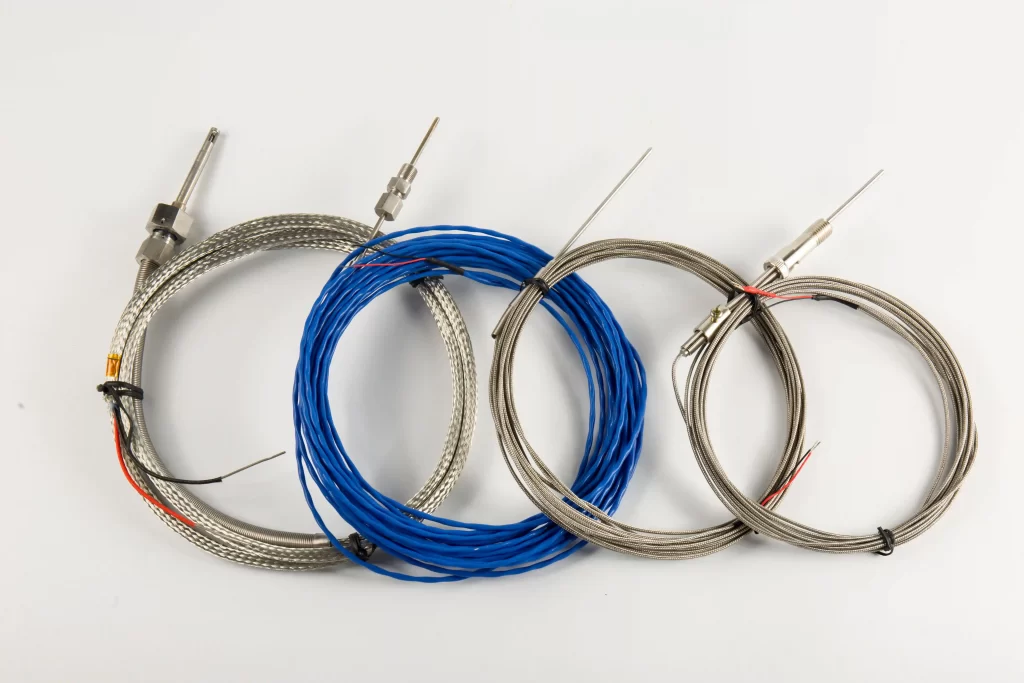
A type K thermocouple is a widely used thermocouple in temperature measurement. Type K thermocouples are typically composed of two different metal alloys: a chromium-nickel alloy and an aluminum-nickel alloy.
Type K thermocouples are inexpensive, highly accurate, reliable, and have a wide temperature range. Their maximum continuous operating temperature is approximately 1100°C. They provide accurate temperature readings even under harsh conditions. Therefore, they are the preferred choice for many industries.
What is a K-type Thermocouple?
K Type thermocouples are commonly used temperature sensors in industrial environments. They are typically used with display instruments, recording instruments, and electronic controllers. Type K thermocouples can directly measure the surface temperature of liquids, gases, and solids from 0°C to 1300°C.
The working principle of a K Type thermocouple is based on the Seebeck effect. When a temperature gradient exists between two different metals, a voltage is generated.
K Type thermocouples offer a wide temperature measurement range, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Therefore, they are the best choice for manufacturing, aerospace, and food processing industries.
Why Choose a K-Type Thermocouple?
K Type thermocouples offer the advantages of a wide temperature range, high durability, excellent cost-effectiveness, and ample supply. These characteristics make them suitable for numerous industrial applications.
Features
Wide Temperature Range
K Type thermocouples are suitable for both low and high temperature applications. Their temperature range is -200°C to 1260°C.
Fast Response
K Type thermocouples have a simple structure and compact size. They can respond quickly to temperature changes.
Rugged and Durable
K Type thermocouples are robust and durable. Their performance does not significantly degrade even in harsh industrial environments.
Affordable
K Type thermocouples are generally cheaper than other thermocouples and are readily available.
The Working Principle of K Type Thermocouple

A K Type thermocouple operates based on the Seebeck effect. When two different metals are joined together and exposed to a temperature difference, a voltage is generated.
The measuring junction exposed to the heat source generates a thermoelectric voltage. This voltage is proportional to the temperature difference between it and the reference junction. The temperature is then determined by measuring this voltage using compatible equipment.
K Type Thermocouple Resistance Chart
| Temp ℃ | 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 |
| K-type thermoelectric potential mV | ||||||||||
| -200 | -5.981 | -6.158 | -6.158 | -6.262 | -6.344 | -6.404 | -6.441 | -6.458 | ||
| -100 | -3.553 | -3.825 | -4.138 | -4.41 | -4.669 | -4.912 | -5.144 | -5.354 | -5.55 | -5.73 |
| 0 | 0 | -0.392 | -0.777 | -1.156 | -1.527 | -1.889 | -2.243 | -2.585 | -2.29 | -3.224 |
| 0 | 0 | 0.397 | 0.798 | 1.203 | 1.611 | 2.022 | 2.463 | 2.85 | 3.266 | 3.681 |
| 100 | 4.095 | 4.058 | 4.919 | 5.327 | 5.733 | 6.137 | 6.539 | 6.939 | 7.338 | 7.737 |
| 200 | 8.137 | 8.537 | 8.938 | 9.341 | 9.745 | 10.151 | 10.56 | 10.969 | 11.381 | 11.79 |
| 300 | 12.027 | 12.923 | 13.039 | 13.456 | 13.874 | 14.292 | 14.712 | 15.132 | 15.552 | 15.974 |
| 400 | 16.395 | 16.395 | 17.241 | 17.664 | 18.088 | 18.513 | 18.938 | 19.363 | 19.788 | 20.214 |
| 500 | 20.64 | 20.64 | 21.493 | 21.919 | 22.346 | 22.772 | 23.198 | 23.624 | 24.05 | 24.476 |
| 600 | 24.902 | 24.902 | 25.751 | 26.176 | 26.599 | 27.022 | 27.445 | 27.867 | 28.288 | 28.709 |
| 700 | 29.128 | 29.128 | 29.965 | 30.383 | 30.799 | 31.214 | 31.659 | 32.042 | 32.455 | 32.866 |
| 800 | 33.277 | 33.277 | 34.095 | 34.502 | 34.909 | 35.314 | 35.718 | 36.121 | 36.524 | 36.925 |
| 900 | 37.325 | 37.325 | 38.122 | 38.519 | 38.915 | 39.31 | 39.703 | 40.096 | 40.488 | 40.879 |
| 1000 | 41.269 | 41.269 | 42.045 | 42.432 | 42.817 | 43.202 | 43.585 | 43.968 | 44.349 | 44.729 |
| 1100 | 45.018 | 45.108 | 45.863 | 46.238 | 46.612 | 46.985 | 47.356 | 47.726 | 48.095 | 48.462 |
| 1200 | 48.828 | 48.828 | 49.555 | 49.916 | 50.276 | 50.633 | 50.99 | 51.344 | 51.697 | 52.049 |
| 1300 | 52.398 | 52.398 | 53.093 | 53.439 | 53.782 | 54.125 | 54.466 | 54.807 | ||
Advantages and Disadvantages of K Type Thermocouples
| Advantages | Wide Temperature RangeTemperature range from -200°C to 1260°C. |
| Fast Response: Type K thermocouples have a simple and compact design. | |
| Rugged and Durable: Performance remains largely unaffected even in harsh industrial environments. | |
| Affordable: Type K thermocouples are typically less expensive than other types of thermocouples. | |
| Disadvantages | Susceptible to drift |
| Susceptible to corrosive environments | |
| Limited low-temperature sensitivity | |
| Susceptible to magnetic field interference |
Industrial Applications
Metal Processing
In heat treatment, K-type thermocouples are used for furnace temperature monitoring. cc can monitor the temperature during the forging process.
Food Processing and Autoclaves
K-type thermocouples ensure that the sterilization cycle in an autoclave meets temperature standards. K type thermocoupless monitor temperatures in food processing applications.
Power Generation and Aerospace
K type thermocoupless are used in turbines, engines, and boilers. They provide real-time temperature data to monitor and optimize combustion.
Industrial and HVAC
In general industrial applications, K-type thermocouples are used to monitor engine temperatures. For HVAC systems, providing temperature readings for heating and cooling equipment is crucial.
Material of K-type Thermocouples
A K-type thermocouple typically consists of two nickel alloy wires. The positive wire is a chromium-nickel alloy. It helps improve the thermocouple’s Seebeck coefficient and overall sensitivity. The negative wire is an aluminum-nickel alloy. It can generate a voltage when heated.
The aluminum-nickel alloy consists of approximately 95% nickel, 2% aluminum, 2% manganese, and 1% silicon. This alloy offers a wide temperature range and high sensitivity.
Insulation and Sheathing Materials
Wires typically use insulation materials capable of withstanding the expected temperature. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is used for low-temperature environments. Fiberglass is used for medium-temperature environments. Compacted mineral insulation is used for high-temperature environments.
A metal sheath usually surrounds the insulation layer. It protects the wire and prevents contamination of the tested environment. The sheath material for K-type thermocouples must be selected based on the operating environment.

Key Considerations When Selecting a K-Type Thermocouple
Temperature Range and Atmospheric Conditions
K Type thermocouples are suitable for a wide temperature range. However, the maximum temperature limit depends on the wire size.
K Type thermocouples perform best in clean oxidizing environments. However, they are not suitable for reducing or inert atmospheres. Performance degrades in sulfur-containing gases.
Accuracy
The standard accuracy of a K Type thermocouple is ±2.2 °C or ±0.75% of the measured value, suitable for general applications. Special error limits are ±1.1 °C or ±0.4%. For higher accuracy, consult the “Special Limits” tolerance class. This class provides tighter tolerances within a specific temperature range.
Contacts and Response Time
The contact type affects response time and durability. Grounded contacts are directly welded onto the shield. They offer faster response speeds than non-grounded types but are more susceptible to electrical noise interference.
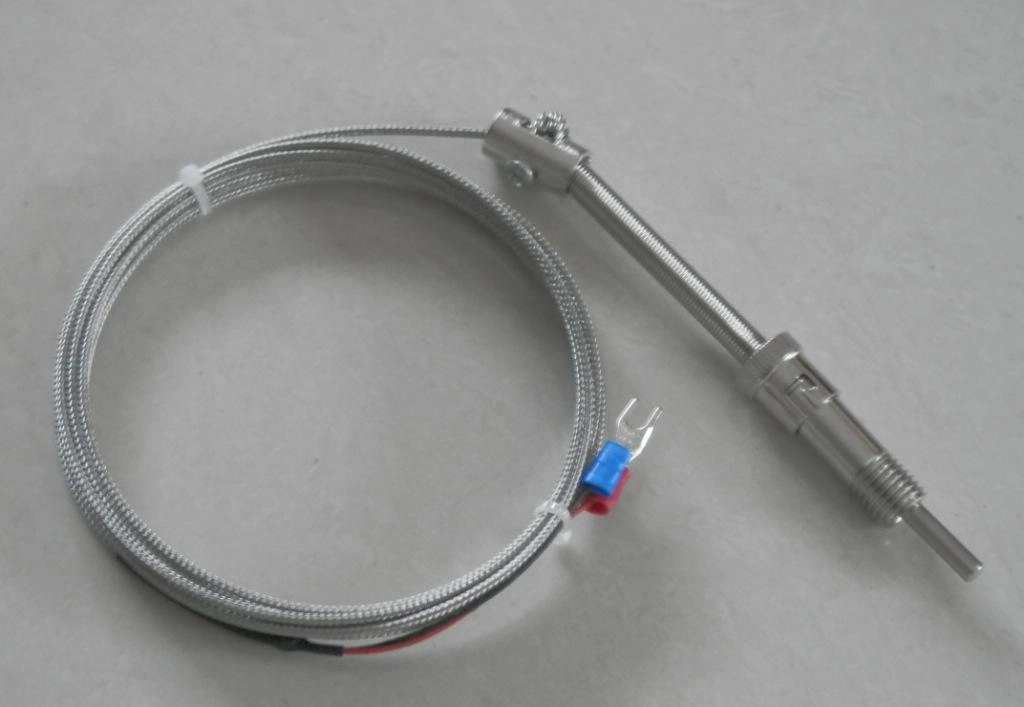

Grounded thermocouples are directly welded to the sheath. They have a faster response time and better thermal conductivity than ungrounded thermocouples. But they are more susceptible to electrical noise interference.
Ungrounded thermocouples have the slowest response time. However, this method provides excellent noise immunity due to electrical isolation from the sheath. It is best suited for corrosive or high-voltage environments requiring electrical shielding.
Calibration of K-type Thermocouples
Preparation before calibration:
- Select a standard temperature source and a high-precision reference thermocouple.
- Clean the thermocouple contacts and sheath.
- Check electrical continuity and insulation resistance.
- Preheat the calibration equipment to the target temperature and maintain stability.
Calibration Procedure:
- Insert the thermocouple under test and the reference thermocouple into a stable heat source.
- Record the potential difference at multiple temperature points and compare it with the reference value.
- Simultaneously record the readings from both the thermocouple under test and the reference sensor.
Data Analysis:
- Use the recorded data to create a calibration table or formula for your specific thermocouple.
- For medium accuracy, you can compare the readings to the response curve of a standard K-type thermocouple, but a full calibration provides the highest accuracy and takes into account the error of individual devices.
FAQ
More Temperature Measurement Solutions
K Type thermocouples serve as temperature measurement sensors. They can directly measure the temperature of fluid, steam, gas media, and solid surfaces. They are widely used in manufacturing, energy, aerospace, and process industries.
Sino-inst specializes in providing high-quality K Type thermocouples. Our K Type thermocouples deliver accurate temperature readings even under harsh conditions. Therefore, our K Type thermocouples are the preferred choice for numerous industries.
If you need to purchase or have any related technical questions, please feel free to contact us!
-1.jpg)