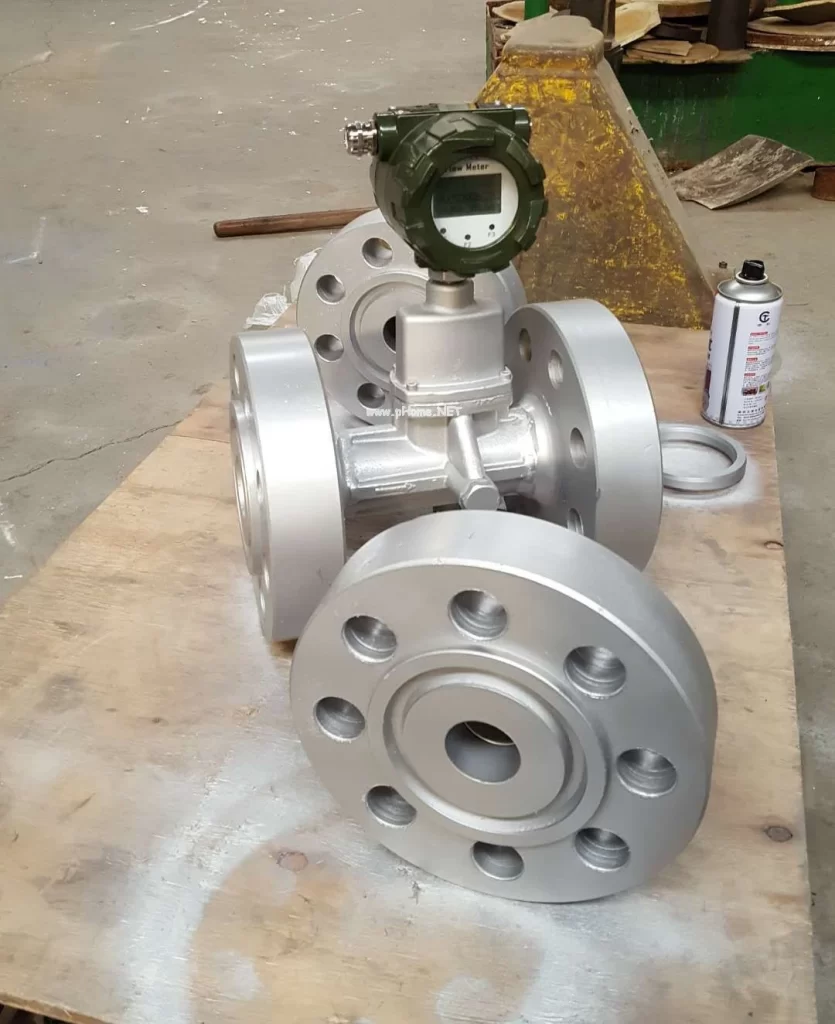
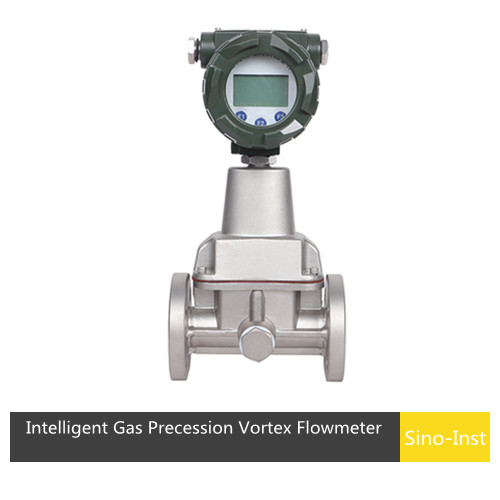
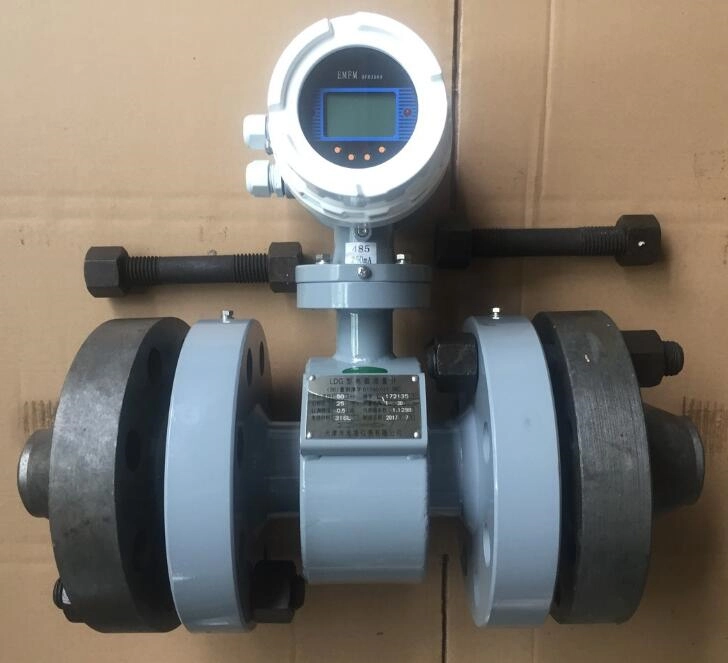
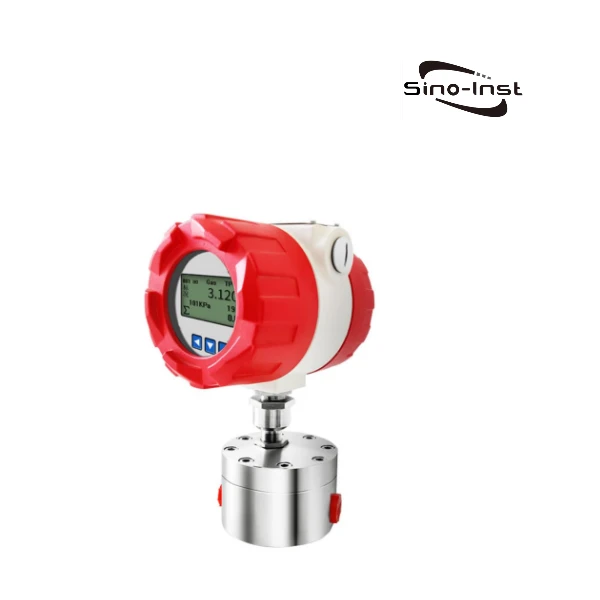
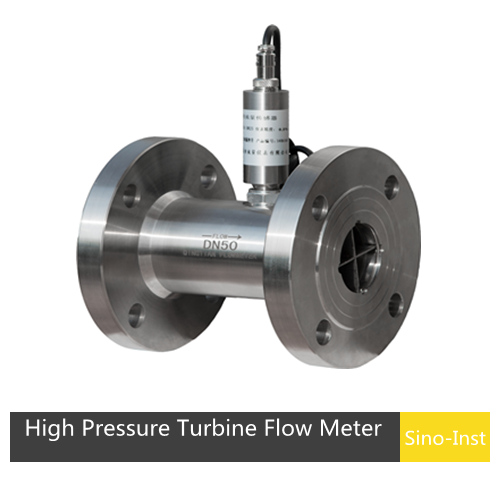
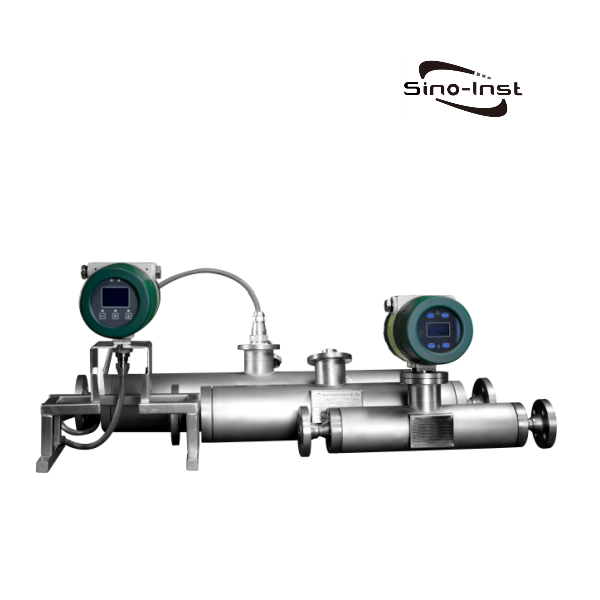
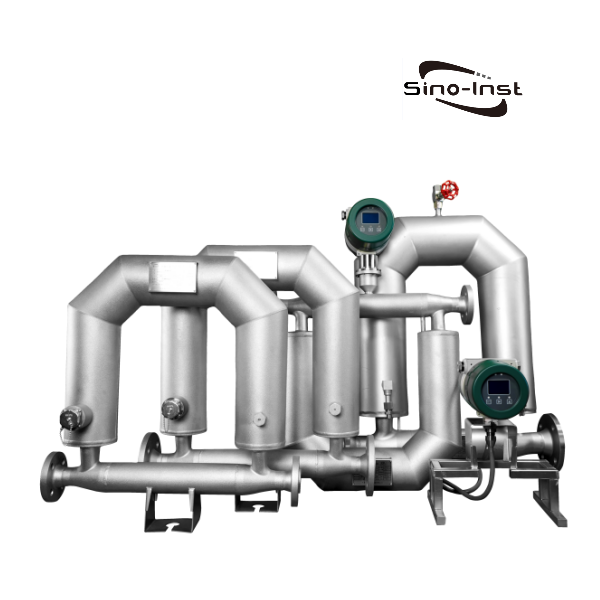
When it comes to high-pressure applications, choosing the right flow meter is necessary for checking accuracy, reliability, and safety.
High Pressure Flow Meters are perfect when measuring the flow of fluids under high pressures, such as in hydraulic testing. It is also perfect for chemical injection systems, as it withstands pressures up to 6.3MPA~42MPA and is available in a variety of different flow ranges.
This blog post will delve into the various types of high-pressure flow meters, including high-pressure gas meters, high-pressure water flow meters, and high-pressure rotameters, reflecting their features, applications, and considerations for selection and installation.
What is Flow from a layman’s perspective?
Flow is a term used to describe the movement of materials or energy from one place to another in a continuous and organized manner. This can refer to the flow of fluids such as water, gas, and oil.
Flow is an important concept in engineering and manufacturing in understanding how systems and processes work.
Let’s refer to flow as it applies to fluids in pipes. And in this application, flow is typically divided into two types: Open channel flow and closed conduit flow.
Open Channel Flow
Open channels are streams with an exposed surface and unrestricted access to the atmosphere. For example, canals and pipelines that are not completely full, such as drains and sewers.
In open channel flow, gravity is responsible for the motion of the liquid. The water level will gradually decrease down the stream as the flow progresses.
Closed Conduit Flow
Closed conduit flow is the flow of a liquid or gas through a pipe, channel, or another closed vessel. Closed conduit flow typically occurs at a constant velocity and depends on factors such as the pressure difference between the ends of the conduit and its length.
Water supply and district heating pipes are common places to observe closed conduit flow. Even drinking straws are a simple but efficient example of this.
The flow rate here is largely determined by the pressure difference between the two ends, the distance between them, and the area of the conduit. Additionally, the hydraulics of the pipeline – such as its shape, roughness, and bends – also have an impact. All these factors come together to create the rate of flow.

Key Characteristics of High Pressure Flow Meters
- High-pressure flow meters are typically rated for pressures exceeding 350 psi(2.5MPa). They can go up to several thousand psi depending on the application.
- The materials used in high-pressure flow meters must withstand the corrosive nature of the fluids they measure, including chemicals, gases, and high-temperature fluids.
- High-pressure flow meters are designed for high accuracy to minimize errors that can lead to significant financial implications and safety hazards.
Types of High Pressure Flow Meters : Let’s understand it in a better way
High Pressure Gas Meters
Application of High Pressure Gas Meters
- Monitoring and regulating gas flow in pipelines. Very much effective in natural gas distribution.
- Used in chemical manufacturing and power generation where precise gas flow control is required.
- High-pressure gas flow meters are crucial for testing and verifying propulsion systems in Aerospace.
High Pressure Water Flow Meters
The most common types of high-pressure water flow meters include:
Turbine Flow Meters: Turbine meters have found widespread use for accurate high pressure liquid measurement applications. Customizable up to 25MPa, 40MPa.
Electromagnetic Flow Meters: Electromagnetic meters can handle most liquids and slurries under high pressure, providing that the material being metered is electrically conductive. Customizable 6.3MPa-16MPa-25MPa-35MPa-42MPa.
Gear Flow Meters: GF Gear Flow Meters are particularly suitable for high pressure and small flow media measurement. High pressure can reach 40MPa. It can even meet special conditions such as high temperature, low temperature, and high viscosity.
High Pressure Rotameters: The rotameter is an industrial flow meter that measures the volumetric flow rate of gases and liquids in a closed tube. It is a variable area meter and provides a simple and inexpensive indication of flow rates. It has fair accuracy. Can measure 4MPa high pressure.
Application of High Pressure Water Flow Meters
- Monitoring water supply and ensuring quality control.
- Managing water distribution effectively in agricultural applications.
- Used in cooling systems, boilers, and other machinery that require precise water flow measurement.
- The flow of other high pressure liquids can be measured according to the actual measurement parameters.
Considerations for Selecting High Pressure Flow Meters
Fluid Properties
Understand the properties of the fluid being measured, including viscosity, temperature, pressure, and chemical composition. This data will help determine the appropriate meter type and material.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings

Ensure the selected flow meter can handle the maximum expected pressure and temperature of the application. It’s crucial to choose a device that exceeds these limits for safety and longevity.
Accuracy Requirements
Consider the required accuracy level for your application. High-precision applications may necessitate specific types of meters, such as Coriolis or electromagnetic flow meters.
Installation Constraints
Evaluate the installation environment and constraints, including available space, orientation, and access for maintenance. Some meters require straight pipe runs for accurate readings, while others may have flexible installation options.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that the chosen flow meter complies with relevant industry standards and regulations. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and oil and gas, there are the requirement of highly regulated protocols.
More Flow Measurement Solutions
- Guide To Low Temperature Flow Meters: Accuracy In Cold Fluid Measurement
- Customized Case: High Temperature and High Pressure Pressure Measurement -100MPa-700℃
- Solution For Low Flow And Low Volume Applications: Low Flow Meter In Detail
- BTU Meter Optimizes Energy Efficiency of Hot and Cold Water Systems
- Turbine Water Flow Meter: A Versatile And Reliable Choice For Water Flow Measurement
- Pulse Output Flow Meters for Better Water Flow Measurement
- Ultrasonic Clamp On Flow Meter – For Easier Water Flow Measurement
- Guide On Industrial Air Flow Measurement Devices
Understanding the various types of high pressure flow meters, their working principles, applications, and selection criteria is essential for ensuring operational efficiency and safety.
By considering the specific requirements of your application and following proper installation practices, you can achieve optimal performance and reliability from your high-pressure flow measurement systems. Sino-inst is a reliable destination for various kinds of high pressure flow meters for the customers across various fields.
-1.jpg)