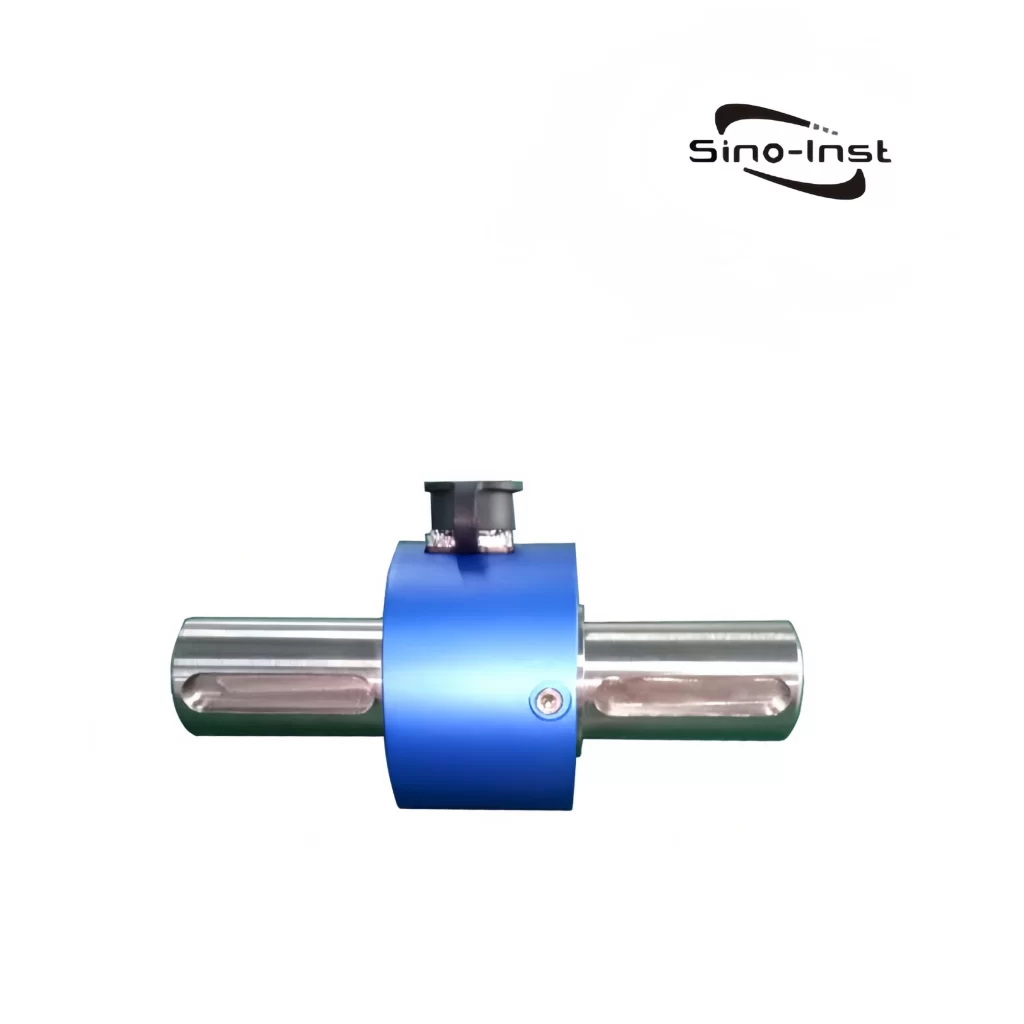
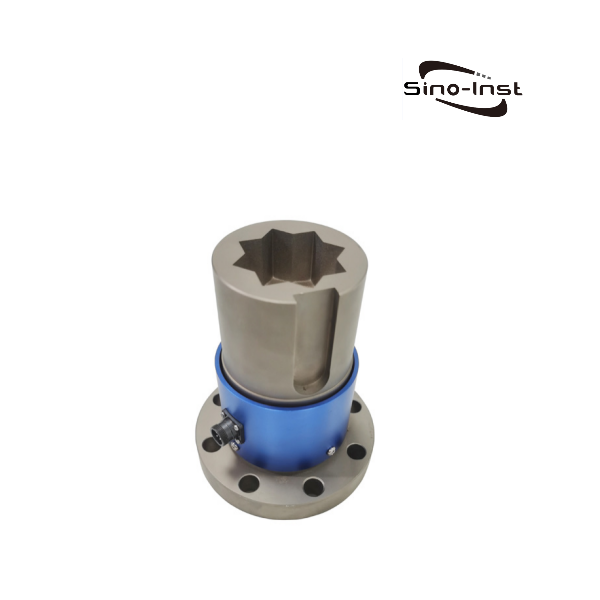
What is torque?
Torque is the rotational force applied to an object, which refers to the moment of rotation of an object around a certain axis. It is a physical quantity that measures the rotational force. It is determined by the product of force and lever arm, and the unit is Newton meter (N m).
Torque is a typical mechanical quantity that can reflect the performance Q of mechanical transmission system, and has a very wide range of applications. For example, the torque of the engine refers to the torque output from the crankshaft end of the engine. Under the condition of fixed power, it is inversely proportional to the engine speed. The faster the speed, the smaller the torque, and vice versa. It reflects the load capacity of the car within a certain range.
Torque measurement is very important
Torque measurement plays a key role in many industries. Especially in mechanical engineering, test bench construction, and manufacturing.
In the mechanical manufacturing industry, especially in rotating power systems, torque is a very important measurement quantity. From the tightening of screws to wind power generation. It can prevent mechanical failures, improve safety and ensure consistent production.
Torque is also an important measurement parameter in the development of internal combustion engines, drives and pumps. It is used to define performance, efficiency and friction coefficients.
In the fields of research and development, industrial process monitoring and quality assurance, torque measurement provides a reliable basis. Ensure that test objects such as threaded joints and drives meet the highest safety and efficiency requirements.
In safety-critical industries such as automotive and aerospace, the correct application of torque is crucial. Ensure that components such as wheel nuts, engine parts and structural bolts are fixed with optimal tightness.
For engine test benches, it is more preferable to use rotary torque sensors for online torque measurement. Dynamic torque measurement can also optimize the interaction between mechanisms.
Modern engines require higher speeds to improve mechanical performance and increase efficiency. Therefore, high-precision and reliable torque measurement is required.
Torque measurement is becoming increasingly important in the field of electric vehicles. Advanced testing and simulation programs can improve the efficiency of the drive and thus the efficiency of the entire system. Targeted efficiency improvements can reduce energy consumption. The company’s costs are significantly reduced, which can improve market positioning in the long term.
Benefits of torque measurement
- Prevent mechanical failures.
- Ensure consistency and precision in assembly processes.
- Torque combined with speed measurement can be used to obtain mechanical power.
- Improve the efficiency of the drive and thus the efficiency of the entire system.
- Targeted efficiency improvements can reduce energy consumption.
Classification and units of torque
Generally speaking, we divide torque into two types: rotational torque and reaction torque.
Rotational torque is also called dynamic torque;
Reaction torque is also called static torque.
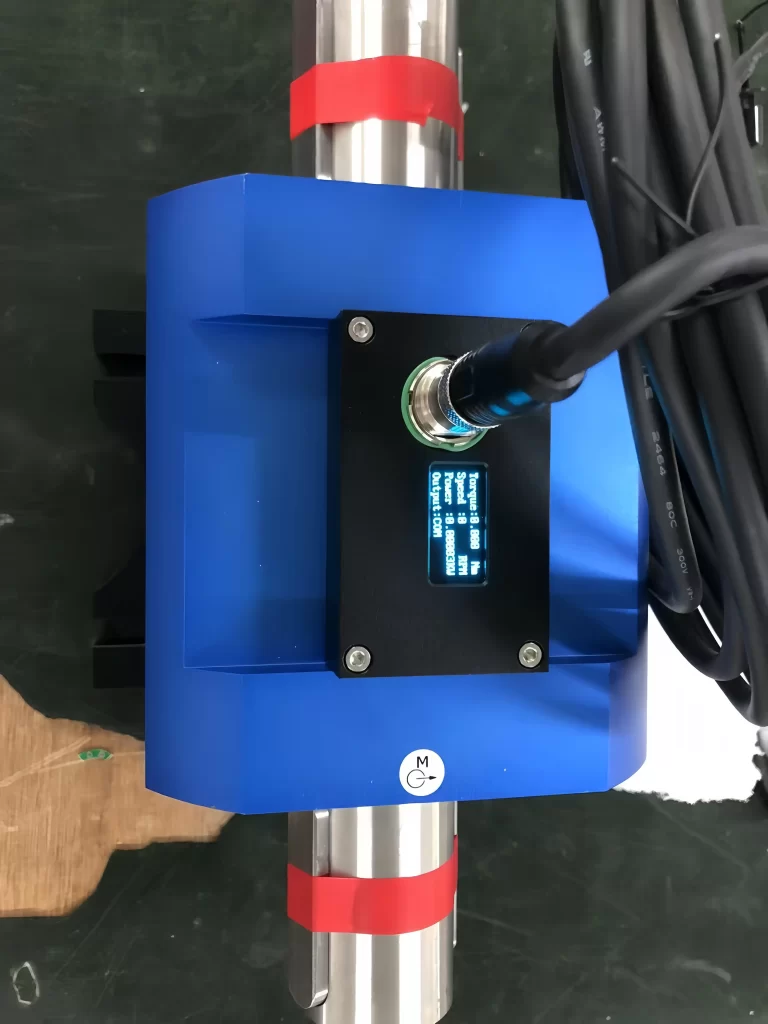

Dynamic torque refers to the torque displayed in real time by the tool or equipment during the assembly process, which is the torque achieved by the bolt overcoming dynamic friction. The torque value pre-set by the general torque-fixed tool and tightening machine is also the dynamic torque value.
Static torque refers to the maximum torque achieved by the bolt overcoming static friction in the tightening direction after the tightened bolt stops. The peak torque usually measured by a pointer-type manual wrench is the static torque.
Torque is a physical quantity that describes the rotation of an object in a rotating machine. It is the product of force and radius. The unit of torque is usually Newton meter (N·m). However, in some engineering fields, kilogram meter (kg·m) or foot pound (ft·lb) are also used as units. These units all represent the result of multiplying the force arm by the force.
In practical applications, 1 kg·m is equal to 9.8 N·m, and 1 ft·lb is approximately equal to 1.355 N·m.
Measurement and Control of Torque
In order to achieve accurate torque measurement and control, scientists and engineers have developed various methods and devices. Here are some common torque measurement and control technologies:
- Torque Sensor
Torque sensors are devices used to measure torque, usually based on the principle of strain measurement. They can be installed on rotating shafts to measure the deformation of the force-bearing parts and thus calculate the magnitude of the torque. - Torque Limiter
In some applications, the magnitude of torque needs to be limited to prevent excessive force on mechanical parts. Torque limiters usually include clutch and limiter devices that can cut off or limit the transmission of force when a certain torque value is reached. - Torque Control System
Torque control systems are used to monitor and adjust torque in real time to meet the needs of specific applications. These systems usually include sensors, controllers, and actuators to achieve highly accurate torque control.
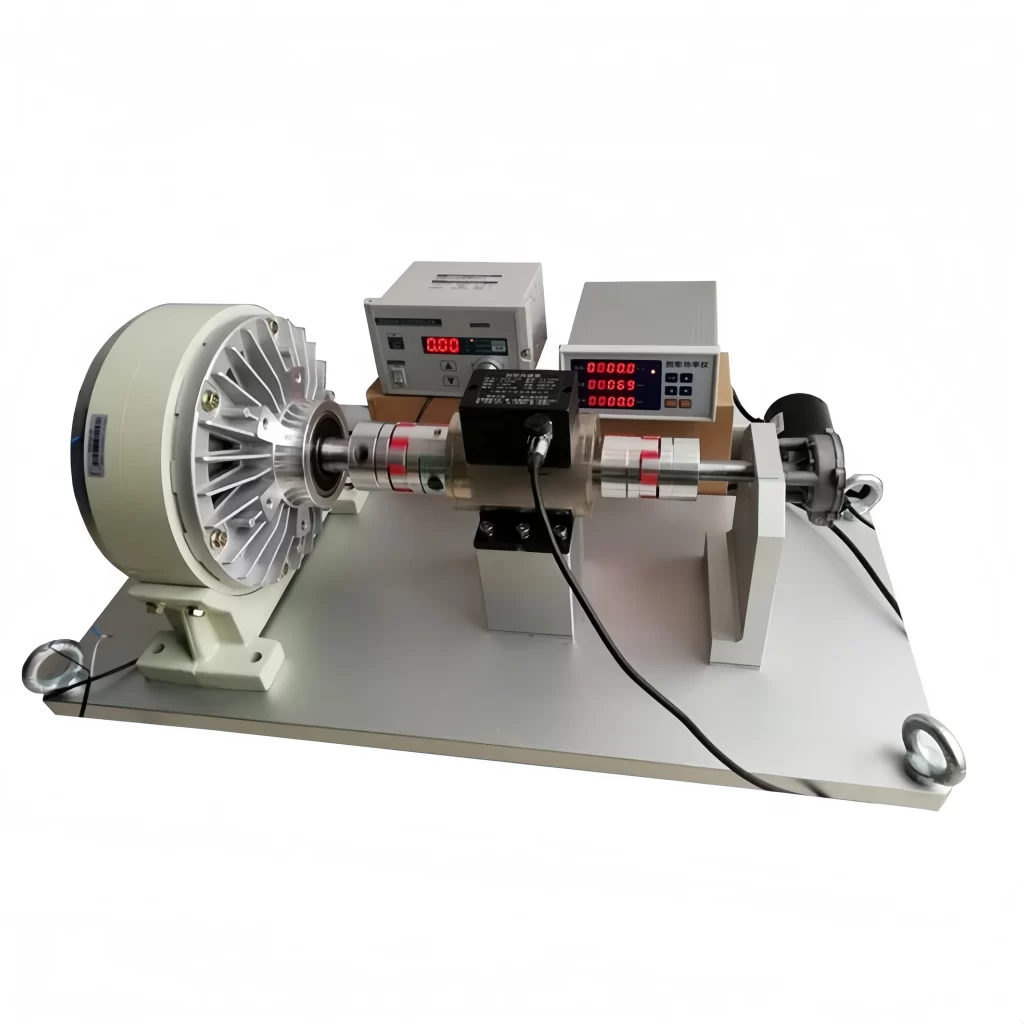
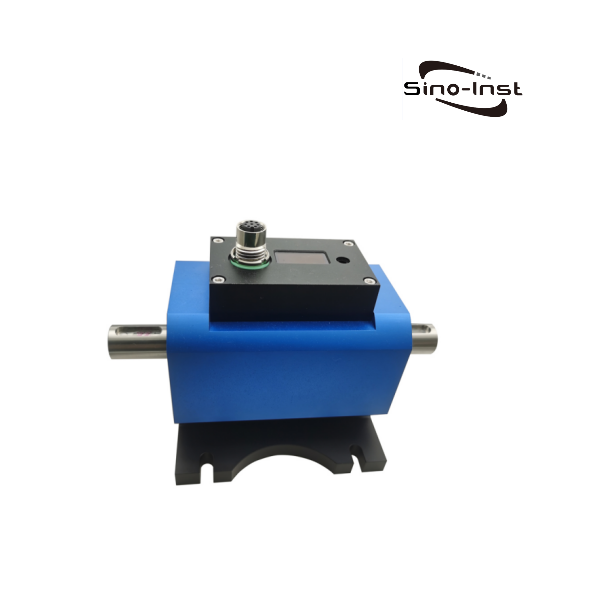
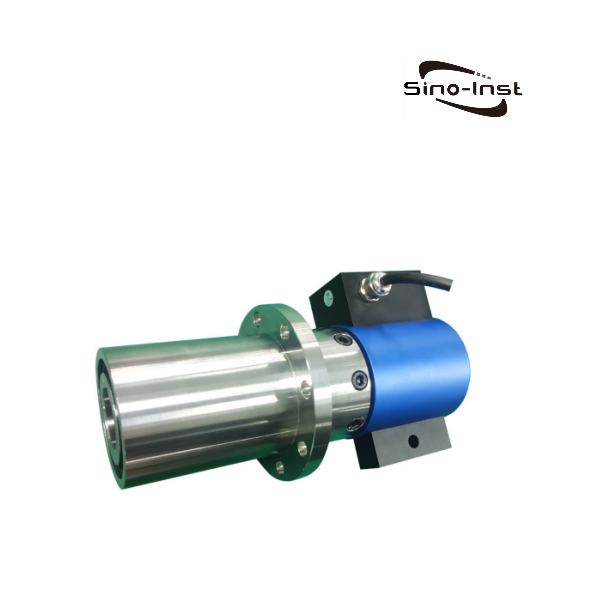
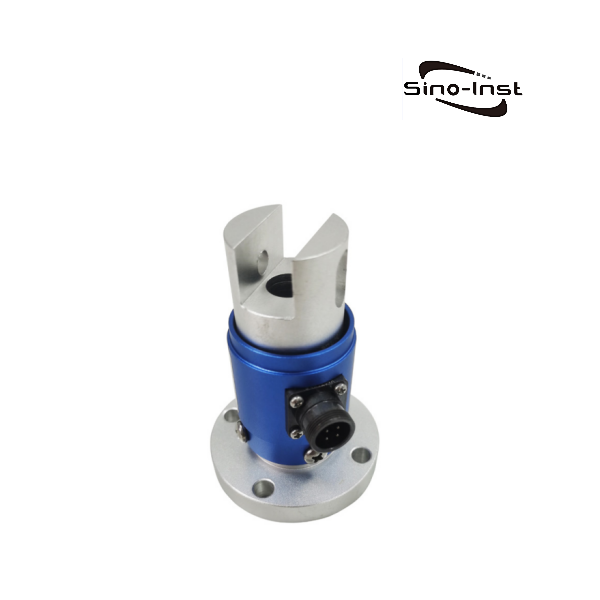
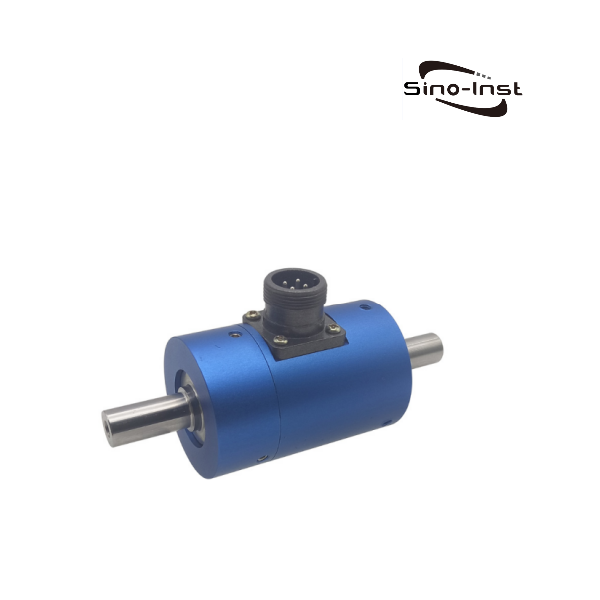
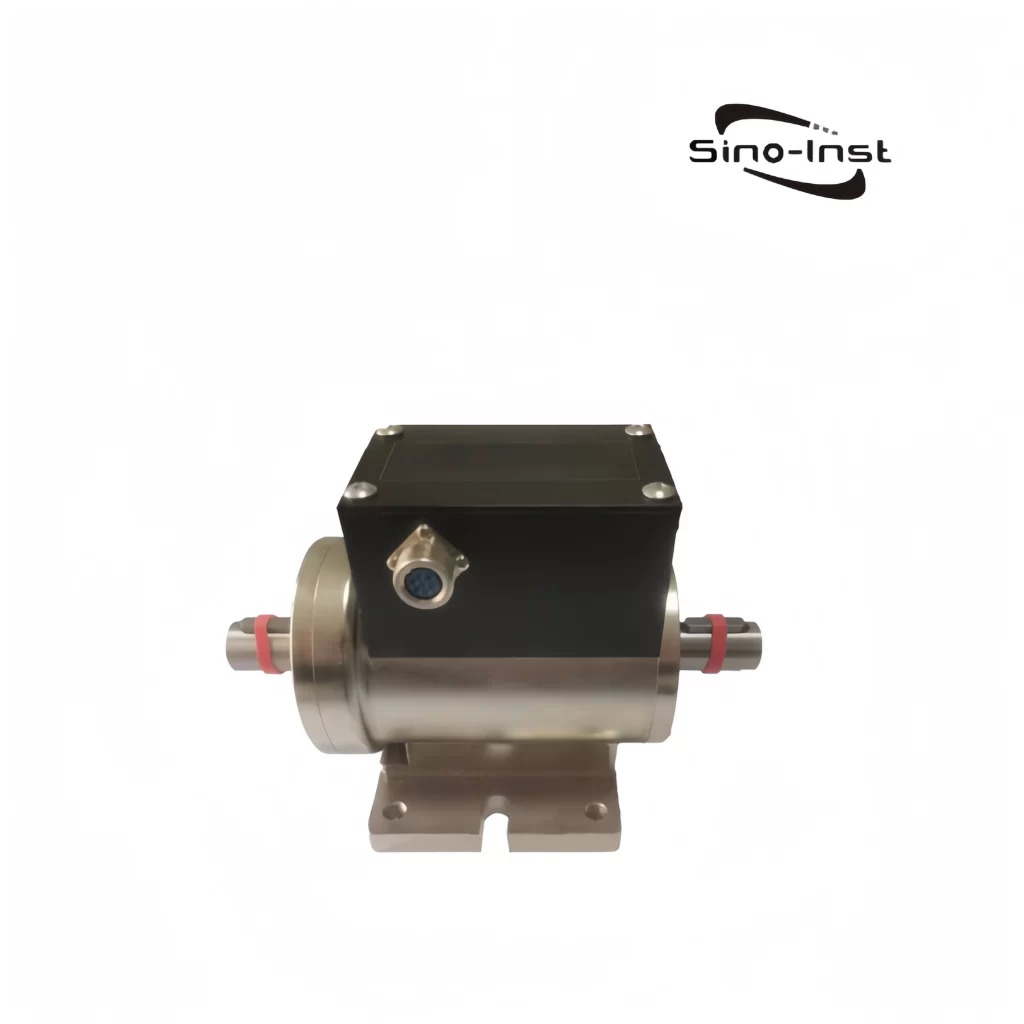
Featured Torque Sensors
Torque is an important parameter of rotating power machinery. Torque measurement is widely used in various industrial fields such as automobiles, ships, aerospace, electric locomotives, energy, and chemicals. Correct torque measurement is the guarantee for product development, condition monitoring, fault identification and prediction, automatic control, energy saving, and power balance indication. As the main method and core component of torque measurement, the correct selection of torque sensor is particularly important.
Sino-Inst produces and supplies various types of torque sensors. If you need to measure torque, purchase torque sensors, or have related technical questions, please feel free to contact us.
-1.jpg)