-conductive liquids or temporary measurement needs.
- Large-diameter pipelines (DN300 and above) with limited budget.
- Scenarios where pipelines cannot be cut off or rapid deployment is required.
Compromise
- Insertion electromagnetic flowmeter: Combines electromagnetic accuracy with insertion convenience, suitable for large-diameter conductive liquids.
- Multi-channel ultrasonic flowmeter: Improves accuracy through multi-channel design, close to the performance of electromagnetic flowmeter.
More Flow Measurement Solutions
- Case: Flow Meter for Liquid Cement Additive
- Cryogenic Flow Meters Custom Cases
- Customer Case: Customized DN10 Flow Meter for Petrol
- Variable Area Flow Meter Case: Oxygen Flow Measurement
- Insertion Magnetic Flow Meter | Better Solution for Large Diameter Pipes
- Annubar Flow Measurement: Principles, Applications, And Advantages
- Industrial Water Flow Meter Types and Selection Guide
In summary, ultrasonic and electromagnetic flowmeters have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of technical principles, medium adaptability, accuracy characteristics and installation requirements. When selecting a model, we need to comprehensively consider the physical and chemical properties of the measured medium, measurement accuracy requirements, installation environment and long-term maintenance costs to achieve the optimal configuration and reliable operation of the measurement system.
Sino-Inst produces and supplies various types of electromagnetic flowmeters and ultrasonic flowmeters. Including special styles such as customized materials, high pressure, and small diameter. If you need to measure water or other liquid flow, please feel free to contact our sales engineers. We will configure a suitable solution for you!
-1.jpg)