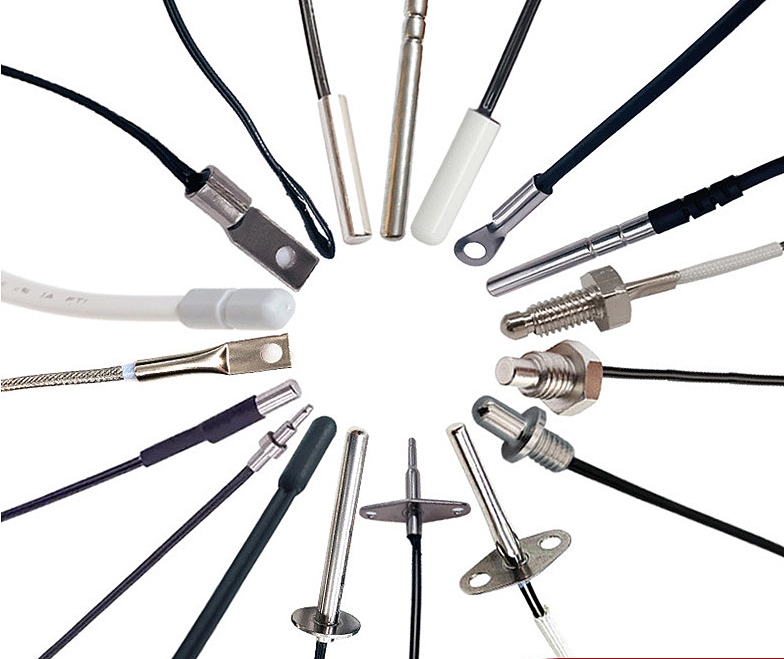
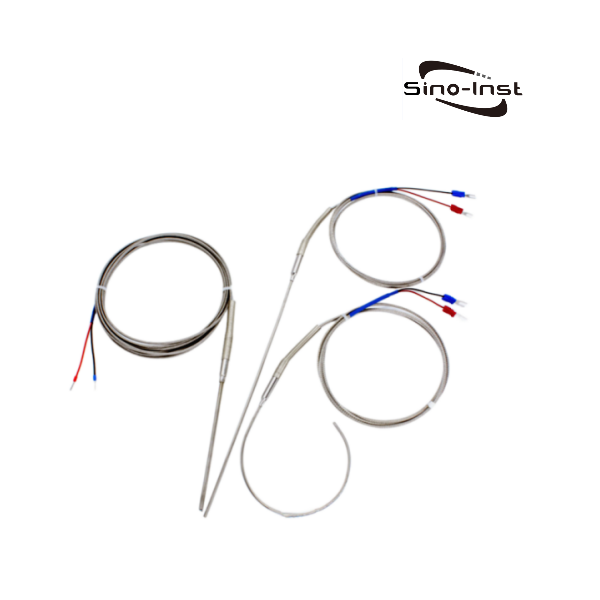
The process control industry almost entirely uses Pt100/Pt1000 platinum thermal resistors as temperature measuring elements. Their resistance changes with temperature. The industry also uses this principle of thermal resistors for accurate temperature measurement.
The 1000 after the letter “PT” means that its resistance is 1000 ohms at 0°C, while Pt100 is 100 ohms, and the other properties are basically the same. The curves of the two with temperature change are basically the same, both are straight lines of a certain degree.
Featured Temperature Sensors
What is PT100?
Pt100 is a platinum thermal resistor, and its resistance is proportional to the change in temperature. The relationship between the resistance of pt100 and temperature change is: when the temperature of pt100 is 0℃, its resistance is 100 ohms, and at 100℃, its resistance is about 138.5 ohms.
Its industrial principle: when pt100 is at 0 degrees Celsius, its resistance is 100 ohms, and its resistance will increase at a uniform rate as the temperature rises.
What is PT1000?
The resistance of pt1000 is a platinum thermal resistor, which is proportional to the change in temperature. The relationship between the resistance of pt1000 and the temperature change is: when the temperature of pt1000 is 0℃, its resistance is 100 ohms, and at 100℃, its resistance is about 2120.515 ohms.
Its industrial principle: when pt1000 is at 0 degrees Celsius, its resistance is 100 ohms, and the resistance of pt1000 thermal resistor will increase at a uniform rate as the temperature rises.
Because the resistance ranges of the two are different, the accuracy of the two is different. The accuracy of pt1000 is much greater than that of pt100.

Similarities between PT100 and PT1000
Both are resistance temperature detectors made of platinum (Pt), with positive resistivity. As the temperature rises, the resistance value also increases.
The two principles are similar, but 1000 is more accurate than 100.
PT100 vs PT1000 Difference
Different sensitivity
- PT1000 has a higher reaction sensitivity than PT100.
- When the temperature of PT1000 changes by 1℃, its resistance value increases and decreases by about 3.8 ohms.
- When the temperature of PT1000 changes by 1℃, its resistance value increases and decreases by about 0.38 ohms.
Different measurement temperature range
- PT1000 is suitable for measuring small range temperature (common temperature range: -50~300℃).
- PT100 is suitable for measuring slightly large range temperature (common temperature range: -200~650℃)
Different nominal resistance
PT1000 and PT100 are both platinum thermal resistors. PT1000 is 1000 ohms at 0℃ and 1385.055 ohms at 100℃.
PT100 is 100 ohms at 0℃ and 138.5055 ohms at 100℃, which is 10 times different.
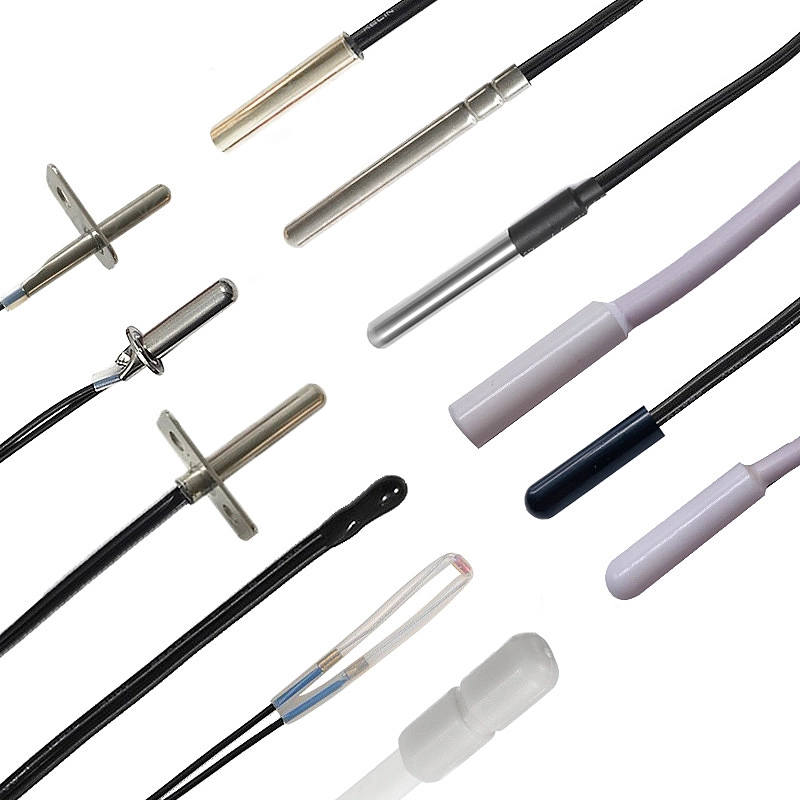
PT100 vs PT1000 Applications
Both types of sensors work well in 3-wire and 4-wire configurations, where additional wires and connectors compensate for the effects of lead resistance on temperature measurements. Their various application characteristics are as follows:
- Generally speaking, P100 temperature sensors are more commonly found in process applications. Whereas Pt1000 sensors are used in refrigeration, heating, ventilation, automotive, and machine manufacturing applications.
- Pt100 sensors are available in both wirewound and thin-film constructions, giving users choice and flexibility. Pt1000RTDs are almost always thin-film.
- Because Pt100 RTDs are so widely used across industries, they are compatible with a wide range of instruments and processes.
- Pt1000 sensors work better in 2-wire configurations and when used with longer lead lengths. The fewer wires and the longer the length, the more resistance is added to the reading, resulting in inaccuracies. The greater nominal resistance of the Pt1000 sensor can compensate for these added errors.
- Pt1000 sensors are better suited for battery-powered applications. Sensors with higher nominal resistance use less current and therefore require less power to operate. Lower power consumption extends battery life and maintenance intervals, reducing downtime and costs.
- Because the P1000 sensor consumes less power, it also self-heats less. This means fewer false readings due to above-ambient temperatures.

More Process measurement and control Solutions
- What Is Temperature Compensation and Pressure Compensation for Flow Meters?
- Differences Between Thermocouples: Type S, K, N, J, E, T
- High Temperature Pressure Transducers|800℃~1200℃
- What Is a BTU Meter? | BTU Energy Measurement Systems
Sino-Inst provides all commonly used temperature measuring components and temperature sensors for the process control industry. Including RTD, thermocouple, PT100, thermowell etc. 4-20mA signal output can also be configured.
Sino-Inst customizes various temperature sensors for different industries and working conditions. Meet the needs of special industries and working conditions. There are also general sensors that meet common working conditions. As long as you have a need for temperature sensors, please feel free to contact our sales engineers!
-1.jpg)