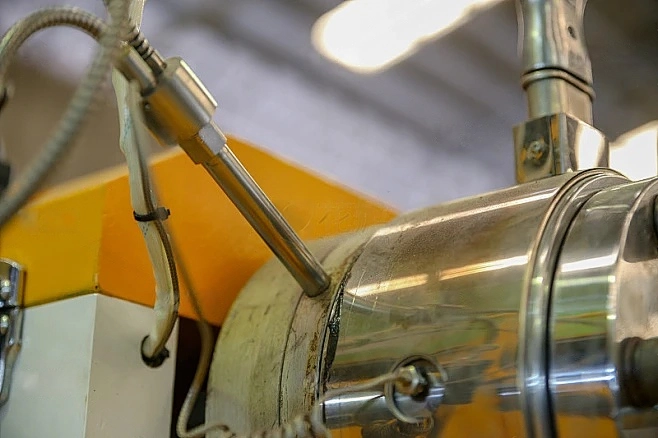
What is Cold Junction Compensation in Thermocouples?
Cold junction compensation is a corrective measure taken in thermocouple measurements to eliminate measurement errors caused by the cold junction temperature deviating from 0°C.
The need for cold junction compensation in thermocouples stems from their working principle. Let’s analyze this in detail.
Why is Cold Junction Temperature Compensation Necessary for Thermocouples?
From the working principle of thermocouples, it is known that the magnitude of the thermoelectric potential of a thermocouple is related not only to the temperature of the measuring end but also to the temperature of the reference end. In practical applications, the reference end of the thermocouple is usually called the cold junction.
For a selected thermocouple, when the cold junction temperature is constant, the total thermoelectric potential becomes a single-valued function of the measuring end temperature. That is, a certain thermoelectric potential corresponds to a certain temperature, and in the thermocouple calibration table, the cold junction temperature is assumed to be zero.
However, in practical applications, the cold junction temperature varies greatly and cannot always be kept at zero. This will lead to measurement errors. To ensure the accuracy of the measurement results, temperature compensation for the cold junction of the thermocouple is necessary.
Read more about: Differences Between Thermocouples: Type S, K, N, J, E, T
Calculation of the Effect of Cold Junction Temperature
According to the thermoelectric potential formula of a thermocouple:
E = S(T_hot – T_cold)
(S is the Seebeck coefficient, T is the temperature)
When the cold junction temperature T_cold changes, even if the hot junction temperature T_hot remains constant, the measured potential E will change.
For example, for a K-type thermocouple at a hot junction temperature of 500℃:
- If the cold junction is stable at 0℃, the output is 20.644mV
- If the cold junction rises to 30℃, the output decreases to 20.644mV – 1.203mV = 19.441mV
The corresponding temperature display will change from 500℃ to 487℃, resulting in a measurement error of 13℃.
5 Cold Junction Compensation Methods
1. Ice Bath Method
The ice bath method is commonly used in laboratories, where the reference junction temperature is kept constant at 0°C. However, this method is expensive and difficult to implement.
2. Cold Junction Temperature Correction Method
The cold junction temperature correction method is commonly used in applications where high accuracy is not required. When the cold junction temperature cannot be kept constant at 0°C, the instrument’s indicated value needs to be corrected. This method is easy to implement but has a larger error.
3. Compensation Bridge Method
The compensation bridge method is rarely used alone. It utilizes the potential generated by an unbalanced bridge to compensate for the change in thermoelectric potential caused by the change in the thermocouple’s cold junction temperature. Compensation bridges are available as separate products.
4. Compensation Wire Method
This is the most commonly used method. It involves extending the thermocouple. The cold junction is led to a place with a relatively stable temperature (usually the control room), and then the cold junction temperature is adjusted manually. This involves adjusting the instrument’s zero point to room temperature, or using the instrument’s internal circuitry for automatic compensation.
For noble metal thermocouples, extending the thermocouple is impractical due to the high cost. Therefore, base metals with similar thermoelectric characteristics are used to make compensation wires. The intermediate temperature law is the theoretical basis for using compensation wires.
Compensation wires do not automatically compensate for changes in the thermocouple’s cold junction temperature; they only lead the thermocouple’s cold junction to a place with a relatively stable temperature. Compensation still requires manual adjustment or instrument-based compensation.
5. Automatic Compensation Method within the Display Instrument
Whether it’s early electronic potentiometers, modern display instruments, miniature color paperless recorders, or related DCS boards, they all invariably employ automatic compensation methods. Some use copper resistance compensation, some use compensation bridges, and others use the change in junction voltage of a transistor’s PN junction with temperature for compensation.
More Temperature Measurement Solutions
Cold junction compensation is not simply a matter of temperature addition, but rather a systems engineering process involving materials science, circuit design, and algorithm optimization. Modern intelligent temperature transmitters have achieved automatic compensation, but understanding the underlying principles remains crucial for ensuring measurement reliability.
Sino-Inst supplies various types of thermocouples and supports customization. Please feel free to contact us!
-1.jpg)