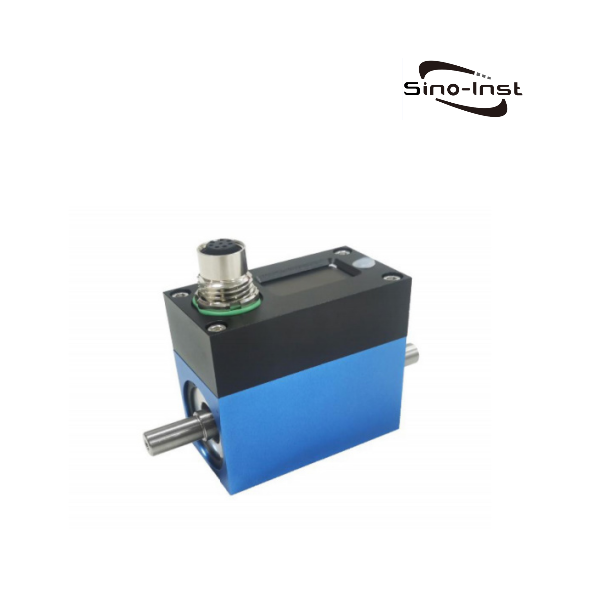
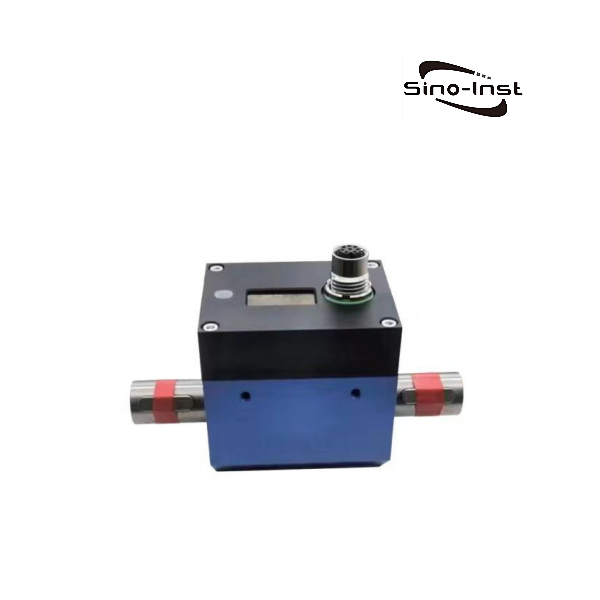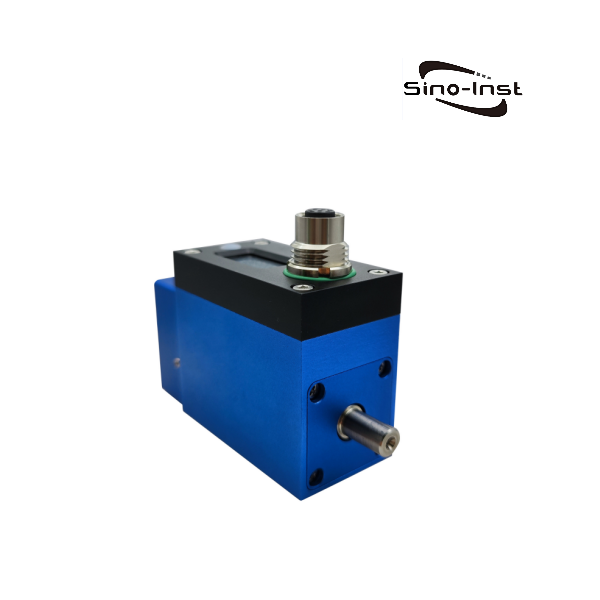
- Non-contact, no internal friction;
- Range 0.1-5Nm;
- Stainless steel shaft;
- Maximum speed 16000RPM;
- Can be equipped with speed output;
- Can be equipped with panel display of torque/speed/power;
CL1-104 Shaft Rotary Torque Sensor Technical Parameters
| Range | 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 5 Nm | ||||
| Accuracy | ±0.1, ±0.2%FS | Supply voltage | 12~24VDC | ||
| Zero-point temperature effect | ±0.02%FS | Supply current | Less than 100mA | ||
| Full-scale temperature effect | ±0.02%FS | Electrical connection | 8-Pin | ||
| Compensated temperature range | -10-60℃ | Overload protection | 200%FS | ||
| Operating temperature range | -20~75℃ | Material | Full-scale temperature effect | ||
| Torque output | 10±5kHz(5V amplitude), 0-±5VDC, 0-±10VDC, 0-5-10VDC, 4-12-20mA, 0-5V, 0-10V, 4-20mA, RS485, RS232, CAN, etc. | ||||
| Options | |||||
| Rotation speed measurement | 30 pulses/circle 4-20mA, 0-5VDC, 0-10VDC, RS485, RS232, CAN, etc. | ||||
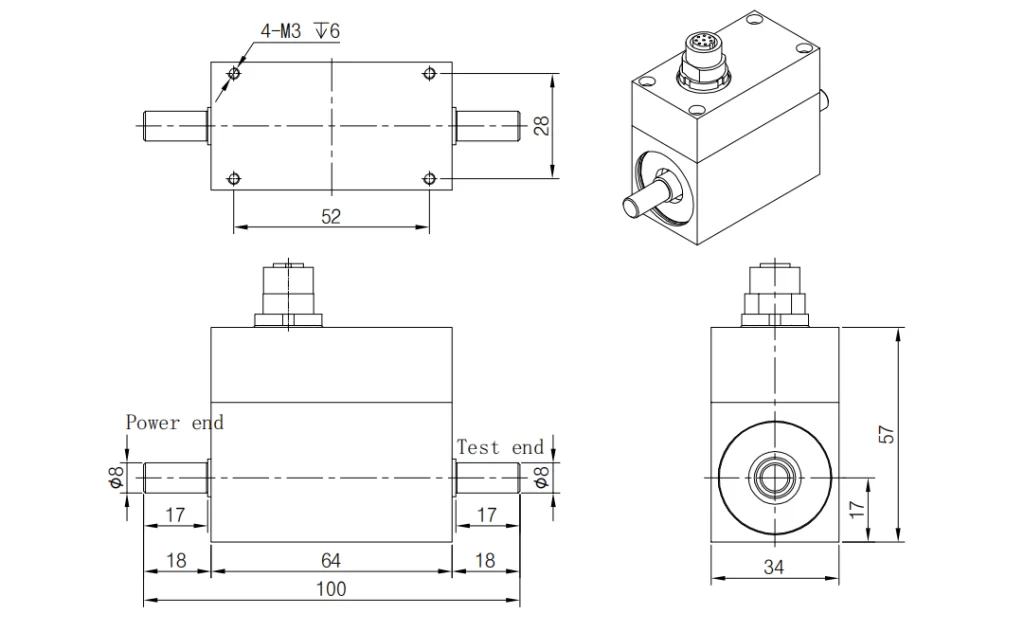
Dimensions
rotary torque sensor working principle
Torque sensors use strain technology to measure torque. Its working principle can be summarized as follows:
Basic structure: The core of the torque sensor usually contains a metal elastomer. This elastomer is designed to withstand and transmit torque. And a strain gauge is attached to its surface. A strain gauge is an electronic component that can convert mechanical deformation (such as tension or compression) into an electrical signal.
Strain effect: When an external force acts on the sensor, that is, when torque is applied to the elastomer, the elastomer will deform slightly. The strain gauge attached to the elastomer will deform accordingly. This deformation will cause the resistance of the strain gauge to change. Because the resistance change of the strain gauge is proportional to the mechanical deformation it is subjected to. Therefore, the magnitude of the torque can be inferred by measuring the resistance change.
Signal processing: Each strain gauge constitutes part of the Wheatstone bridge. Such a circuit design can greatly improve the sensitivity and accuracy of the sensor. When four strain gauges are configured as a full-bridge circuit, not only can the resistance change caused by torque be detected. It can also effectively offset the error caused by temperature changes.
Dynamic and static torque measurement: Dynamic torque sensors are designed to measure rapid changes in torque during acceleration or deceleration, while static torque sensors are used to measure relatively stable torque values, such as when the rotation angle does not exceed 360 degrees.
Non-contact torque sensors: In addition to the contact torque sensors mentioned above, there are also non-contact torque sensors. Such as magnetoelectric or photoelectric. These sensors indirectly measure torque by monitoring changes in magnetic fields or interference effects of light. No physical contact is required, reducing wear. Suitable for applications in high speed or extreme environments.
Data output: Regardless of the type of torque sensor, the measured physical changes will eventually be converted into electrical signals (such as voltage or current). And transmitted to the control system or display device via wired or wireless means. For further analysis and processing.
Through the above steps, the torque sensor realizes real-time and accurate measurement of torque. It is widely used in many fields such as automobiles, aviation, industrial automation, and precision instruments.

How is the maximum rotational speed of the torque sensor determined?
The maximum speed of a torque sensor is mainly determined by its design structure, material properties, and manufacturing process. When determining the maximum speed of a torque sensor, the following key factors need to be considered:
- Mechanical strength: The shaft and other rotating parts inside the sensor must be able to withstand the centrifugal force caused by high-speed rotation. If these parts are not strong enough, they may deform or break at high speeds.
- Signal transmission method: For wired sensors, collector rings (slip rings) are a common signal and power transmission method. The design of the collector ring limits the maximum speed. Because too high a speed may cause poor contact or increased wear. For wireless or contactless signal transmission (such as magnetic coupling, optical or radio frequency). Such sensors can usually support higher speeds. Because there is no wear problem caused by physical contact.
- Temperature effect: As the speed increases, the sensor and its surrounding environment may heat up due to friction and other reasons. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that the materials and electronic components can work properly in a high temperature environment.
- Bearing performance: Bearings are key components that support rotating parts. They must be able to withstand long-term high-speed operation without failure. Selecting the right bearing type (e.g., ball or roller bearings) and quality grade is critical to ensuring sensor reliability.
- Electrical characteristics: Electronic components, including strain gauges, can be sensitive to temperature changes. They can also produce signal distortion under high-frequency vibrations. Therefore, the selection and arrangement of these components will also affect the maximum operating speed of the sensor.
- Manufacturer specifications: Finally, each manufacturer will set a safe operating range based on the above factors and their own test results. The maximum allowable speed is provided as part of the product specifications.
In summary, the maximum speed of a torque sensor is the result of a combination of engineering considerations. Users should carefully refer to the technical parameters provided by the manufacturer when selecting a torque sensor for a specific application. To ensure that the selected device can meet the requirements under actual operating conditions.
More Torque Sensors and Solutions
CL1-104 Shaft Rotary Torque Sensor Up is a precision measuring instrument that can measure various high-speed, small-range torques. The maximum speed is up to 16000 RPM. It is widely used in the detection of output torque of rotating power equipment such as motors, engines, and internal combustion engines.
Sino-Inst produces and supplies a full range of Rotary Torque Sensors for various process industries and process industries. If you need to purchase a high-speed Shaft Rotary Torque Sensor, or have related technical questions, please feel free to contact our engineers!
CL1-104 Shaft Rotary Torque Sensor Up to 16000 RPM

CL1-104 Shaft Rotary Torque Sensor Up is a precision measuring instrument that can measure various high-speed, small-range torques. The maximum speed is up to 16000 RPM. It is widely used in the detection of output torque of rotating power equipment such as motors, engines, and internal combustion engines.
Product SKU: CL1-104 Shaft Rotary Torque Sensor Up to 16000 RPM
Product Brand: Sino-Inst
Product Currency: USD
Price Valid Until: 2029-09-09
Product In-Stock: InStock
5
-1.jpg)


