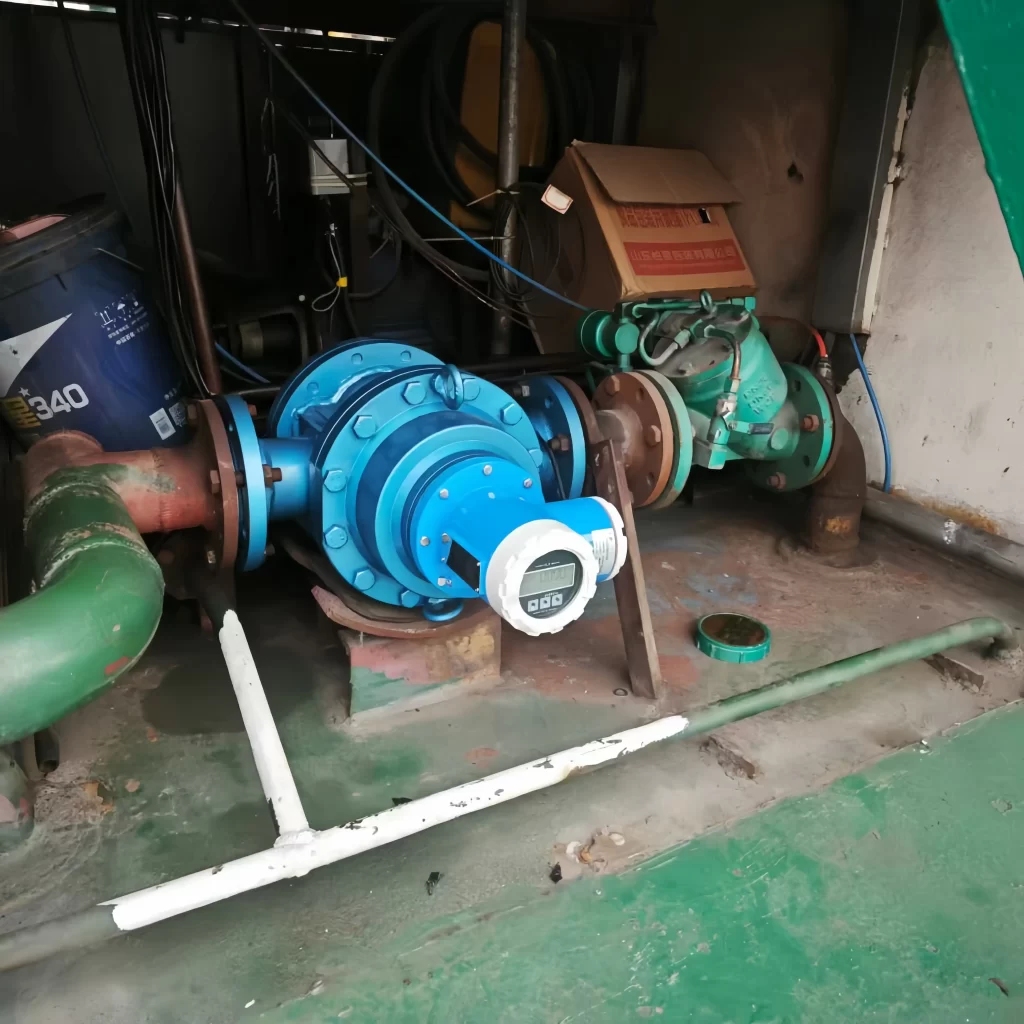
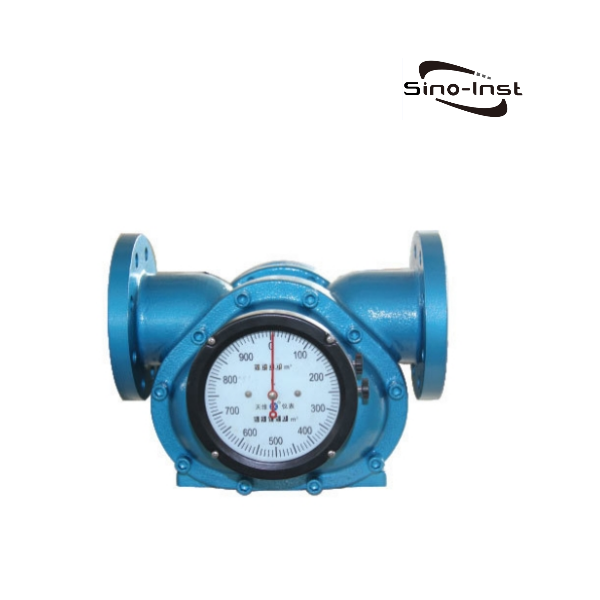
In practice, most machines involve rotary motion as well as linear motion. Rotary motion is defined by stable operation and low impact on mechanical equipment. Therefore, it is very important for the smooth operation of the instrument.
Rotary flow meters have been in use for a long time. Over time, they have become the preferred method of measurement for industrial and commercial gas loads. The rotary meter is designed to measure fluid with a very high degree of accuracy and reliability.
This blog post explores the working principle, types, applications, advantages, and installation considerations of rotary flow meters.
What is a Rotary Flow Meter?
A rotary flow meter is a type of positive displacement (PD) flow meter that measures the flow rate of a fluid by trapping and displacing a fixed volume of liquid or gas through its rotating components.
Unlike other flow meters that infer flow rate from velocity, rotary flow meters provide a direct measurement of volume, making them highly accurate.
Principles of Operation
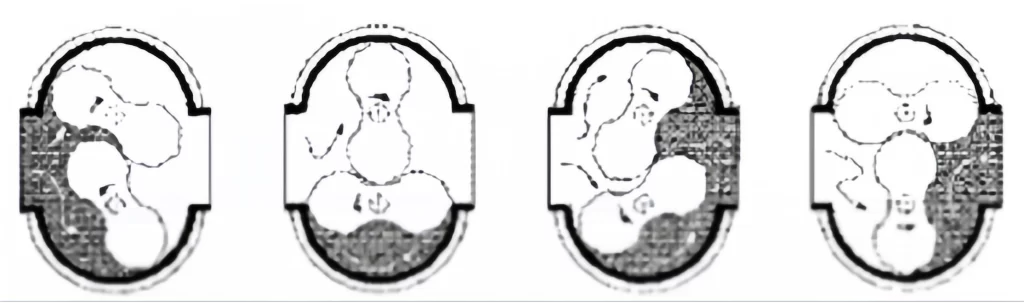
- The lobed impeller type rotary meter consists of two figure-eight shaped impellers, positioned at 90° from each other, which rotate in opposite directions inside a cylinder of fixed volume .
- Fluid flowing through the meter cylinder causes the impellers to turn, thereby creating a measurement chamber bounded by the impeller, cylinder and the head plates. This known volume is then discharged and another identical volume of fluid is trapped by the other impeller, cylinder and head plates.
- Fluid is alternately trapped and discharged four times for each impeller revolution.
- The displaced fluid per revolution is multiplied by the number of impeller revolutions to determine the volume of fluid passed by the meter.
- A gear reduction system is used to totalize the displaced volume for instrument drives and counter readouts in engineering units (i.e., cubic feet).
Types of Rotary Flow Meters
Rotary flow meters come in different designs, each suited for specific applications:
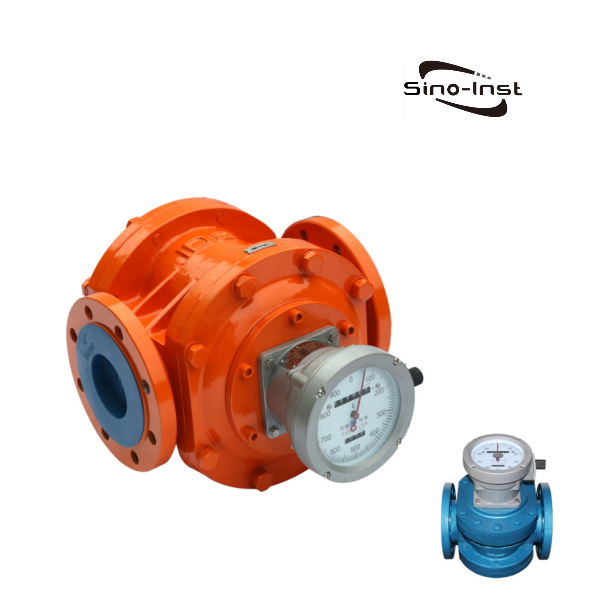
- Oval Gear Flow Meters
These meters use two oval-shaped gears that rotate within a precision-machined chamber. Each rotation of the gears traps a fixed volume of fluid. Oval gear meters are known for their high accuracy and are commonly used for measuring fuel oils, lubricants, and chemical fluids.
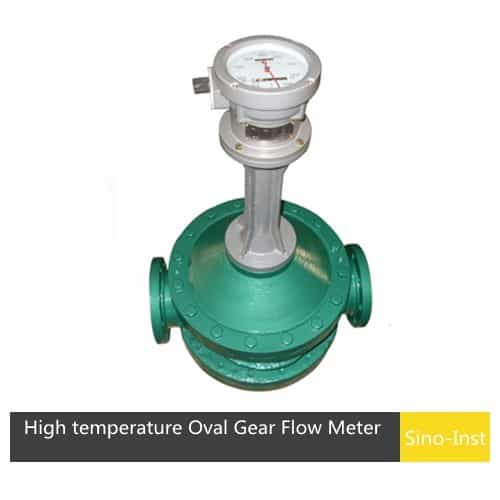
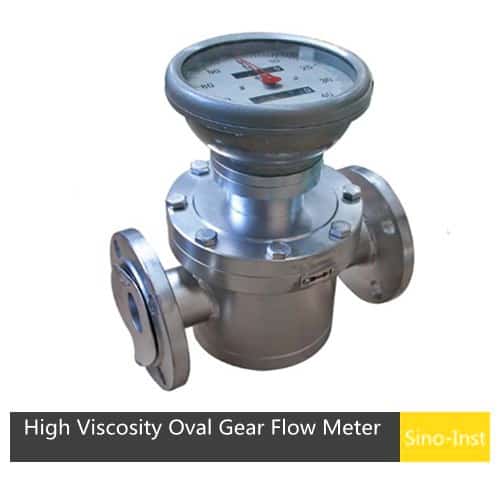
SI-3601 Positive Displacement Oval Gear Fuel Flow Meter, SI-3602 High temperature Oval Gear Flow Meter, SI-3603 High Viscosity Oval Gear Flow Meter are some of the products from Sino-Inst.
- Lobe Flow Meters
Lobe meters consist of two lobed rotors that rotate in opposite directions. They handle high-viscosity fluids and are commonly used in food and beverage industries for syrups and oils.
- Helical Gear Flow Meters
These meters use helical-shaped gears that rotate smoothly to measure fluid volume. Their design reduces pulsation and is ideal for high-viscosity fluids like crude oil and molasses.
- Sliding Vane Flow Meters
These meters use vanes that slide in and out of a rotor to create displacement. They are used in fuel transfer applications and provide excellent accuracy.
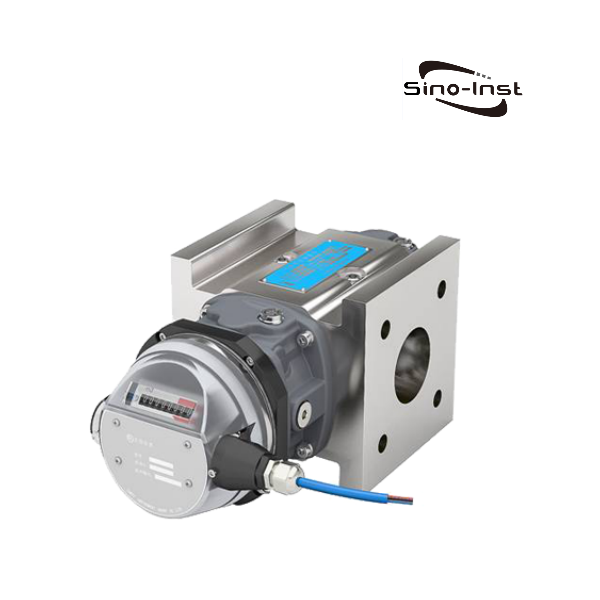
- Gas rotary flowmeter.
Intelligent gas rotary flowmeter is a new generation of flowmeter that integrates flow, temperature and pressure detection functions and can automatically compensate for temperature and pressure. The flowmeter is based on the volumetric measurement principle and is used to accurately measure the total amount of gas flowing through the sealed tube.
Accuracy and Range-ability of Rotary Flow Meter: Important Parameters
Accuracy:
The accuracy of a meter is defined as the degree to which a meter correctly measures the volume of fluid passing through its measuring chamber. Accuracy is determined by comparing the volume registered by the meter with a known volume registered by a connected proving device.
The accuracy of a rotary meter is built-in through the careful organization of its components and cannot be adjusted. Since the volume of the measurement chamber does not change, the only factor that can affect accuracy is an increase in internal friction within the meter. Increased friction allows fluid to slip through the clearances associated with the impellers, head plates, and meter cylinder.
Range-ability:
The range-ability of a meter provides information regarding the operating range of the meter and is defined as the meter’s maximum rated capacity divided by a selected “minimum capacity.”
Assuming that a meter “runs” at 100% accuracy, minimum capacity is determined to be the point where the meter’s accuracy moves above or below a specified tolerance (usually ± 1% or ± 2%) from the 100% accuracy point.
Newer designs of rotary meters, by using lighter materials, have greatly improved range-abilities by reducing start rates and thus pushing the lower end (knee) of the accuracy curve to the left.
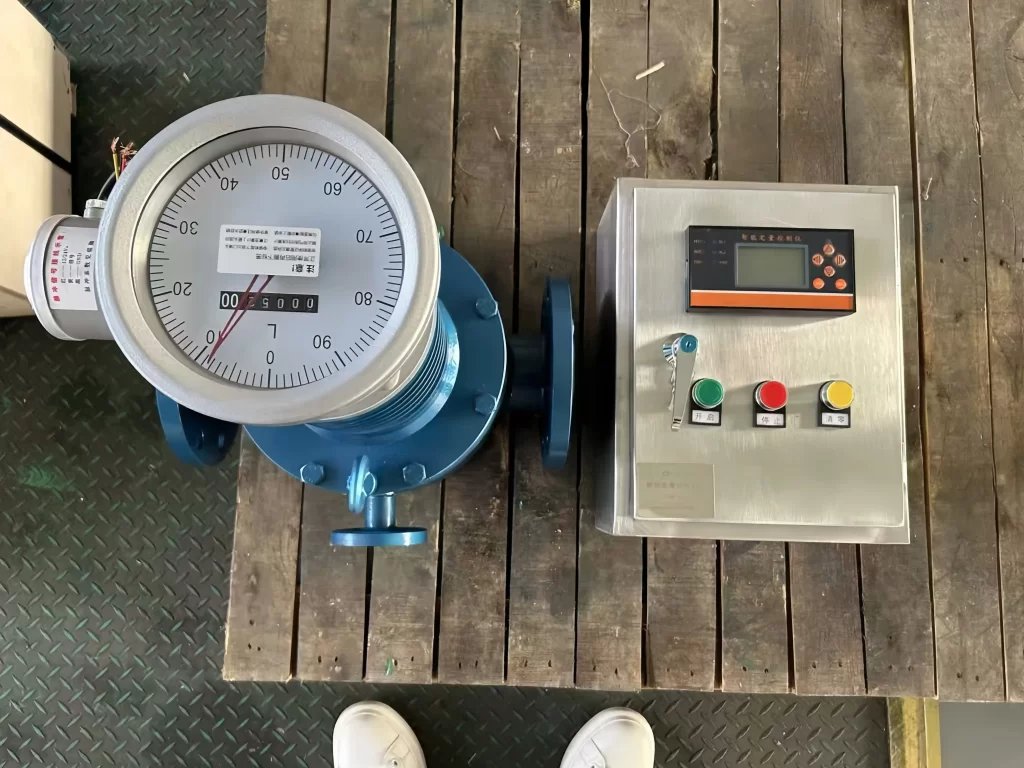

Advantages of Rotary Flow Meters
- High Accuracy
- Wide Range of Fluid Compatibility
- No Requirement for Straight Pipe Runs
- Durability and Longevity
- Capability for High Pressure and Temperature Applications
- Minimal Pressure Drop
Applications of Rotary Flow Meters
Rotary flow meters are widely used across multiple industries, including:
- Oil and Gas Industry
- Chemical Industry
- Marine and Fuel Dispensing
- Food and Beverage Industry
- Pharmaceutical Industry

Installation Considerations for Rotary Flow Meters
- Prior to meter installation, the line should be cleaned of pipe dope, weld slag, liquids, sand, valve grease or other debris.
- The meter should not be installed at the low point in the piping system where liquids or particulate matter tend to collect, or behind a lubricated valve where excess grease from the valve could block the impellers and cause the meter to stop.
- Care should be exercised in installing the meter with proper support devices. Piping connected to the meter should be supported to prevent strains or tension on the meter body (cylinder).
- Proper leveling of the meter is important during installation and will maximize meter life and efficiency.
- Where a meter may be subject to possible over-speeding because of sudden pressure drops or flow surges, a restricting orifice should be installed downstream of the meter in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendation.
- Most manufacturers recommended installing the meter using a bypass loop. This allows for easy maintenance or testing without the interruption of service, as well as a smooth, controlled start-up of the meter.
- Regular inspections and calibration help maintain accuracy over time.
More Flow Measurement Solutions
- Fertilizer Flow Monitoring: Liquid Fertilizer Flow Meters
- Calorimetric Flow Meter: An Economical Solution For Hot Water Flow Measurement
- Knowing Paint Flow Meters – Choose the Right One!
- Comprehensive Guide On Chlorine Flow Meters
- How To Calculate Pressure From Flow Rate And Vice Versa
- Non-Contact Flow Meters: An Advanced Approach To Fluid Measurement
- Relationship Between Pressure And Flow Rate: Key Insights
- High Accuracy Flow Meters: Technology, Applications, And Benefits
- Right Flow Meter For Molasses
Significant improvements in rotary flow meters have been realized in the last few years because of improvements in manufacturing techniques. Better machinability has led to improved range-abilities.
Rotary flow meters from Sin-Inst supports parameter customization for DN25~DN200. It can provide on-site instructions, and can also be connected to an explosion-proof pulse or 4~20mA transmitter for remote measurement to achieve automated control.
Our Sino-Inst Rotary flow meters can be widely used in automobiles, agriculture, flow measurement of liquids in hydrocarbon processing (refining) and numerous other industries. If you need to purchase Rotary flow meters, please feel free to contact our sales engineers!
-1.jpg)







