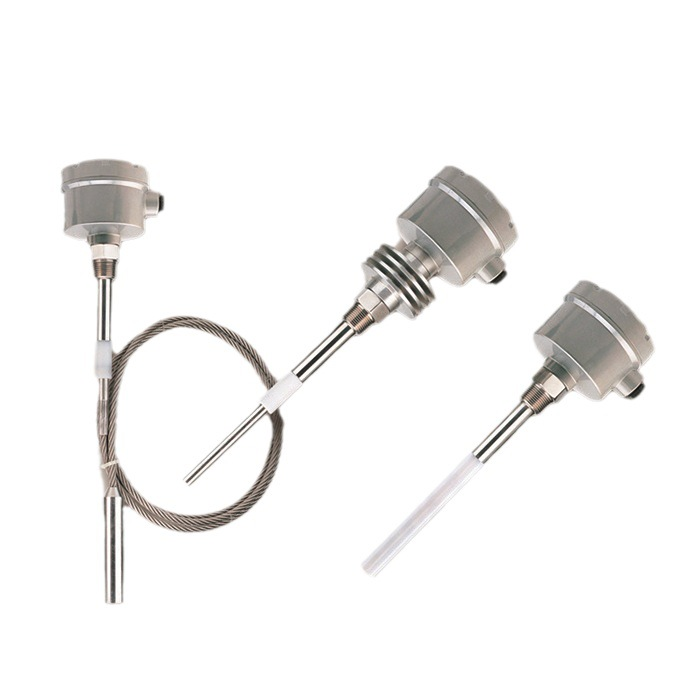
The conductive level switch utilizes the conductivity of the liquid to detect the liquid level. When the substance in the tank touches the electrodes, it conducts electricity, thus generating a signal. After the signal is amplified by the controller, a set of relay contact signals is output for the user to control the liquid level.
The electrode-type level switch is suitable for conductive liquids, features surge protection, and effectively prevents surge interference. It can provide multi-point control, and the control positions can be customized according to customer needs.
Features
Technical Parameters
| Power supply: | 220V AC 50/60Hz, 24VDC |
| Contact capacity: | 5A 240VAC/30VDC |
| Control method: | Supports low-level start/high-level stop or high-level start/low-level stop modes; the relay is energized when the liquid level is below E2, and de-energized when it is above or equal to E1. |
| Mounting type: | 3/8″~6″ flange, or threaded BSP, NPT, customizable |
| Withstand voltage: | 10bar~40bar, customizable |
| Electrode material: | SUS304, SUS316, SUS316L, PP coated |
| Number of electrodes: | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 |
| Temperature: | -10℃~250℃ |
| Length: | 50~6000mm, customizable |
| Measured medium: | Conductive liquids |
| Protection class: | IP65 |
| Controller: | Integrated type, separate type |
Conductive Level Switch Working Principle
The conductive level switch utilizes the conductivity of the liquid to detect the liquid level. By amplifying the current in the circuit, it reaches the activation point and outputs a signal. When the conductive medium in the tank contacts the electrode rod, a set of switching signals is output.
As shown in the figure, when the liquid level is below electrode E3, the liquid level controller is powered on, the WATER SUPPLY indicator light illuminates, the NO-COM contact is closed, and the NC-COM contact is open. When the liquid level rises to E1, the drainage indicator light illuminates, the NO-COM contact opens, and the NC-COM contact closes. When the liquid level drops below E2, the drainage indicator light turns off, the NO-COM contact closes, and the NC-COM contact opens. This completes one control cycle.
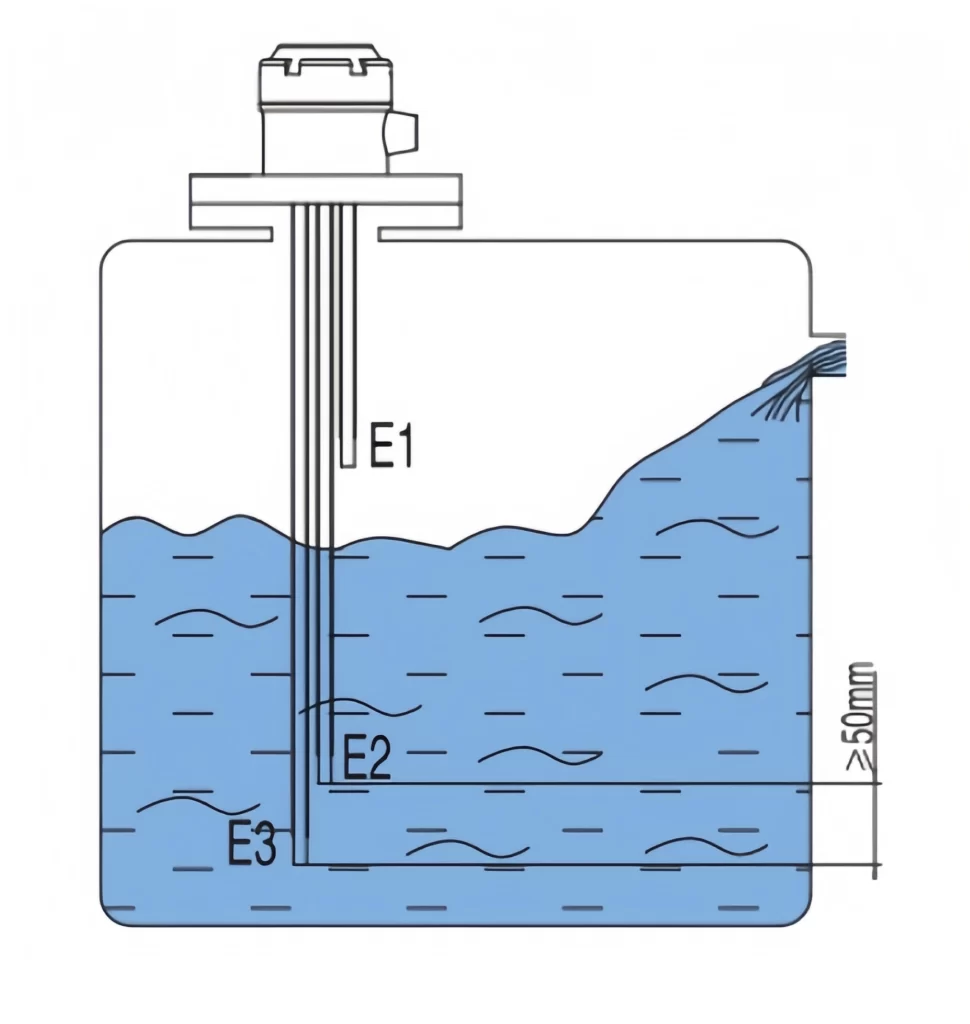
Installation Precautions
- For vertical installation only.
- The voltage fluctuation range should be within ±5%, and the voltage must be stable.
- Avoid installation in locations with strong vibration or shock (which may cause malfunctions).
- This product is not suitable for non-conductive liquids, such as gasoline, diesel fuel, heavy oil, pure water, etc.
- All electrodes must be at least 50mm apart from the longest electrode.
- When the liquid contacts the electrodes, the operating position may vary depending on the type of liquid and changes in power supply voltage.
- To ensure that the electrode rods do not come into contact with each other in the water, insulating sleeves can be added to the rods.
Featured Applications
Conductive level switches are suitable for the following industries: shipbuilding, power generation equipment, petrochemicals, wastewater/water treatment, electronics, dyeing and finishing, chemical, chemical fiber, and other industrial applications.
- Power plants: fuel storage tanks, reservoirs, exhaust gas purification tanks, ash silos, oil tanks, etc.
- Chemical industry: distillation towers, raw material and intermediate material silos, reaction tanks, ammonia water tanks, toxic liquid tanks, solid material silos, separators, etc.
- Petrochemicals: oil pipelines, distillation towers, concentration tanks, liquefied gas tanks, ammonia water tanks, steam drums, refinery oil depots, etc.
- Water and water treatment: reservoirs, sewage tanks, water treatment tanks, sedimentation tanks, digestion towers, gas pipelines, deep wells, drinking water pipelines, etc.
- Cement: cement silos, coal powder silos, slag storage silos, etc.
- Metallurgy: auxiliary material silos, alumina powder silos, electrolytic cell buffer tanks, etc.
- Oil fields: crude oil or refined oil storage tanks, three-phase separators, settling sewage tanks, drilling mud tanks, etc.
- Paper industry: storage towers, drying drums, etc.
The number and length of electrodes can be customized according to user requirements:
- 1 electrode is suitable for liquid level alarm in metal tanks and pipeline leak detection alarms, with the tank serving as the common terminal;
- 2 electrodes are suitable for single-point alarms in non-metallic tanks and water tanks, and for leak detection alarms in non-metallic pipelines;
- 3 electrodes are the most commonly used, suitable for water supply and drainage and other liquid inlet or outlet control, and can achieve automatic control of water supply and drainage when combined with pumps;
- 4 electrodes add upper limit alarm or lower limit alarm functions on the basis of liquid inlet or outlet functions, preventing overflow due to excessively high water levels or dry running of the pump due to excessively low water levels.
Water Level Control Wiring Diagram
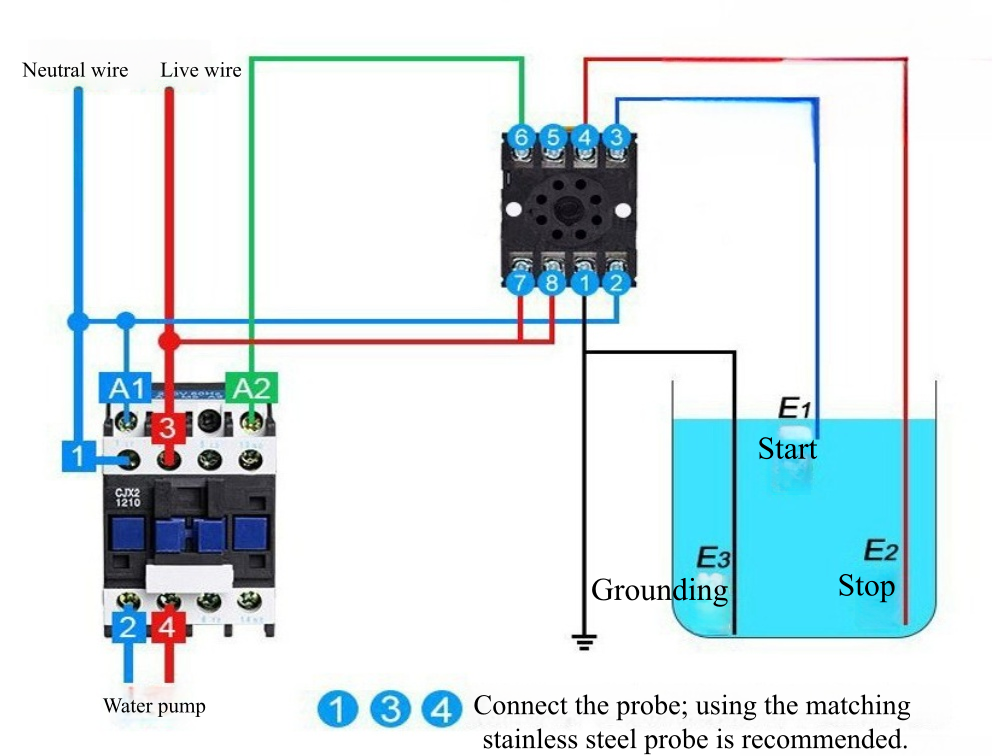
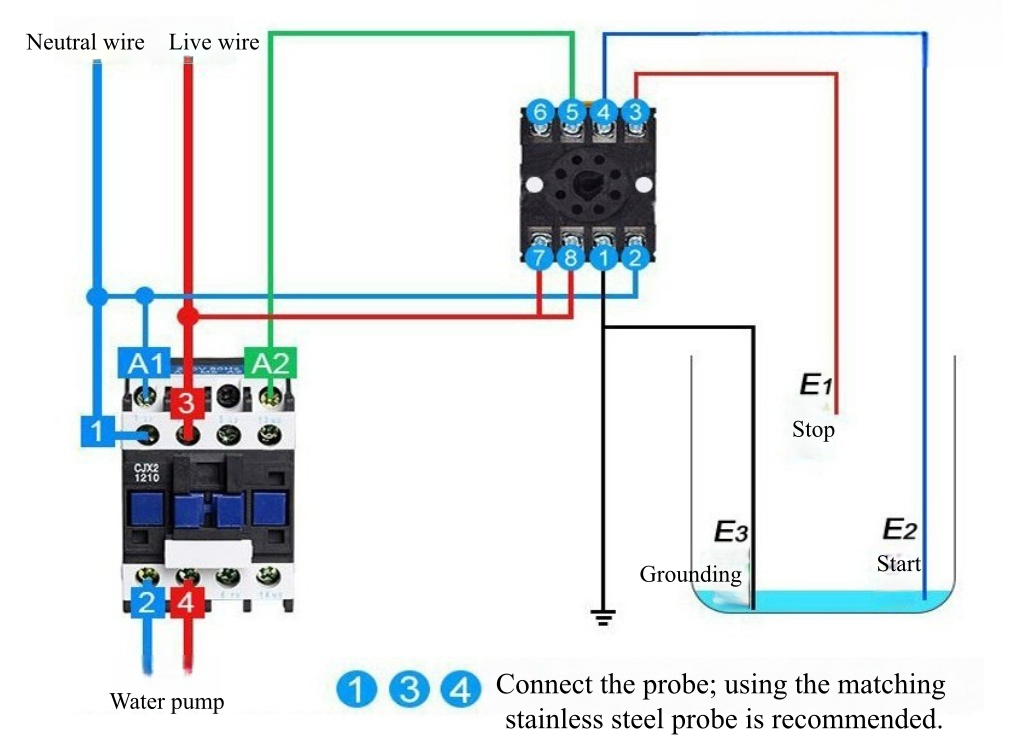
More Level Control Solutions
Conductive Level Switches are widely used in industrial applications. For example, in storage tanks, Conductive Level Switches can be used to monitor the liquid level to prevent overflow or drying out. In chemical processes, Conductive Level Switches can monitor the liquid level in chemical reactors to control the reaction process or prevent reactor overflow. In addition, Conductive Level Switches can also be used in wastewater treatment, automatic irrigation systems, and drinking water equipment.
In short, Conductive Level Switches determine the liquid level by measuring the conductivity of the liquid and utilizing the change in resistance between the electrodes. It is a simple and reliable liquid level control device. However, it is not suitable for flammable, explosive, or poorly conductive liquids, such as oil, ultrapure water, volatile liquids, and high-density wastewater.
If you need a customized Conductive Level Switches, please feel free to contact us!
-1.jpg)



