
What is a pressure transmitter 4-20mA?
A 4-20mA pressure transmitter is an instrument that measures medium pressure and converts it into a 4-20mA current output signal. In industrial processes, the most common method for transmitting analog signals is using a 4-20mA current loop. The signal is transmitted to a remote control panel for pressure monitoring and control. For example, this can involve audible and visual alarms or initiating certain trip and shutdown procedures.
In a 4-20mA pressure transmitter, the 4-20mA output is linearly proportional to the pressure range. 4mA corresponds to a zero reading, the lower limit of the pressure range. 20mA corresponds to a full-scale reading, the upper limit of the pressure range.
What is the purpose of a pressure transmitter?
Pressure transmitters are used to measure the pressure of liquids, gases, or steam and convert it into a standard electrical signal for output. They are widely used in industrial automation, environmental monitoring, and medical equipment.
Main Applications:
- Pressure Measurement and Control.
Pressure transmitters measure and display pressure in real time. The output signal can be connected to a control system for real-time pressure monitoring and regulation.
- Flow Measurement.
By detecting the pressure changes exerted by liquid or gas within a pipeline, pressure transmitters can accurately monitor and control flow.
- Liquid Level Measurement.
In liquid storage tanks or deep wells, pressure transmitters can measure liquid levels to ensure they remain within safe limits.

- Leak Detection:
On tanks or pipelines, pressure transmitters detect real-time pressure changes and monitor for leaks.
- Environmental and Weather Monitoring:
Pressure transmitters are used in weather stations and environmental protection equipment to monitor atmospheric pressure changes, influencing weather forecasts and environmental monitoring.
Pressure transmitter 4-20mA working principle
The working principle of a 4-20mA pressure transmitter is to convert pressure into a 4-20mA standard current signal output.
First, the medium pressure acts on the pressure sensor diaphragm, causing the diaphragm to deform. This causes a change in resistance or capacitance. The signal from the measuring element is filtered, amplified, and temperature compensated before being converted into an analog signal (4-20mA current) for transmission to the control system.
Read more about: Analog output signal of pressure transmitter: DC voltage 0~10 V, DC voltage 1~5 V, DC voltage 1~10 V
Pressure transmitter 4-20mA wiring
Wiring Principle
- Power supply positive (24V+) → transmitter positive (+).
- Transmitter negative (-) → DRO current input positive (AI+).
- DRO current input negative (AI-) → power supply negative (24V-), forming a closed circuit.
Key Point: The signal and power supply share a common circuit; ensure that the series connection has no branches.
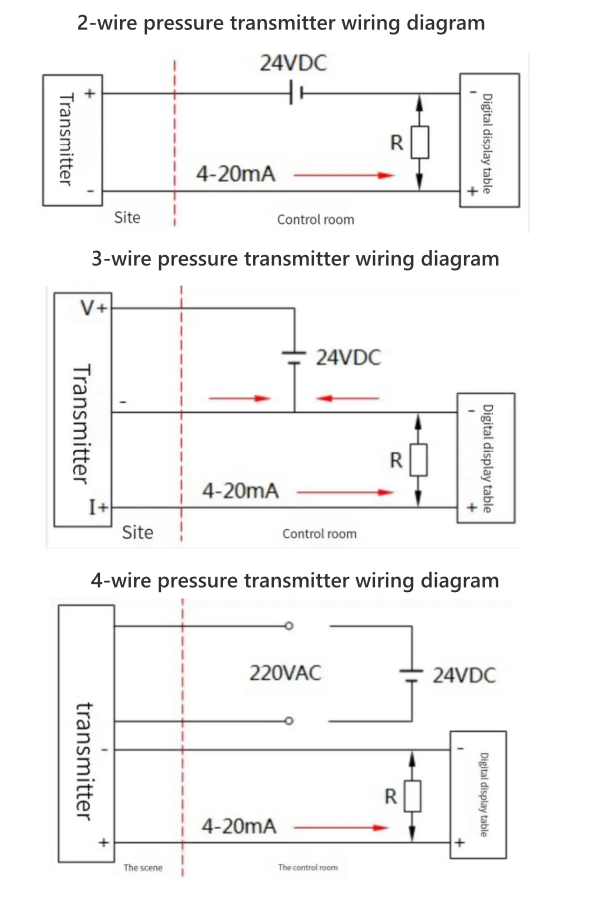
The power supply and current signal circuit of the two-wire transmitter is: 24V power supply positive terminal → transmitter positive terminal → transmitter negative terminal → digital display positive terminal → digital display negative terminal → 24V power supply negative terminal. The digital display receives the current signal. If a resistor R is connected in parallel between the DRO positive and negative terminals, the DRO receives a voltage signal.
Example Wiring Steps:
Using a 24V DC power supply, connect the red wire to the transmitter positive terminal, the blue wire (signal line) to the DRO AI+, and short the black wire (power supply negative) to the DRO AI-.
Read more about: 2 Wire-3 Wire-4 Wire Pressure Transducer Wiring Diagram
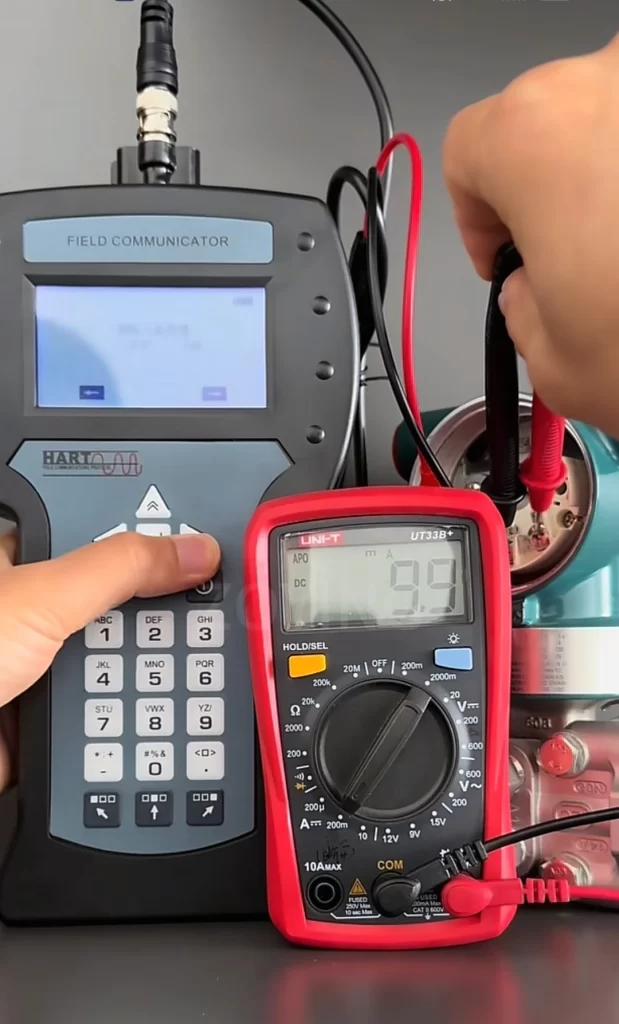
How to Test the 4-20mA of a Pressure Transmitter?
The 4-20mA signal is the converted value of the output generated by a pressure transmitter. At zero-scale output, the transmitter displays a 4mA signal output, while at maximum or full-scale output, the readout scale displays a 20mA signal.
Verifying the 4-20mA current loop signal is a critical step in pressure transmitter calibration and troubleshooting. Below are two recommended methods for measuring the 4-20mA current loop signal.
Use a process clamp meter to measure the 4-20mA signal.
The 4-20mA current loop signal can be measured without disconnecting the two-wire circuit.
Open the transmitter’s wiring terminals and connect the process clamp meter to the signal wires.
Identify the mA output signal at the zero value of the process clamp meter. The mA output value must be within the range of 4mA to 20mA.
If a reading between 4mA and 20mA is not displayed, troubleshooting and calibration are necessary. If the value is within this range, the transmitter’s performance is guaranteed.
Use a loop calibrator or multimeter to measure the 4-20mA signal.
Set the multimeter to current measurement mode. Connect the red test lead to the positive output terminal of the transmitter and the black test lead to the negative terminal. The value displayed on the meter will indicate the measured current.

8 Types 4-20mA Pressure Transmitter Troubleshooting
Okay, now let’s look at some common 4-20mA pressure transmitter faults and their solutions.
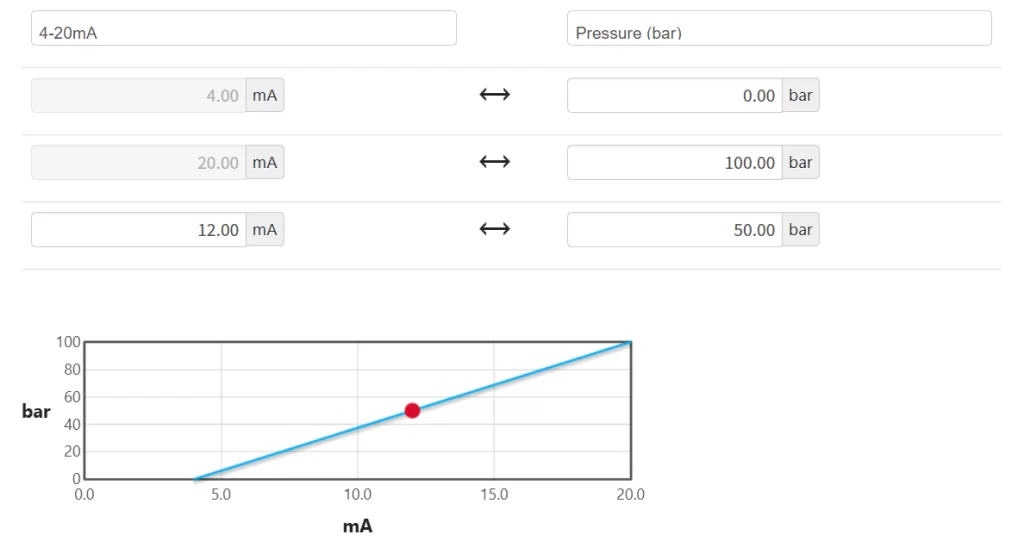
How do you convert 4-20 mA to pressure?
We know that the 4-20mA signal of a pressure transmitter and the pressure measurement range are linearly proportional. They can be converted to each other.
For example, if the pressure transmitter has a range of 0-40MPa and the output current is 12mA, what is the pressure value?
First, map the transmitter’s output current (4-20mA) to the corresponding pressure range (0-40MPa). The calculation formula is as follows:
Pressure = (Output Current – 4) * (40 – 0) / (20 – 4)
Based on the above formula, the result is:
Pressure = (12 – 4) * (40 – 0) / (20 – 4) = 8 * 40 / 16 = 20MPa
Therefore, when the output current is 12mA, the corresponding pressure is 20MPa!
Of course, there are many existing tools that can perform this conversion directly for you. For example, there is an online 4-20mA scaling calculator from DIVIZE b.v.
More Pressure Measurement Solutions
In the industrial automation field, the 4-20mA current signal, the standard output for pressure transmitters, has become a core sensing method for process control due to its strong anti-interference capabilities and long transmission distance.
Sino-Inst’s 4-20mA pressure transmitters can be directly connected to computers, control instruments, and display instruments. They are easy to install and offer high vibration and shock resistance, ensuring long-term operation in harsh environments. Customizable measurement parameters are also supported.
If you require pressure measurement or have any technical questions, please feel free to contact our sales engineers!
-1.jpg)