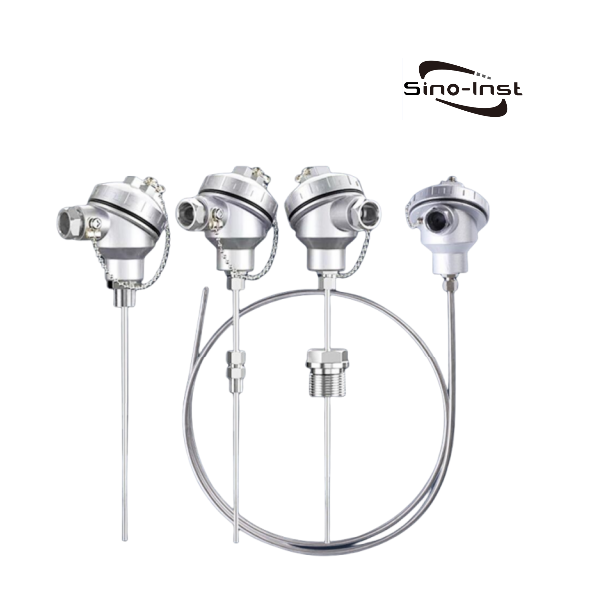
Thermocouples have the advantages of simple structure, wide measurement range, and easy processing of output signals. Therefore, thermocouples have become our preferred sensor for temperature measurement.
The graduation numbers of thermocouples mainly include S, R, B, N, K, E, J, T, etc. Among them, S, R, and B belong to precious metal thermocouples, and N, K, E, J, and T belong to cheap metal thermocouples. So what’s the difference? Understanding the Differences between Thermocouples can help us choose the most suitable thermocouple.
Thermocouple working principle
A thermocouple is a passive sensor that uses the thermoelectric effect as its measurement principle.
The so-called thermoelectric effect is when the two ends of conductors with different components (called thermocouple wires or hot electrodes) are connected to form a loop. When the temperatures of the two junctions are different, an electromotive force will be generated in the circuit. This will also involve the calculation of the effect of cold junction temperature.
Therefore, different types of thermocouples can be obtained according to the different materials of the two wires that make up the thermocouple. They have different advantages, disadvantages and scope of application.
Let’s talk about it in detail below.

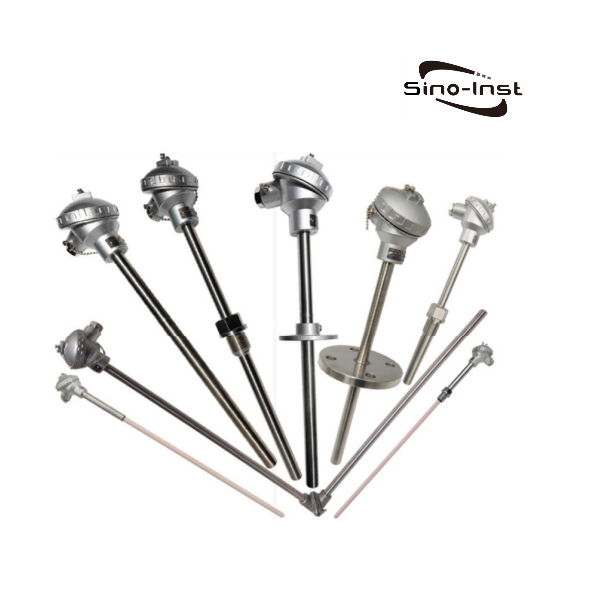
Types of thermocouples
What are the different types of thermocouples? There are 8 main types of thermocouple graduation numbers: S, R, B, N, K, E, J, and T.
Among them, S, R, and B belong to precious metal thermocouples, and N, K, E, J, and T belong to cheap metal thermocouples.
- The S grade is characterized by strong oxidation resistance and should be used continuously in oxidizing and inert atmospheres. The long-term use temperature is 1400°C and the short-term use temperature is 1600°C. Among all thermocouples, the S graduation number has the highest accuracy level and is usually used as a standard thermocouple;
- Compared with the S-grading type, the heat removal electromotive force of the R-grading type is about 15% larger, and other properties are almost identical;
- The thermal electromotive force of the B graduation number is extremely small at room temperature, so compensation wires are generally not needed during measurement. Its long-term use temperature is 1600℃ and short-term use temperature is 1800℃. Can be used in oxidizing or neutral atmospheres, and can also be used under vacuum conditions for short periods of time;
- The characteristics of the N graduation number are strong high-temperature oxidation resistance at 1300°C, good long-term stability of thermoelectromotive force and short-term thermal cycle reproducibility, and good nuclear radiation resistance and low temperature resistance. It can partially replace the S graduation number. thermocouple;
- The K grade is characterized by strong oxidation resistance and is suitable for continuous use in oxidizing and inert atmospheres. The long-term use temperature is 1000°C and the short-term use temperature is 1200°C. The most widely used of all thermocouples;
- The characteristic of the E graduation number is that it has the largest thermal electromotive force among commonly used thermocouples, that is, the highest sensitivity. It should be used continuously in an oxidizing and inert atmosphere, with a service temperature of 0-800°C;
- The characteristic of the J graduation number is that it can be used in both oxidizing atmospheres (the upper limit of the operating temperature is 750°C) and reducing atmospheres (the upper limit of the operating temperature is 950°C), and is resistant to H2 and CO gas corrosion. It is mostly used in oil refining and chemical industry;
- The T graduation number is characterized by the highest accuracy level among all low-cost metal thermocouples, and is usually used to measure temperatures below 300°C.

Differences Between Thermocouples
The main differences between various thermocouples are based on the different metal materials used, which results in different measurement ranges and characteristics.
These different types of thermocouples can be used directly, or as part of a sheathed assembly, or with a Thermocouple Sheath.
Featured Industrial Thermocouples
FAQ
The above is an introduction to Differences Between Thermocouples. All precious metal thermocouples have the advantages of high accuracy, best stability, wide temperature measurement range, long service life, and good oxidation resistance at high temperatures. The disadvantages are that the thermoelectric potential rate is small, the sensitivity is low, the mechanical strength decreases at high temperatures, it is very sensitive to pollution, and it is expensive.
We at Sino-Inst supply various types of industrial thermocouples, including K-type, T-type, etc. When selecting and purchasing, the thermocouple model should be selected reasonably based on the needs of the working conditions. If you have relevant technical questions, please feel free to contact us.
-1.jpg)