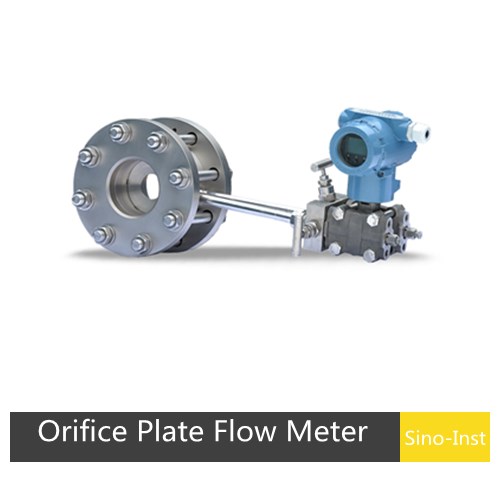
An orifice plate flow meter is a high-range differential pressure flow measurement device consisting of a standard orifice plate and a multi-parameter differential pressure transmitter. Orifice plate tapping refers to the method of extracting the differential pressure before and after the orifice plate. Common types of orifice plate pressure taps include: flange taps, corner taps, and radius taps (D-D/2 taps).
In orifice differential pressure flow measurement systems, the choice of tapping method significantly affects measurement accuracy, installation complexity, and maintainability.
1. Flange Pressure Tapping
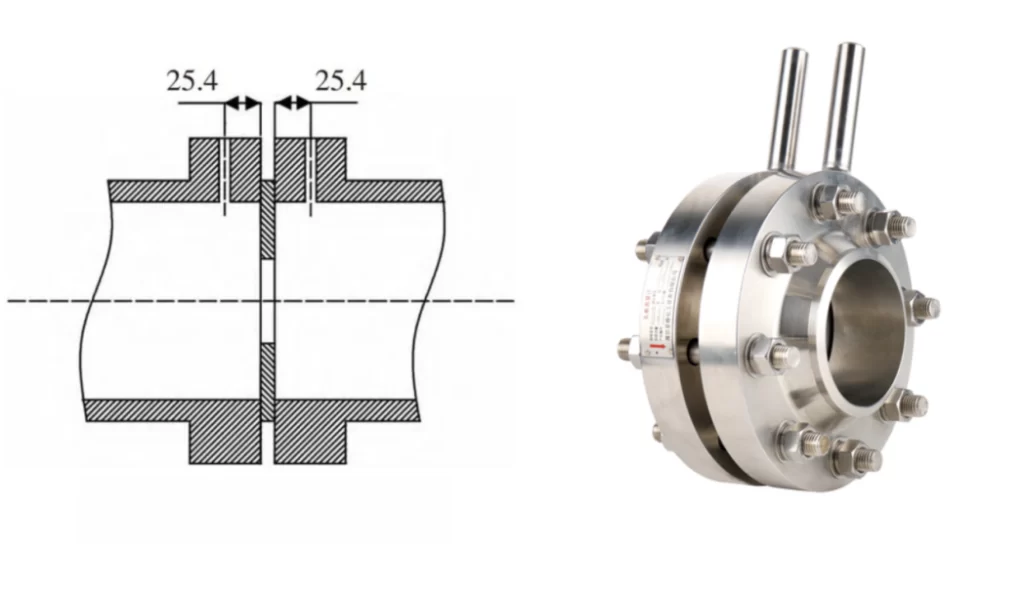
Flange pressure tapping involves placing the pressure taps on a dedicated tapping flange. The distance between the upstream and downstream pressure taps is 25.4 mm (or “1-inch tapping”) from the upstream and downstream faces of the orifice plate.
Structure: The flange pressure tapping structure is relatively simple. The flange is a dedicated orifice plate flange with a high-pressure rating (e.g., 300LB).
It is easy to install and suitable for various media, especially widely used in low-pressure conditions. It is easy to clean, therefore it is quite common in industrial applications.
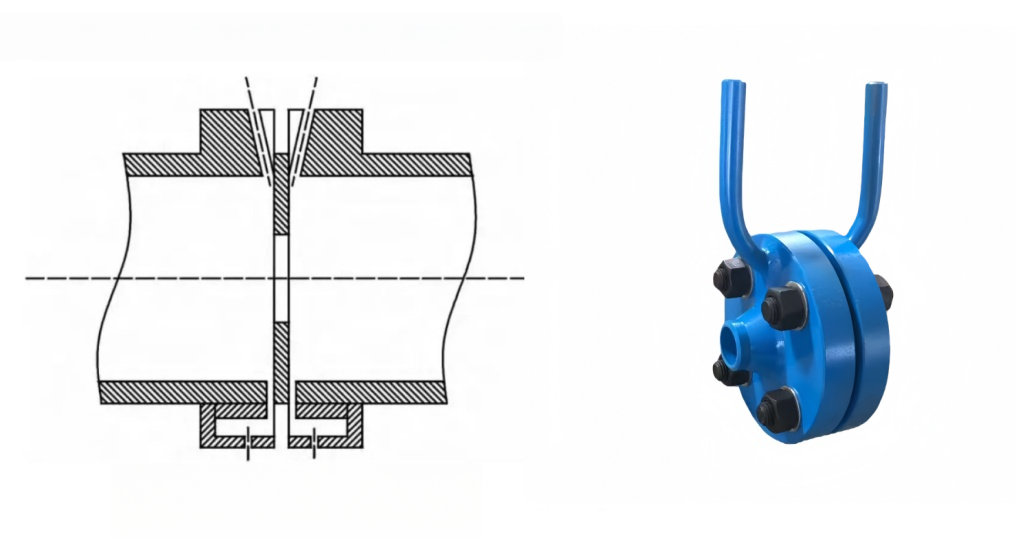
2. Corner Tapping
Corner tap pressure measurement is divided into two forms: annular chamber tapping and separate drilling. The two pressure taps are located at the angle between the upper and lower end faces of the orifice plate and the pipe wall. The distance from the center of the upstream and downstream pressure taps to the front and rear end faces of the orifice plate is equal to half of the pressure tap diameter (for single-hole tapping); in the case of annular chamber tapping, it is equal to half of the annular gap width.
Annular chamber tapping can improve measurement accuracy and is suitable for clean media, especially under high temperature and high pressure conditions. However, the annular chamber structure is complex, time-consuming and costly to manufacture, and is prone to clogging and difficult to clean.
Separate drilling for pressure tapping is relatively simple, but the accuracy is lower.
Corner tap pressure measurement is usually used in situations with smaller pipe diameters or where high-precision measurement is required. Annular chamber tapping is suitable for pipe diameters below DN400, while separate drilling is suitable for pipe diameters above DN400.
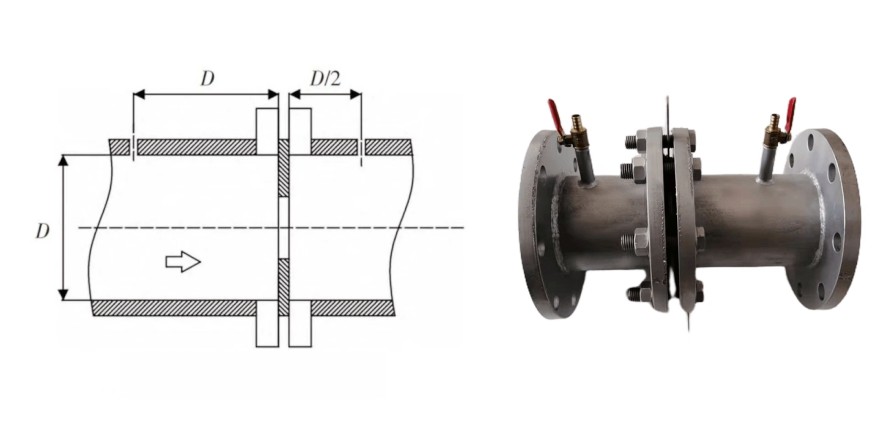
3. Radius Tapping (D – D/2 Tappings)
In this pressure tapping method, the distance between the pressure taps is the distance between the centerline of the pressure tap and a specified end face of the orifice plate. The upstream pressure tap distance is the pipe diameter D, and the downstream pressure tap distance is D/2. To avoid installation errors on-site, when using radius tapping, the throttling device is generally supplied as a complete set with straight pipe sections.
Radius tapping does not require complex machined parts and is easy to install and use on-site, especially in European and American countries. Radius tapping is suitable for large-diameter pipes and situations with high Reynolds numbers, but its signal-to-noise ratio is lower, and the measurement accuracy may not be as good as other methods.
More Flow Measurement Solutions
As a mature flow measurement method, orifice plate flow meters utilize different types of orifice plates and pressure tapping methods depending on various operating conditions. Understanding the common types of orifice plate flow meters and pressure tapping methods helps in better selecting and applying this flow measurement instrument, thereby improving measurement accuracy and reliability.
Sino-Inst will consider factors such as media characteristics, pipeline conditions, and measurement requirements to select the appropriate orifice plate type and pressure tapping method for you. Please feel free to contact us anytime.
-1.jpg)